(Press-News.org) WHAT:
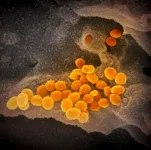
The experimental antiviral drug MK-4482 significantly decreased levels of virus and disease damage in the lungs of hamsters treated for SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to a new study from National Institutes of Health scientists. SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes COVID-19. MK-4482, delivered orally, is now in human clinical trials. Remdesivir, an antiviral drug already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use against COVID-19, must be provided intravenously, making its use primarily limited to clinical settings.
In their study, published in the journal Nature Communications, the scientists found MK-4482 treatment effective when provided up to 12 hours before or 12 hours after infecting the hamsters with SARS-CoV-2. These data suggest that MK-4482 treatment potentially could mitigate high-risk exposures to SARS-CoV-2, and might be used to treat established SARS-CoV-2 infection alone or possibly in combination with other agents.
The same research group, located at Rocky Mountain Laboratories, part of NIH's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases in Hamilton, Montana, developed the hamster model last year to mimic SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild disease in people. The University of Plymouth in the United Kingdom collaborated on these most recent studies.
The project involved three groups of hamsters: a pre-infection treatment group; a post-infection treatment group; and an untreated control group. For the two treatment groups, scientists administered MK-4482 orally every 12 hours for three days. At the conclusion of the study, the animals in each of the treatment groups had 100 times less infectious virus in their lungs than the control group. Animals in the two treatment groups also had significantly fewer lesions in the lungs than the control group.
The scientists determined the MK-4482 treatment doses for this study based on previous experiments performed in mouse models of SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV. In those studies, MK-4482 was effective at stopping the viruses from replicating.
With funding support from NIAID, Emory University's Drug Innovation Ventures group in Atlanta developed MK-4482 (also known as molnupiravir and EIDD-2801) to treat influenza. Merck and Ridgeback Biotherapeutics are now jointly developing and evaluating MK-4482 as a potential COVID-19 treatment. The drug is in Phase 2 and 3 human clinical studies.
INFORMATION:
ARTICLES:
K Rosenke et al. Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model. Nature Communications DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22580-8 (2021).
K Rosenke et al. Defining the Syrian hamster as a highly susceptible preclinical model for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Emerging Microbes and Infections DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1858177 (2020).
WHO:
Heinz Feldmann, M.D., Ph.D., chief of NIAID's Laboratory of Virology; Michael A. Jarvis, Ph.D., a guest researcher in the Laboratory of Virology from the University of Plymouth; and Kyle Rosenke, Ph.D., Laboratory of Virology, are available to comment on these studies.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Ken Pekoc, (301) 402-1663, kpekoc@niaid.nih.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research--at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide--to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has sped up the process of detecting flooded buildings immediately after a large-scale flood, allowing emergency personnel to direct their efforts efficiently. Now, a research group from Tohoku University has created a machine learning (ML) model that uses news media photos to identify flooded buildings accurately within 24 hours of the disaster.
Their research was published in the journal Remote Sensing on April 5, 2021.
"Our model demonstrates how the rapid reporting of news media can speed up and increase the accuracy of damage mapping activities, accelerating ...
Collaborative research of the University of Jyvaskyla and Natural Research Institute Finland presents new evidence of the effects of enriched rearing on well-being of aquaculture fishes. The research demonstrates that stone enrichments that have been previously conditioned in lake water significantly improve survival of fish compared to clean stones. Also a higher number of stones has a similar positive effect. The results have practical implications for prevention of aquaculture diseases. The study was published in Antibiotics in March 2021.
The volume of aquaculture is continuously increasing. Parasitic diseases represent a significant threat to farmed fishes and ecological solutions to minimize use of medication are being sought.
Enriched rearing, where rearing tanks ...
A survey of star formation activity in the Orion Nebula Cluster found similar mass distributions for newborn stars and dense gas cores, which may evolve into stars. Counterintuitively, this means that the amount of gas a core accretes as it develops, and not the initial mass of the core, is the key factor in deciding the final mass of the produced star.
The Universe is populated with stars of various masses. Dense cores in clouds of interstellar gas collapse under their own gravity to form stars, but what determines the final mass of the star remains an ...
Academic medical centers continuously strive to enhance patient care. One of the major mechanisms to improve patient health outcomes is through translational research - bringing research breakthroughs from the lab to patients via clinical trials. Making clinical trials more efficient, and ultimately more successful, would significantly advance patient care. However, fragmentation of the relevant data necessary to implement improvements to translational science is a significant barrier.
While some bioinformatic tools have attempted to address this problem, they often lacked the ability to assess the efficiency of translational science. ...
Gas accidents such as toxic gas leakage in factories, carbon monoxide leakage of boilers, or toxic gas suffocation during manhole cleaning continue to claim lives and cause injuries. Developing a sensor that can quickly detect toxic gases or biochemicals is still an important issue in public health, environmental monitoring, and military sectors. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has developed an inexpensive, ultra-compact wearable hologram sensor that immediately notifies the user of volatile gas detection.
A joint research team led by Professor Junsuk Rho of departments of mechanical and chemical engineering and Dr. Inki Kim of Department of Mechanical ...
A person who owns a car or who has a college education may be less vulnerable to COVID-19, according to an analysis of cases in Tehran, Iran, one of the early epicenters of the pandemic. While such variables do not inherently lower a person's risk, they do indicate an infrastructure of protection that persists despite how densely populated a person's district might be.
The international collaboration published their results on April 3 in Sustainable Cities and Society.
"In the past few decades, there have been various efforts aimed at increasing urban density to enhance efficiency and contribute to climate change mitigation -- but the COVID-19 pandemic has brought questions about ...
The nervous system is the internet of the human body and can in the same way transfer signals over long distances very quickly. Some of the most important elements in this signaling are the axons. They are projections of the nerve cells which send signals to other nerve cells or muscles. For instance, axons that jut out from nerve cells in the spinal cord can be over one meter long.
Researchers from the Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen have now in a new study examined how signal molecules are transported in ...
Scientists have called for the use of climate projections in conservation planning, to ensure that areas most at risk from biodiversity loss and climate impacts are protected. Protected areas are often created in areas of low population density and remote locations, rather than because of their biodiversity conservation potential. Conservation planning in tropical forests especially tends to be less rigorous and climate rarely taken into account, they said.
But climate projections and science-based information are critical to actively seek out and safeguard areas where species are most at risk and ecosystems are fast declining, said authors of the ...
New research has shed light on how autism-spectrum disorder (ASD) manifests in the brains of girls, prompting the scientists to warn that conclusions drawn from studies conducted primarily in boys should not be assumed to hold true for girls.
The researchers discovered that there is a significant difference in the genes and "genetic burden" that underpin the condition in girls and boys. They also identified specific ways the brains of girls with ASD respond differently to social cues such as facial expressions and gestures than do those of girls without ASD.
"This new study provides us with a roadmap for understanding how to better match current and future evidenced-based interventions to underlying ...
A candidate vaccine that could provide protection against the COVID-19 virus and other coronaviruses has shown promising results in early animal testing.
The candidate coronavirus vaccines, created by Virginia Tech's University Distinguished Professor X.J. Meng and UVA Health's Professor Steven L. Zeichner, prevented pigs from being becoming ill with a pig coronavirus, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV).
The researchers have recently published their findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"The candidate vaccine was developed using an innovative vaccine platform targeting a highly conserved genomic region of coronaviruses," said Meng, a University ...