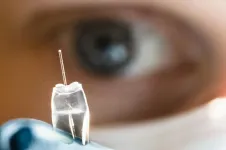
(Press-News.org) Despite surgery and subsequent treatment with chemotherapy and radiation, the majority of patients experience recurrence of malignant brain tumours. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, and the Medical University of Graz, Austria, have shown in cells in culture that an ion pump can deliver drugs more accurately, which gives less severe adverse effects in chemotherapy. The results have been published in Advanced Materials Technologies.
"This is the first time an ion pump has been tested as a possible method to treat malignant brain tumours. We used cancer cells in the lab, and the results are extremely promising. However, it will probably take five to ten years before we see this new technology used in treatments for brain tumours", says Daniel Simon, associate professor at the Laboratory of Organic Electronics at the Department of Science and Technology at Linköping University .
The scientists have used cells from glioblastoma, which is the most common and most aggressive type of cancer that can arise in the brain. When a brain tumour is surgically removed, small parts of the tumour are often left behind, embedded between the brain cells. Even high-precision surgery cannot remove these cells without damaging the surrounding healthy brain tissue. This means that radiation treatment and chemotherapy are used to stop the recurrence of the tumour.
In Sweden, around 30 cytostatics are available to treat different types of cancer. These chemotherapy agents are most often given either intravenously or as a tablet. But in order to reach the brain, they must first spread through the circulatory system and then pass through the blood-brain barrier. The walls of the small blood vessels in the brain are much less permeable than blood vessels in the rest of the body, and can prevent many substances in the blood entering the brain. Thus, only a few drugs that work against cancer can pass through.
Scientists at Linköping University and at the Medical University of Graz have now developed a method in which an implanted ion pump can be used to get around the blood-brain barrier and supply gemcitabine - an extremely effective chemotherapy agent that cannot normally pass the blood-brain barrier - directly into the brain with high precision. Gemcitabine is currently used to treat cancers in the pancreas, bladder and breast, where it acts by disrupting the cell division process in rapidly growing tumours. This means that gemcitabine does not affect brain cells, since these do not, in general, undergo cell division.
"The traditional glioblastoma treatment currently used in the clinics harms both cancer and neuronal cells to the same extent. However, with the gemcitabine ion pump, we tackle only the cancerous cells, while neurons stay healthy. In addition, our experiments on cultured glioblastoma cells show that more cancer cells are killed when we use the ion pump than when we use manual treatment", says Linda Waldherr, postdoctoral fellow at the Medical University of Graz. She has conducted the study together with researchers at Linköping University.
When the ion pump is to transport gemcitabine from an electrolyte reservoir into cells or a tumour, a low current is used to "pump" the positively charged drug through an ion transport channel. The method is known as electrophoresis. The ion pump needs only a low current to pump the gemcitabine, which is an advantage since it avoids the risk that brain cells are activated and transmit unintended nerve signals. The low current and voltage also mean that eventual therapeutic technology will not require large power supplies or batteries to operate.
Rainer Schindl, associate professor at the Medical University of Graz, describes other advantages.
"The pressure inside the brain is extremely sensitive, and using an ion pump to transport the drug instead of a fluid-driven device means that the pressure is not affected. Also, the dosage is controlled by electrical charging, which makes the supply of the chemotherapy agent extremely precise. The next step will be to use the ion pump to evaluate different chemotherapy agents that have previously given adverse effects that are too serious or that are unable to pass the blood-brain barrier", he says.
INFORMATION:
Principal funding bodies for the research have been The Austrian Science Fund, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research.
The article: Targeted chemotherapy of glioblastoma spheroids with an iontronic pump Linda Waldherr, Maria Seitanidou, Marie Jakešová, Verena Handl, Sophie Honeder, Marta Nowakowska, Tamara Tomin, Meysam Karami Rad, Tony Schmidt, Joachim Distl, Ruth Birner-Gruenberger, Gord von Campe, Ute Schäfer, Magnus Berggren, Beate Rinner, Martin Asslaber, Nassim Ghaffari-Tabrizi-Wizsy, Silke Patz, Daniel T. Simon, Rainer Schindl Advanced Materials Technologies 2021 doi: 10.1002/admt.202001302
As females age, their bodies typically undergo two significant changes that generally occur during adolescence and middle age. The first, known as menarche, is the time during puberty when a girl begins having monthly menstruation cycles, which often tends to range from 8-13 years of age. She enters the second change, known as menopause, 12 months following her last menstruation cycle when her ovarian function ceases, usually sometime in her 40s or 50s.
The time after menarche and prior to menopause is known as a woman's reproduction life span and marks the years when she is most able to bear children. For many women, these events occur naturally. However, women can enter menopause earlier than ...
Researchers at King's College London Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, & Neuroscience, in collaboration with King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, have found small clusters of cells in the brain that identify locations where tumours could become malignant.
The study, which has been published in Neuro-Oncology Advances today, analysed pieces of living human brain tissue from 20 people undergoing brain tumour surgery at King's College Hospital, the largest neuro-oncology centre in Europe. The researchers found groups of tumour cells clustered around blood vessels and believe that these sites could be the seedbeds for malignant progression, the process by which a tumour becomes a fast growing and uncontrolled cancer. ...
- Study finds for the first time, in Africa, that mutations are associated with delayed clearance of the parasite among children with malaria treated with common Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs).
- While drug efficacy remains high so far, authors call for increased monitoring in the region.
New data provide the first clinical evidence that drug-resistant mutations in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum may be gaining a foothold in Africa. The study, conducted in Rwanda, is published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases journal and finds for the first time that the mutations are associated with delayed parasite clearance, as was first shown in South-East Asia when artemisinin-resistance started to emerge.
The study ...
Psilocybin, the active compound in magic mushrooms, may be at least as effective as a leading antidepressant medication in a therapeutic setting.
This is the finding of a study carried out by researchers at the Centre for Psychedelic Research at Imperial College London.
In the most rigorous trial to date assessing the therapeutic potential of a 'psychedelic' compound, researchers compared two sessions of psilocybin therapy with a six-week course of a leading antidepressant (a selective serotonin uptake inhibitor called escitalopram) in 59 people with moderate-to-severe depression.
The results, published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, show that while depression ...
New research by University of Texas at Dallas scientists could help solve a major challenge in the deployment of certain COVID-19 vaccines worldwide -- the need for the vaccines to be kept at below-freezing temperatures during transport and storage.
In a study published online April 13 in Nature Communications, the researchers demonstrate a new, inexpensive technique that generates crystalline exoskeletons around delicate liposomes and other lipid nanoparticles and stabilizes them at room temperature for an extended period -- up to two months -- in their proof-of-concept experiments.
The Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines use lipid nanoparticles -- basically spheres of fat molecules -- to protect and deliver the messenger ...
Biomedical engineers at Duke University have developed a self-assembling nanomaterial that can help limit damage caused by inflammatory diseases by activating key cells in the immune system. In mouse models of psoriasis, the nanofiber-based drug has been shown to mitigate damaging inflammation as effectively as a gold-standard therapy.
One of the hallmarks of inflammatory diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and psoriasis, is the overproduction of signaling proteins, called cytokines, that cause inflammation. One of the most significant ...
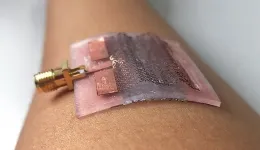
Current research on flexible electronics is paving the way for wireless sensors that can be worn on the body and collect a variety of medical data. But where do the data go? Without a similar flexible transmitting device, these sensors would require wired connections to transmit health data.
Huanyu "Larry" Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Assistant Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics in the Penn State College of Engineering, and two international teams of researchers are developing devices to explore the possibilities of wearable, flexible antennae. They published two papers in April in Nano-Micro Letters and Materials & Design.
Wearable antenna bends, ...
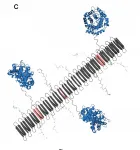
Biological energy flows, such as in photosynthesis and respiration, depend on the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another. Despite its importance to sustaining life, factors governing the rate of electron transfer, especially over long distances, are not well understood because the systems that mediate such ultrafast processes are very complex. A better understanding of electron transfer rates would help scientists improve chemical transformations, energy conversion, electronic devices, and photonic technologies.
Now, an international team of researchers led by UC Riverside has observed picosecond charge transfer mediated by hydrogen bonds in peptides. A picosecond is one trillionth of a second. ...
The coronavirus pandemic has led researchers to switch gears or temporarily abandon projects due to health protocols or not being able to travel. But for Patrick Keys and Elizabeth Barnes, husband and wife scientists at Colorado State University, this past year led to a productive research collaboration.
They teamed up with Neil Carter, assistant professor at the University of Michigan, on a paper published in END ...
As older teens and young adults become eligible for COVID-19 vaccination across the country, and younger teens await their turn, new survey data suggest a strong readiness that has grown since fall.
But just as with older generations, a shrinking but still sizable minority of people age 14 to 24 say they're not willing to get vaccinated, or that their decision will depend on safety.
That makes it crucial for public health authorities, health care providers and others to create vaccination-related materials that reach young people in ways that are relevant to them.
The data, from the text-message-based END ...