(Press-News.org) The leading newspapers in two nuclear waste management forerunner countries, Finland and France, fulfil their "watchdog" roles in highly distinct ways. The Finnish Helsingin Sanomat (HS) tends to reproduce government and industry framings, whereas Le Monde cherishes its role as an independent critic of the powers that be. These differences reflect distinct cultural, political and media traditions in the two countries.
"The critical watchdog model works in a liberal democracy such as the French, based on mistrust towards the governing elites. But would it backfire in Finland by undermining the very institutional trust that the Nordic democracies have been built upon throughout history?" asks the first author of the article, Research Fellow Markku Lehtonen from the Department of Humanities at the Pompeu Fabra University in Barcelona. Lehtonen continues: "Or perhaps the near-absence of criticism reflects weaknesses in the Finnish democracy?"
During the analysis period, from 2005 to 2018, both countries' deep geological disposal projects were advancing towards implementation.
The study, published in the journal Risk, Hazards, & Crisis in Public Policy, examined nuclear waste reporting - in particular related to risks and safety - in Helsingin Sanomat and Le Monde. During the analysis period, from 2005 to 2018, both countries' deep geological disposal projects were advancing towards implementation.
In its reporting on the final disposal of nuclear waste, Helsingin Sanomat focused on "performance?relevant information", exhibiting strong confidence in the safety and viability of the repository and trust in the actors behind the project. Le Monde, in turn, prioritised "morality-relevant information", highlighting the challenges of trust and mistrust between the involved parties, and, to a lesser extent, scepticism in relation to the viability and safety of the project.
Where Helsingin Sanomat underlined the consistent advancement towards a reliably operating repository, Le Monde evoked the numerous uncertainties and obstacles still facing the repository project, including the multiple conflicts and controversies among the involved actors.
"Le Monde constantly reminded of the ambiguous legacy of the French nuclear sector, as a symbol of modernisation, technological prowess, and economic prosperity on the one hand, and as an incarnation of failed promises on the other. Helsingin Sanomat, in turn, underlined continuity, predictability, and certainty. It described the Finnish repository project as a success story essential for the national interest," Lehtonen points out.
In addressing intergenerational equity, Helsingin Sanomat echoed the government and industry argument that a deep geological repository spares future generations from having to tackle the waste problem. By contrast, Le Monde pointed out a major dilemma: burying waste in a repository would deprive future generations of the freedom to decide what to do with the waste, including the possibility that thanks to technological development the waste could be turned into a resource.
"The findings help to understand why the nuclear waste disposal project has advanced in such an unproblematic manner in Finland," notes Research Fellow Matti Kojo from Tampere University, a co-author of the article.
A comprehensive analysis of leading newspapers over fourteen years
The now published study examined nuclear waste reporting - in particular related to risks and safety - in Helsingin Sanomat and Le Monde. The authors underline that the final set of material included only those articles in which the country's own repository project was a central topic (135 articles in HS and 210 in Le Monde).
Finland expects to become the first country in the world to have solved its problem of high-level radioactive waste, with its ONKALO repository expected to become operational by the mid-2020s. France's "Cigéo" facility is to start operating in the early 2030s.
The authors underline that the final set of material included only those articles in which the country's own repository project was a central topic.
The research group has previously compared, among other things, the processes of citizens participation, the role of host communities, and press reporting on nuclear waste management in Finland and Sweden.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the Finnish Research Programme on Nuclear Waste Management (KYT2022) 2019-2022 and the European Commission through the Marie Sk?odowska-Curie Individual Fellowships scheme (grant number 794697-TENUMECA).
The research included also scholars from the universities of Tampere and Jyväskylä, in Finland.
Reference article: Markku Lehtonen, Matti Kojo, Mika Kari, Tapio Litmanen: "Healthy mistrust or complacent confidence? Civic vigilance in the reporting by leading newspapers on nuclear waste disposal in Finland and France". Risk, Hazards, & Crisis in Public Policy. 2021; 1-28
https://doi.org/10.1002/rhc3.12210
A new study has shown that underweight and overweight women are at a significantly higher risk of experiencing recurrent miscarriages compared to those of average weight.
A research team led by the University of Southampton assessed the link between women's lifestyle and risk of recurrent pregnancy loss, defined as women having two or more consecutive early miscarriages. The systematic review and meta-analysis study has been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Miscarriage is the most common complication of early pregnancy, affecting 15 - 20% of all pregnancies. Recurrent pregnancy loss is a complex disease and although often attributed to numerous medical factors and lifestyle influences, the cause is deemed "unexplained" ...
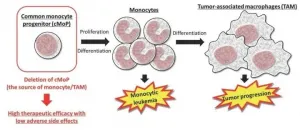
Tokyo, Japan - Leukemias are debilitating cancers of the hematopoietic or blood-forming cells of the bone marrow. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) describe an ingenious strategy against chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) wherein an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) comprising a cytotoxic drug payload linked to an antibody that selectively targets specific cell lines effectively blocks malignant cell proliferation at source.
Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) continually differentiate into the entire panoply of blood cells, as many as 500 ...
Since fast radio bursts (FRBs) were first discovered over a decade ago, scientists have puzzled over what could be generating these intense flashes of radio waves from outside of our galaxy. In a gradual process of elimination, the field of possible explanations has narrowed as new pieces of information are gathered about FRBs - how long they last, the frequencies of the radio waves detected, and so on.
Now, a team led by McGill University researchers and members of Canada's CHIME Fast Radio Burst collaboration has established that FRBs include radio waves at frequencies lower than ever detected before, a discovery that redraws the boundaries for theoretical astrophysicists trying to put their finger on the source of FRBs.
"We ...
WHAT:
The experimental antiviral drug MK-4482 significantly decreased levels of virus and disease damage in the lungs of hamsters treated for SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to a new study from National Institutes of Health scientists. SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes COVID-19. MK-4482, delivered orally, is now in human clinical trials. Remdesivir, an antiviral drug already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use against COVID-19, must be provided intravenously, making its use primarily limited to clinical settings.
In their study, published in the journal ...
Artificial intelligence (AI) has sped up the process of detecting flooded buildings immediately after a large-scale flood, allowing emergency personnel to direct their efforts efficiently. Now, a research group from Tohoku University has created a machine learning (ML) model that uses news media photos to identify flooded buildings accurately within 24 hours of the disaster.
Their research was published in the journal Remote Sensing on April 5, 2021.
"Our model demonstrates how the rapid reporting of news media can speed up and increase the accuracy of damage mapping activities, accelerating ...
Collaborative research of the University of Jyvaskyla and Natural Research Institute Finland presents new evidence of the effects of enriched rearing on well-being of aquaculture fishes. The research demonstrates that stone enrichments that have been previously conditioned in lake water significantly improve survival of fish compared to clean stones. Also a higher number of stones has a similar positive effect. The results have practical implications for prevention of aquaculture diseases. The study was published in Antibiotics in March 2021.
The volume of aquaculture is continuously increasing. Parasitic diseases represent a significant threat to farmed fishes and ecological solutions to minimize use of medication are being sought.
Enriched rearing, where rearing tanks ...
A survey of star formation activity in the Orion Nebula Cluster found similar mass distributions for newborn stars and dense gas cores, which may evolve into stars. Counterintuitively, this means that the amount of gas a core accretes as it develops, and not the initial mass of the core, is the key factor in deciding the final mass of the produced star.
The Universe is populated with stars of various masses. Dense cores in clouds of interstellar gas collapse under their own gravity to form stars, but what determines the final mass of the star remains an ...
Academic medical centers continuously strive to enhance patient care. One of the major mechanisms to improve patient health outcomes is through translational research - bringing research breakthroughs from the lab to patients via clinical trials. Making clinical trials more efficient, and ultimately more successful, would significantly advance patient care. However, fragmentation of the relevant data necessary to implement improvements to translational science is a significant barrier.
While some bioinformatic tools have attempted to address this problem, they often lacked the ability to assess the efficiency of translational science. ...
Gas accidents such as toxic gas leakage in factories, carbon monoxide leakage of boilers, or toxic gas suffocation during manhole cleaning continue to claim lives and cause injuries. Developing a sensor that can quickly detect toxic gases or biochemicals is still an important issue in public health, environmental monitoring, and military sectors. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has developed an inexpensive, ultra-compact wearable hologram sensor that immediately notifies the user of volatile gas detection.
A joint research team led by Professor Junsuk Rho of departments of mechanical and chemical engineering and Dr. Inki Kim of Department of Mechanical ...
A person who owns a car or who has a college education may be less vulnerable to COVID-19, according to an analysis of cases in Tehran, Iran, one of the early epicenters of the pandemic. While such variables do not inherently lower a person's risk, they do indicate an infrastructure of protection that persists despite how densely populated a person's district might be.
The international collaboration published their results on April 3 in Sustainable Cities and Society.
"In the past few decades, there have been various efforts aimed at increasing urban density to enhance efficiency and contribute to climate change mitigation -- but the COVID-19 pandemic has brought questions about ...