A new treatment for rare muscular disease
UC researchers present findings that could give patients with Pompe disease a better quality of life
2021-04-16
(Press-News.org) Rare diseases are sometimes the most difficult to treat because of a lack of research and fewer participants to study.
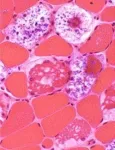
An example would be those who have Pompe disease, a genetic condition when a body can't make a protein that breaks down a complex sugar, called glycogen, for energy. Too much glycogen builds up and damages muscles and organs. The disease causes muscle weakness and trouble breathing and can affect the heart and muscles.
In the case of Pompe disease, however, University of Cincinnati researchers have found a newer, more effective treatment for the rare condition that could become the new standard of care.
Hani Kushlaf, MD, an associate professor in both the Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation Medicine and the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at UC and principal investigator of a study led at UC, will present findings on this new treatment virtually at the American Academy of Neurology on April 20.
Kushlaf, a UC Health physician, says Pompe disease affects about 1 in 40,000 people in the United States. It can impact children, but it can also present later in life as well. Left untreated, it can result in progressive loss of function of muscles in limbs and respiration leading to the need for wheelchair use and respiratory support.
"In this clinical trial, we tested a new drug, or enzyme replacement therapy (avalglucosidase alfa), to see if it was more effective and safer than the currently approved therapy, also an enzyme replacement therapy, in patients with late-onset Pompe disease," he says. "It turns out that it is safer and more effective than the current FDA-approved therapy. This new enzyme will likely become the standard of care for patients with the disease and has already been submitted for Food and Drug Administration approval. This is a big deal for patients with this rare disease, as t-PA was for stroke."
This study was double-blinded, meaning neither the participants nor the researchers knew which treatment was being administered via an infusion. In 51 patients who received the new treatment, researchers saw an improvement in respiratory muscle function, endurance and muscle strength, in addition to an overall better quality of life, when compared to patients on the current standard of care therapy.
"These results are extremely promising for finding a new and effective treatment for this disease," adds Kushlaf, who is also a member of the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute. "With these results, we can take the next steps in having it used widely in this patient population, improving their outcomes and giving them a better life."
INFORMATION:
The trial is sponsored by the pharmaceutical company Sanofi. Kushlaf belongs to an author group appointed by Sanofi and is responsible for disseminating the findings of this trial.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-16
COVID-19 needs no introduction. Last year, the disease, which is caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2, reached every continent across the globe. By the end of March 2021, there had been an estimated 128 million cases recorded with almost three million of these being fatal. As scientists' race to develop vaccines and politicians coordinate their distribution, fundamental research on what makes this virus so successful is also being carried out.
Within the Mathematics, Mechanics, and Materials Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST), postdoctoral researcher, Dr. Vikash Chaurasia, and Professor Eliot Fried have been using energy minimization techniques to look at charged proteins on biological particles. Previously they researched ...
2021-04-16
Researchers from University of British Columbia, Emory University, and New York University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that investigates the relationship between branding and counter-marketing in the cigarette industry.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Investigating the Effects of Excise Taxes, Public Usage Restrictions, and Anti-Smoking Ads across Cigarette Brands" and is authored by Yanwen Wang, Michael Lewis, and Vishal Singh.
While the goal of marketing is usually to boost purchase rates and strengthen relationships between consumers and brands, counter-marketing is an increasingly common strategy for reducing the consumption of "vice" goods such as cigarettes. Counter-marketing activities may ...
2021-04-16
A past COVID-19 infection does not completely protect against reinfection in young people, according to an observational study of more than 3,000 healthy members of the US Marines Corps most of whom were aged 18-20 years, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine journal.
The authors say that despite previous infection and the presence of antibodies, vaccination is still necessary to boost immune responses, prevent reinfection, reduce transmission, and that young people should take up the vaccine wherever possible.
In the study, between May and November 2020, around 10% (19 out of 189) of participants who were previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 (seropositive) became reinfected, compared with new infections in 50% (1,079 out of 2,247) ...
2021-04-16
There is consistent, strong evidence that the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19, is predominantly transmitted through the air, according to a new assessment published today in the medical journal Lancet. Therefore, public health measures that fail to treat the virus as predominantly airborne leave people unprotected and allow the virus to spread, according to six experts from the UK, USA and Canada, including Jose-Luis Jimenez, chemist at the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) and University of Colorado Boulder.
"The evidence supporting airborne transmission is overwhelming, and evidence supporting large droplet transmission is almost ...
2021-04-15
Neurological disorders are the number one cause of disability in the world, leading to seven million deaths each year. Yet few treatments exist for these diseases, which progressively diminish a person's ability to move and think.
Now, a new study suggests that some of these neurological disorders share a common underlying thread. Staufen1, a protein that accumulates in the brains of patients with certain neurological conditions, is linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Lou Gehrig's disease, along with other neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease, according to University of Utah Health scientists.
The findings connect Staufen1 ...
2021-04-15
ITHACA, N.Y. - Since state austerity policies initiated a potable water crisis seven years ago in Flint, Michigan, public health monitoring has focused on potential developmental deficits associated with lead exposure in adolescents or fetuses exposed in utero.
New research from Cornell and the University of Michigan offers the first comprehensive evidence that the city's adult residents suffered a range of adverse physical and mental health symptoms potentially linked to the crisis in the years during and following it, with Black residents affected disproportionately.
In a survey of more than 300 residents, 10% reported having been diagnosed by a clinician with elevated ...
2021-04-15
PASADENA, Calif. -- The numbers of recommended vaccine doses, including measles vaccine, administered to children decreased dramatically after the declaration of a national state of emergency on March 13, 2020, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a Kaiser Permanente study published in Pediatrics. While the decrease was lower and recovered in children under 2 years of age, it was more severe and persistent in older children.
"When vaccination rates decline, we worry about an increase in vaccine-preventable diseases that can be harmful to children," said the study's lead author, Bradley Ackerson, MD, a Kaiser Permanente South Bay Medical Center pediatric infectious disease specialist and an investigator with the Kaiser Permanente Southern ...
2021-04-15
Two MIT professors have proposed a new approach to estimating the risks of exposure to Covid-19 under different indoor settings. The guideline they developed suggests a limit for exposure time, based on the number of people, the size of the space, the kinds of activity, whether masks are worn, and the ventilation and filtration rates. Their model offers a detailed, physics-based guideline for policymakers, businesses, schools, and individuals trying to gauge their own risks.
The guideline, appearing this week in the journal PNAS, was developed by Martin .Z. Bazant, professor of chemical engineering and applied mathematics, and John W. M. Bush, professor of applied mathematics. They stress that one key feature of their model, which has received less attention in existing public-health policies, ...
2021-04-15
URBANA, Ill. - Australian pineapple, Danish trout, and Midwestern U.S. corn farmers are not often lumped together under the same agricultural umbrella. But they and many others who raise crops and animals face a common problem: excess nitrogen in drainage water. Whether it flows out to the Great Barrier Reef or the Gulf of Mexico, the nutrient contributes to harmful algal blooms that starve fish and other organisms of oxygen.
But there's a simple solution that significantly reduces the amount of nitrogen in drainage water, regardless of the production system or location: denitrifying bioreactors.
"Nitrogen pollution from farms is relevant around the world, ...
2021-04-15
LA JOLLA, CA--Some survivors of ebolavirus outbreaks make antibodies that can broadly neutralize these viruses--and now, scientists at Scripps Research have illuminated how these antibodies can disable the viruses so effectively. The insights may be helpful for developing effective therapies.
Ebolavirus is a family of often-deadly viruses that includes Ebola virus and many lesser-known viruses such as Bundibugyo virus, Sudan virus and Reston virus.
Structural biologists at Scripps Research used electron microscopy techniques to visualize a set of antibodies that target a key site on these viruses called the "glycan cap." Their research showed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new treatment for rare muscular disease
UC researchers present findings that could give patients with Pompe disease a better quality of life

