The fate of the planet
Unconventional takes on pandemics and nuclear defense could protect humanity from catastrophic failure
2021-04-16
(Press-News.org) From engineered pandemics to city-toppling cyber attacks to nuclear annihilation, life on Earth could radically change, and soon. Scientists will forecast the fate of the planet at a END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tarantula's ubiquity traced back to the cretaceous
2021-04-16
Tarantulas are among the most notorious spiders, due in part to their size, vibrant colors and prevalence throughout the world. But one thing most people don't know is that tarantulas are homebodies. Females and their young rarely leave their burrows and only mature males will wander to seek out a mate. How then did such a sedentary spider come to inhabit six out of seven continents?
An international team of researchers, including Carnegie Mellon University's Saoirse Foley, set out on an ancestry.com-like investigation to find the answer to this question. They looked to the transcriptomes, ...
On the pulse of pulsars and polar light
2021-04-16
Faced with the tragic loss of the Arecibo observatory in Puerto Rico and the often prohibitive cost of satellite missions, astronomers are searching for savvy alternatives to continue answering fundamental questions in physics.
At a END ...
Neural plasticity depends on this long noncoding RNA's journey from nucleus to synapse
2021-04-16
JUPITER, FL--Making memories involves more than seeing friends or taking photos. The brain constantly adapts to new information and stores memories by building connections among neurons, called synapses. How neurons do this--reaching out arm-like dendrites to communicate with other neurons--requires a ballet of genes, signaling molecules, cellular scaffolding and protein-building machinery.
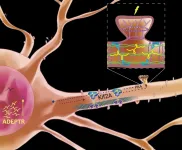
A new study from scientists at Scripps Research and the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience finds a central role for one signaling molecule, a long, noncoding RNA that the scientists named ADEPTR.
Using a variety of technologies, including confocal and two-photon microscopy, they track ADEPTR's moves, watching as it forms, travels, amasses at the ...
A new guide for communicating plant science
2021-04-16
AMES, Iowa - A lot is riding on the continued advancement of plant sciences.
Take the food supply, for starters. Climate change and population growth will continue to pose challenges in the future, and crop production will require innovation and progress by plant scientists in order to keep pace. It isn't an overstatement to say that populations around the world will go hungry if plant science stagnates, said Gustavo MacIntosh, a professor in the Roy J. Carver Department of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Molecular Biology at Iowa State University.
"At the end of the day, either you eat plants or you eat food that ate plants," MacIntosh said. "Plants are the basis for the food we have."
MacIntosh predicts ...
The future of particle accelerators is here
2021-04-16
When the Electron Ion Collider received the go-ahead in January 2020, it became the only new major accelerator in the works anywhere in the world.
"All the stars aligned," said Elke-Caroline Aschenauer, Brookhaven National Laboratory Staff Scientist and a leader in developing the EIC plans. "We have the technology to build this unique particle accelerator and detector to do the measurements that, together with the underlying theory, can for the first time provide answers to longstanding fundamental questions in nuclear physics."
The EIC isn't the only Brookhaven project poised to reshape nuclear and particle physics. Forthcoming data from the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider could finally detect the elusive chiral magnetic effect. Meanwhile, planned accelerators could run on sustainable ...
Simulations reveal how dominant SARS-CoV-2 strain binds to host, succumbs to antibodies
2021-04-16
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 16, 2021 -- Large-scale supercomputer simulations at the atomic level show that the dominant G form variant of the COVID-19-causing virus is more infectious partly because of its greater ability to readily bind to its target host receptor in the body, compared to other variants. These research results from a Los Alamos National Laboratory-led team illuminate the mechanism of both infection by the G form and antibody resistance against it, which could help in future vaccine development.
"We found that the interactions among the basic building blocks of the Spike protein become ...
New understanding of the deleterious immune response in rheumatoid arthritis
2021-04-16
Researchers within the Biomedicine Discovery Institute at Monash University have made a breakthrough in understanding the role played by high-risk immune genes associated with the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
The findings, published in Science Immunology, were the result of a seven-year collaboration led by Monash University, involving Janssen Research and Development, USA and the Karolinska Institute, Sweden.
Certain immune system genes, called Human Leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR4, cause an increased susceptibility to RA. In this study, using mice genetically ...
The Trojan-Horse mechanism: How networks reduce gender segregation
2021-04-16
The social science literature has long viewed homophily and network-based job recruitment as crucial drivers of segregation. Researchers at Linköping University and ESADE, Ramon Llull University now show that this view must be revised. In their Science Advances article, they call attention to a previously unidentified factor, the Trojan-horse mechanism, which shows that network-based recruitment can reduce rather than increase segregation levels.
The segregation of labor markets along ethnic and gender lines is an important source of socio-economic inequalities. Therefore, the understanding the mechanisms that drive segregation ...
Science Advances publishes proteomics technology from Oblique Therapeutics AB
2021-04-16
Science Advances publishes proteomics technology from Oblique Therapeutics AB with a potential to bring several novel antibody medicines to large patient populations in multiple disease areas
Gothenburg, Sweden, April 16th, 2021 - Oblique Therapeutics AB, a Sweden-based biotech company, in collaboration with Karolinska Institutet (Stockholm, Sweden), Gothenburg University (Sweden) and several local biotechs published promising research results in the highly-acclaimed scientific journal Science Advances (AAAS) entitled: Rational Antibody design for Undruggable Targets using Kinetically Controlled Biomolecular ...
Female protective effect: Yale researchers find clues to sex differences in autism
2021-04-16
New Haven, Conn. -- It is well established that autism occurs much more frequently in boys than in girls, and that girls seem to have a greater resilience to developing the condition. It has been unclear, however, why that is.
In a new Yale-led study, researchers find that autism may develop in different regions of the brain in girls than boys and that girls with autism have a larger number of genetic mutations than boys, suggesting that they require a larger "genetic hit" to develop the disorder.
The findings appear in the April 16 edition of the journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] The fate of the planetUnconventional takes on pandemics and nuclear defense could protect humanity from catastrophic failure