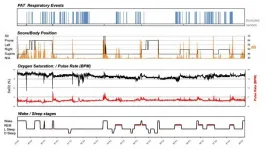
The study of 8001 men and women, which is published today (Tuesday) in the European Heart Journal [1], found that women who experienced unconscious wakefulness most often and for longer periods of time had nearly double the risk of dying from cardiovascular disease during an average of between 6 and 11 years' follow-up, when compared to the risk in general female population. The association was less clear in men, and their risk of cardiovascular death increased by just over a quarter compared to the general male population.
Unconscious wakefulness, also known as cortical arousal, is a normal part of sleep. It occurs spontaneously and is part of the body's ability to respond to potentially dangerous situations, such as noise or breathing becoming obstructed. Pain, limb movements, trauma, temperature and light can also be triggers.
Dominik Linz, associate professor in the cardiology department at Maastricht University Medical Center (The Netherlands), explained: "A common trigger for nocturnal arousals is obstructive sleep apnoea when breathing stops and the arousal system ensures the activation of our body to change our sleep position and to reopen the upper airway. Another cause of arousals can be 'noise pollution' during the night by, for example, night-time aircraft noise. Depending on the strength of the arousal, a person might become consciously aware of the environment, but often that is not the case. Typically, people will feel exhausted and tired in the morning because of their sleep fragmentation but will not be aware of the individual arousals."
Previous research has shown that sleep duration, either too short or too long, is associated with increased risks of death from cardiovascular or other causes. However, until now, it was unknown whether there was also a link with the arousal burden (a combination of the number of arousals and their duration) during a night's sleep and the risk of death.
In a collaboration between a team led by associate professor Mathias Baumert from the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at the University of Adelaide (Australia) and Prof. Linz, researchers looked at data from sleep monitors worn overnight by men and women taking part in one of three studies: 2782 men in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Sleep Study (MrOS), 424 women in the Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF), and 2221 men and 2574 women in the Sleep Heart Health Study (SHHS). The average ages in the studies were 77, 83 or 64 years, respectively. The participants were followed up over a period of several years, which ranged from an average of six years (SOF) to 11 years (MrOS).
After adjusting for factors that could affect the results such as total sleep duration, age, medical history, body mass index (BMI) and smoking habits, the researchers found that women had an arousal burden that was lower than men. However, those who had an arousal burden that accounted for more than 6.5% of their night's sleep had a greater risk of dying from cardiovascular disease than women with a lower arousal burden: double the risk in SOF and 1.6 times the risk in SHHS. Their risk of dying from all causes was also increased by 1.6 times in SOF and 1.2 times in SHHS.
Taking the women from both studies together, those with an arousal burden of more than 6.5% had a 12.8% risk of dying from cardiovascular disease, nearly double that of women of a similar age in the general population who had a risk of 6.7%. The risk of dying from any cause was 21% among women in the general population, which increased to 31.5% among women in the two studies with an arousal burden of more than 6.5%
Men with an arousal burden accounting for more than 8.5% of their night's sleep had 1.3 times greater risk of dying from cardiovascular disease (MrOS) or any cause (SHHS), compared to men with lower arousal burdens, but findings for increased risk of death from any cause in MrOS or cardiovascular disease in SHHS were not statistically significant.
When the researchers looked at all the men in both studies, those with an arousal burden of more than 8.5% had a risk of 13.4% and 33.7% of dying from cardiovascular disease or any cause, respectively, compared to the risk in the general population of men of similar ages of 9.6% and 28%, respectively.
Prof. Linz said: "It is unclear why there is a difference between men and women in the associations, but there are some potential explanations. The triggers causing an arousal or the body's response to arousal may differ in women compared to men. This may explain the relatively higher risk of cardiovascular death in women. Women and men may have different compensatory mechanisms for coping with the detrimental effects of arousal. Women may have a higher arousal threshold and so this may result in a higher trigger burden in women compared to men."
He said that older age, BMI and the severity of sleep apnoea increase arousal burdens. "While age cannot be changed, BMI and sleep apnoea can be modified and may represent an interesting target to reduce arousal burdens. Whether this will translate into lower risks of dying from cardiovascular disease warrants further study. For me as a physician, a high arousal burden helps to identify patients who may be at higher risk of cardiovascular disease. We need to advise our patients to take care of their sleep and practice good sleep 'hygiene'. Measures to minimise noise pollution during the night, lose weight and treat sleep apnoea could also help to reduce the arousal burden."
Prof. Baumert said: "In order to include assessment of arousal burdens into routine strategies for reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, we need easily scalable, widely accessible and affordable techniques to estimate the duration and fragmentation of sleep and to detect arousals. Wearable devices for measuring activity and changes in breathing patterns may provide important information."
Limitations of the study include that it was conducted in older, mainly white people and so its findings cannot be extrapolated to other races or younger men and women. The researchers did not consider the possible effect of medications; monitoring of the participants' sleep was conducted on a single night and so does not take account of night-to-night variations. Finally, it can only show there is an association between greater sleep arousal burden and increased risk of death, not that sleep arousals cause the increased risk.
In an accompanying editorial [2], Professor Borja Ibáñez, clinical research director at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III, Madrid (Spain), and colleagues, who were not involved in the research, write that a strength of the study is that the arousal burden was measured objectively with sleep monitors, rather than being self-reported by the participants. They point out that disruption of the body's natural circadian rhythm is known to be involved in the development of often undetected fat accumulation in arteries and this could be a possible mechanism for the increase in the risk of cardiovascular problems.
They continue: "Even though many knowledge gaps on the relationship between sleep and CVD [cardiovascular disease] remain to be studied in the coming years, this study provides solid evidence supporting the importance of sleep quality for a better CV health. Further evidence combining comprehensive sleep evaluation with biological sampling and long-term follow-ups will be desirable . . . What remains to be determined is whether an intervention aiming at improving sleep quality is able to reduce the incidence of CV events and mortality. While awaiting these trials, we wish you sweet dreams."
INFORMATION:
[1] "Sleep arousal burden is associated with long-term all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in 8,001 community-dwelling older men and women", by Sobhan Salari Shahrbabaki et al. European Heart Journal. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab151
[2] "Good night, sleep tight", by Inés García-Lunar, Valentin Fuster and Borja Ibáñez. European Heart Journal. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab181