(Press-News.org) The worldwide adoption of biotechnologies to improve crop production has stalled, putting global food security at risk, according to an international team of researchers led by the University of Birmingham.
The group, which includes economists, plant breeders and plant scientists, is calling on governments worldwide to put in place policies and regulations that will drive progress in this area.
In an article published in the 25th anniversary edition of Trends in Plant Science, the group, which includes researchers from Australia, Canada and India, also argues that societal acceptance of technologies such as gene editing is a big barrier to adoption. They urge the scientific community to work harder to convince the public and governments of the value of adopting plant breeding technologies to combat the challenges of climate change and improve crop resilience.
Professor Christine Foyer, of the School of Biosciences at the University of Birmingham, says: "Plant science has advanced rapidly over the past 25 years. Adopting these new technologies would enable us to make huge advances in reducing agricultural emissions, improving agricultural sustainability and productivity and increasing the nutritional value of plants.
"Despite this, public acceptance has been slow. This is partly because the benefits are not sufficiently widely recognised, and partly because of historic fears and misconceptions around genetically modified plants. Learning from the harsh lessons of past failures, plant scientists must now be advocates for their achievements in order to gain public confidence in new and emerging technologies."
Dr Sven Anders of the University of Alberta, Canada, agreed that plant scientists must play a greater role in the public debate to gain public confidence in gene-editing and become involved in advocacy and increasing public awareness.
"Harmonised global regulations of new technology is essential for new technologies to contribute to future food security," Dr Anders said.
Professor Wallace Cowling, from the University of Western Australia, added: "Future food security depends on accelerating crop genetic improvement using all sources of valuable genes - from new technology or from wild and landrace relatives.
"Breeding for complex traits, such as heat or drought tolerance, will require optimised breeding strategies in a more rapid and sustainable form of plant breeding. Modelling suggests that we can keep pace with climate change and improve crop yields long into the future if we integrate genes derived from biotechnology into improved breeding schemes."
INFORMATION:
Additional authors include Dr Ashwani Pareek, from the National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute India, Dr Kapuganti Jagadis Gupta from the National Institute of Plant Genome Research, India, and Dr Sneh L Singla-Pareek from the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, India.
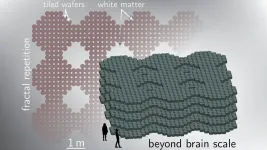
WASHINGTON, April 20, 2021 -- As artificial intelligence has attracted broad interest, researchers are focused on understanding how the brain accomplishes cognition so they can construct artificial systems with general intelligence comparable to humans' intelligence.
Many have approached this challenge by using conventional silicon microelectronics in conjunction with light. However, the fabrication of silicon chips with electronic and photonic circuit elements is difficult for many physical and practical reasons related to the materials used for the components.
In Applied Physics Letters, by AIP Publishing, researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology propose an approach to large-scale artificial intelligence that ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- Patients who suffer from traumatic brain injuries (TBI) often need a great deal of healthcare services after the injury, but the extent of care utilization is unknown. A new study from research scientists affiliated with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), Regenstrief Institute and IUPUI is one of the first to analyze how much care TBI patients use and identify areas of unmet need.
"There is not a lot of information about traumatic brain injury care utilization available," said primary study author Johanne Eliacin, PhD, a Regenstrief research scientist and core investigator at the VA Health Services Research and Development Center for Health Information at Richard L. Roudebush VA Medical ...
A recent study suggests that preserving physical and mental health helps older adults experiencing cognitive impairment stave off declines in cognitive engagement.
"We found that declines in physical and mental health were associated with more pronounced cognitive disengagement," says Shevaun Neupert, corresponding author of the study and a professor of psychology at North Carolina State University. "The impact of declines in physical health was particularly pronounced for study participants who had more advanced cognitive impairment to begin with."
There's ...
With roughly 80% of jobs being sedentary, often requiring several hours of sitting stooped in front of a computer screen, neck pain is a growing occupational hazard. Smartphones and other devices have also caused people to bend their necks for prolonged periods. But is bad posture solely to blame?
In a recent study, researchers at Texas A&M University have found that while poor neck and head postures are indeed the primary determinants of neck pain, body mass index, age and the time of the day also influence the neck's ability to perform sustained or repeated movements.
"Neck pain is one of the leading and fastest-growing ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Have you recently turned to your mobile device or computer to find out if your cough, sniffle or fever could be caused by COVID-19?
The online symptom checker you used may have advised you to stay home and call your medical provider if symptoms worsen, or perhaps told you that you may be eligible for COVID-19 testing. But why did it make the recommendation it did? And how should you know if you can trust it?
Those are questions that researchers at the Penn State College of Information Sciences and Technology recently explored through a project in which they augmented online symptom checkers by offering explanations of how the system generated its probable diagnoses and suggestions ...
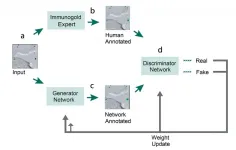
From sample preparation to image acquisition, electron microscopy (EM) requires precise and time-consuming steps to produce the clarity and detail needed to visualize small cell structures with high resolution. Moreover, once EM images are created, extracting the biological information out of them through analysis can be an even more laborious and time intensive task. Especially because current EM analysis software often requires the skilled eye of a scientist to manually review hundreds of images.
With a bit of ingenuity and the application of cutting-edge neural networks, an interdisciplinary team of scientists at the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience (MPFI) have created a new ...
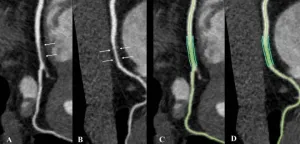
OAK BROOK, Ill. - People living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and without known cardiovascular disease have two to three times the noncalcified coronary plaque burden of non-HIV healthy volunteers, according to a study from Canada published in Radiology. Researchers said the results underscore the importance of a heart-healthy lifestyle in people living with HIV.
HIV/AIDS emerged as a major public health crisis in the 1980s. Disease-related mortality peaked in the mid-1990s and has been dropping since, thanks in large part to antiretroviral therapy, which does not cure the disease but helps control it.
Today, people ...
Researchers at Beam Therapeutics have developed a redesigned base editor that shows considerable promise in directly repairing the single-base mutation that causes sickle-cell disease (SCD). Many strategies are being pursued to harness genome editing approaches including CRISPR to treat patients with SCD and related hemoglobinopathies. The most advanced method in the clinic involves targeting an upstream regulatory pathway to switch on expression of the fetal hemoglobin gene but does not target the SCD mutation directly.
Writing in the April issue of The CRISPR Journal, a team at Beam Therapeutics, led by Ian Slaymaker and Giuseppe Ciaramella, describe the successful ...
In a study conducted at the University of Helsinki, researchers found a cause for severe epilepsy resulting in death in Parson Russell Terrier puppies at a few months of age. A change in the PITRM1 gene can lead to a dysfunction of mitochondria, the cellular energy pumps. Concurrently, amyloid-β accumulation and widespread neurodegeneration associated with Alzheimer's disease were identified in the puppies' brains. Changes to the PITRM1 gene in humans also cause a severe but slowly progressing brain disease.
Some Parson Russell Terrier puppies were seen to suddenly develop epileptic seizures at 6 to 12 weeks of age. The disease progressed very rapidly, in a matter of hours in the worst cases, to a situation where the seizures were continuous and unresponsive to medication.
"All ...
Exposure to certain endocrine-disrupting chemicals could elevate the risk of breast cancer, according to a new comprehensive systematic review of epidemiological research. However, for many chemicals, evidence is inconsistent or still limited. The review was carried out by researchers at the universities of Hong Kong and Eastern Finland and published in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can interfere with the body's hormonal system, also called the endocrine system, and are widely present in the environment. They originate from a variety of ...