(Press-News.org) Current national strategies for bridge maintenance favor replacement over maintenance. A fairly simple depreciation formula is used, resulting in overly conservative assessments of a bridge's long-term health. In a study published in the American Society of Civil Engineers' Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, researchers from UGA's College of Engineering propose a new model for the first time. This new approach considers the interaction of 60 to 80 bridge components in predicting long-term bridge performance and focuses on maintenance instead of replacement.
"Rather than considering a bridge as a monolithic structure, the bridge coactive model assesses a bridge as a system in which changes in the condition of each coactive element not only directly affects the overall bridge performance but indirectly influences the performance of the other dependent elements," said Brian Oyegbile, one of the study's authors.
Oyegbile earned his Ph.D. in engineering from UGA in 2020 and now works with the California Department of Transportation.
As an example, Oyegbile says replacing a damaged bridge expansion joint is inexpensive and has marginal impact on the overall performance of the bridge in the short term. However, salt from de-icing or contaminated water can seep through a damaged expansion joint over time, accelerating the deterioration of more critical elements below, such as a column. Likewise, a bridge deck may deteriorate more quickly when debris accumulates in an expansion joint and restricts the normal expansion and contraction of the deck.
According to the UGA researchers, proactively replacing elements at the right time - even one as small as an expansion joint - can have a big impact on long-term bridge health. They say their model can provide stronger data and more accurate depreciation predictions for state transportation agencies as they schedule bridge maintenance, repair and replacement. Nationally, bridges last an average of 75 years. With timely and efficient application of available resources, the researchers say these bridges can serve for more than 100 years.
"In my eyes, the co-activeness is apparent in the bridge inspection data and we can scientifically leverage data analytics in bridge service-life predictions, saving money for the country's infrastructure maintenance and construction," said Oyegbile.
Regular upkeep would save money
Stephan Durham, a professor in the College of Engineering and one of the study's co-authors, says your home's heating and cooling system serves as a good analogy.
"Like clockwork, I replace my air filters every two months whether the system has been in heavy use or not because it keeps the system operating efficiently," he said. "It's the same thing with a bridge. If you're replacing an expansion joint on a regular basis, whether it's completely worn out or not, your bridge is going to perform better than if you let it degrade to the point a component absolutely must be replaced."
The researchers analyzed data in the Federal Highway Administration's National Bridge Inventory for Alabama, Florida and Georgia to build and test their model. Georgia alone has more than 15,000 bridges. The NBI database includes inspection reports on individual bridge elements, proving a wealth of information for the researchers.
"Prior to our work, we hadn't seen a mathematical model that considers the interaction between bridge elements," said Mi Geum Chorzepa, an associate professor and the study's principal investigator. "We need a more realistic way to assess bridge conditions and prioritize preventive maintenance, particularly in such a challenging budget environment."
The researchers estimate a $10 billion investment in timely and appropriate preventive maintenance on the nation's bridges over three years would generate $20 billion in recurring savings by 2024. Those savings could be devoted elsewhere, such as new infrastructure construction, and help drive economic growth, according to the team.
The Georgia Department of Transportation, which funded the study, recently approved a grant for the researchers to expand their work. In the second phase of the project, the team will work with GDOT's Offices of Transportation Data, Research, and Bridge Maintenance to develop a bridge life-cycle assessment tool for use by GDOT and county governments across the state.
The research team also includes S. Sonny Kim, an associate professor in the College of Engineering.
INFORMATION:
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. - The fearsome tyrannosaur dinosaurs that ruled the northern hemisphere during the Late Cretaceous period (66-100 million years ago) may not have been solitary predators as popularly envisioned, but social carnivores similar to wolves, according to a new study.
The finding, based on research at a unique fossil bone site inside Utah's Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument containing the remains of several dinosaurs of the same species, was made by a team of scientists including Celina Suarez, University of Arkansas associate professor of geosciences.
"This supports our hypothesis ...
TAMPA, Fla (April 20, 2021) — Chaperone protein imbalance can play a significant role in initiating toxic accumulation of tau in the aging brain - an early step in the development of Alzheimer's disease and related neurodegenerative disorders known as tauopathies, a new preclinical study by University of South Florida Health (USF Health) neuroscientists suggests.
In humans, misfolding of the protein tau leads to its toxic accumulation inside brain cells, the formation of these tau aggregates into hallmark neurofibrillary tangles, neuron death, and eventually symptoms of cognitive decline such as memory loss and diminished thinking skills.
In this study the ...
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 19, 2021 -- A recent series of experiments at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory (National MagLab) at Los Alamos National Laboratory leveraged some of the nation's highest-powered nondestructive magnets to reveal an exotic new phase of matter at high magnetic fields. The experiments studied the unusual Kondo insulator ytterbium dodecaboride (or YbB12) and were the first results from the new 75-tesla duplex magnet housed at the National MagLab's Pulsed Field Facility at Los Alamos.
"This magnet and the resulting experiments are the first fruits of the National Science Foundation-supported pulsed magnet surge," said Michael Rabin, director of the Pulsed Field Facility at Los ...
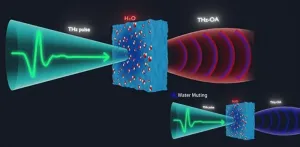
Radiation at terahertz frequencies (wavelengths between 0.03 and 0.3 mm) can be used successfully to analyze the structural dynamics of water and biomolecules. But applying the technique to aqueous solutions and tissues remains challenging, since terahertz (THz) radiation is strongly absorbed by water. While this absorption enables certain analyses, such as the structure of water and its interactions with biological solutes, it limits the thickness of samples that can be analyzed, and it drowns out weaker signals from biomolecules of interest. Strong absorption of THz ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Four decades after their capture more than a half-mile below the ocean's surface, three snailfish species have received their scientific names, two of them from school children on Guam in the island's native Chamorro language.
The rare specimens of liparids were collected in the early 1980s in traps set in the Mariana Archipelago in the western Pacific Ocean, deposited with NOAA's Pacific Islands Fisheries Science Center in Hawaii and did not get examined until recently, when they were noticed during the center's move to a new location. ...
As the back-to-school rush begins, podiatry experts at the University of South Australia are encouraging parents to get their children's school shoes professionally fitted, as new research confirms that ill-fitted footwear can significantly impede foot movement and comfort.
In a new study, researchers tested the effect of shoe size on foot motion and comfort among children aged 8 to 12 years, finding that shoes that were one size too small restricted the normal movement of the heel, arch and big toe joint during walking.
The study also confirmed that a comfortable shoe fit can be determined by a 'rule of thumb', where the wearer's thumb width from their longest toe to the end of their shoe is an effective and accurate measure ...
Metals are one of the most widely used materials in the world - they are used in cookware, tools, electric appliances, electric wires, computer chips, jewelry and so on. With the growing demand for metal products, it is crucial to promote sustainable and environmentally-friendly methods of recycling metal waste to help reduce the environmental impact of using metals in the economy.
The conventional approaches for recycling metal waste are energy intensive and some of these methods also generate environmentally harmful by-products, such as ammonia and methane during aluminium recycling.
To address this challenge, a team of researchers from the National ...
With inherent orthogonality, both SAMs and OAMs of light have been utilized to expand the dimensions of optical communications and signal processing, wherein unambiguous SAM and OAM identification is one of the significant topics. Conventional sorting approaches suffer from complicated optical setups, multiple bulky devices, repeated projection measurements, and cannot simultaneously distinguish SAM and OAM.
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Xiangang Luo from State Key Laboratory of Optical Technologies on Nano-Fabrication and Micro-Engineering, Institute of Optics and Electronics Chinese Academy of Sciences, and co-workers have showed that a single spin-decoupled metasurface that merges the geometric ...
Hand, Foot & Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a generally mild, contagious viral infection common in young children. In Singapore, HFMD is endemic and is most commonly caused by intestinal viruses known as coxsackieviruses and enteroviruses.
While most HFMD patients experience common symptoms such as sore throat, fever, ulcers inside the mouth and blisters and lesions on the palms and soles, infection with Enterovirus-A71 (EV-A71) may lead to serious neurological complications that can be potentially fatal or lead to long-term neurological deficits (cognitive and motor deficits). These complicated HFMD cases are mainly seen in young children.
Researchers from NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine's Infectious Diseases ...
New FLEET research confirms the potential for topological materials to substantially reduce the energy consumed by computing.
The collaboration of FLEET researchers from University of Wollongong, Monash University and UNSW have shown in a theoretical study that using topological insulators rather than conventional semiconductors to make transistors could reduce the gate voltage by half, and the energy used by each transistor by a factor of four.
To accomplish this, they had to find a way to overcome the famous 'Boltzmann's tyranny' that puts a lower limit on transistor switching energy.
They found a surprising result: gate voltage applied to a topological insulator could create a barrier to electron flow larger than the voltage itself times the electron charge, ...