(Press-News.org) In a study conducted at the University of Helsinki, researchers found a cause for severe epilepsy resulting in death in Parson Russell Terrier puppies at a few months of age. A change in the PITRM1 gene can lead to a dysfunction of mitochondria, the cellular energy pumps. Concurrently, amyloid-β accumulation and widespread neurodegeneration associated with Alzheimer's disease were identified in the puppies' brains. Changes to the PITRM1 gene in humans also cause a severe but slowly progressing brain disease.
Some Parson Russell Terrier puppies were seen to suddenly develop epileptic seizures at 6 to 12 weeks of age. The disease progressed very rapidly, in a matter of hours in the worst cases, to a situation where the seizures were continuous and unresponsive to medication.
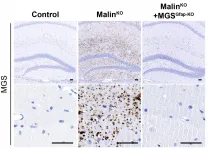
"All of the sick dogs either died spontaneously or had to be euthanised. On the tissue level, neuronal necroses, or dead neurons, were identified throughout the brains of the deceased dogs. In the neurons, we observed crowding of mitochondria, the cellular energy pumps, and accumulation of amyloid-β typical of Alzheimer's disease. Such an accumulation is expected to be found in old dogs only," says Docent Marjo Hytönen from the University of Helsinki and the Folkhälsan Research Center.
With the help of several research groups at the University of Helsinki and international partners, samples were collected from around Europe, making it possible to pinpoint the gene defect underlying the disease to the PITRM1 gene. This gene encodes an enzyme that is important to mitochondrial function. Due to their responsibility for cellular energy metabolism, mitochondria are key to the functioning of cells.
"In the study, we determined the presence of the variant in nearly 30,000 dogs from 374 breeds, identifying the gene defect only in Parson Russell Terriers. Fortunately, the carrier frequency was low, only 5%. The findings will benefit dogs immediately, as a gene test made available based on the results helps identify carriers and avoid breeding them to produce sick puppies. We have already previously reported the gene test results for the roughly 700 dogs tested in the study," says Professor Hannes Lohi from the University of Helsinki.
The disease associated with Parson Russell Terriers is a recessive trait, which means that, for the disease to develop, the defective gene must be copied from both parents to the offspring. The defect is found in this specific breed only.
"The PITRM1 protein serves as a kind of mitochondrial cleaner that breaks up unnecessary pieces of protein and also the harmful amyloid-β. The accumulation of these substances in mitochondria disturbs their function, while neurons in particular tolerate deficient cellular respiration poorly, which explains the early-onset neurodegeneration in dogs. The gene defect results in the disappearance of two amino acids in the PITRM1 enzyme and inhibits it from functioning normally," Hytönen says.
In humans, changes in the same PITRM1 gene also cause neurodegeneration that results in cerebellar ataxia with psychiatric and cognitive abnormalities.
"The human disease progresses slower, but the clinical picture and mechanisms are similar. Our canine study confirms the significance of PITRM1 to mitochondrial and neuronal function, also strengthening the link between mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration. For now, there are few human patients diagnosed with this disease, which makes the canine model groundbreaking in terms of understanding it," says Professor Lohi.
INFORMATION:
The study is part of Professor Hannes Lohi's canine gene research programme at the University of Helsinki and the Folkhälsan Research Center. The study was supported by the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation, the Academy of Finland and HiLIFE - the Helsinki Institute of Life Science.
Exposure to certain endocrine-disrupting chemicals could elevate the risk of breast cancer, according to a new comprehensive systematic review of epidemiological research. However, for many chemicals, evidence is inconsistent or still limited. The review was carried out by researchers at the universities of Hong Kong and Eastern Finland and published in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can interfere with the body's hormonal system, also called the endocrine system, and are widely present in the environment. They originate from a variety of ...
If the CO2 content of the atmosphere is not to increase any further, carbon dioxide must be converted into something else. However, as CO2 is a very stable molecule, this can only be done with the help of special catalysts. The main problem with such catalysts has so far been their lack of stability: after a certain time, many materials lose their catalytic properties.
At TU Wien, research is being conducted on a special class of minerals - the perovskites, which have so far been used for solar cells, as anode materials or electronic components rather than for their catalytic properties. Now scientists at TU Wien have succeeded in producing a special perovskite that is excellently suited as ...
As we accumulate more and more gene-sequencing information, cell-type databases are growing in both size and complexity. There is a need to understand where different types of cells are located in the body, and to map their gene expression patterns into specific locations in tissues and organs. For example, a gene can be actively expressed in one cell while suppressed in another.
One way of mapping genes into tissues is a technique called in situ hybridization. Simply put, a target gene is tagged ("hybridized") with a fluorescent marker within the sections of the tissue it is located in (the "in situ" part). The sections are then visualized under a specialized microscope to see where the gene "lights up". Consecutive photographs of each section are then put together to generate a ...
Lafora disease is an inherited neurodegenerative condition that initially develops with seizures in adolescence and evolves with progressive degeneration of the nervous system to death, about ten years after its onset. It is characterised by the accumulation of abnormal glycogen aggregates called Lafora bodies in the brain. There is currently no treatment for this condition, although some therapies are being tested in clinical trials.
Led by Dr. Joan Guinovart, emeritus professor of the University of Barcelona (UB) and also group leader of CIBERDEM, the Metabolic Engineering lab at IRB Barcelona has discovered that Lafora bodies that accumulate in glial cells, which are essential for the proper ...
You can lubricate a bicycle chain with oil, but what do you do with a Mars rover or a red-hot conveyor belt in the steel industry? Very special nanomaterials have now been studied by the TU Wien together with research groups from Saarbrücken (Germany), Purdue University in the USA and the Universidad de Chile (Santiago, Chile).
The material class of MXenes (pronounced "maxene") has caused quite a stir in recent years in connection with novel battery technologies. But it now turns out that they are also an excellent solid lubricant that is extremely durable and performs its task even under the most difficult conditions. These remarkable properties of MXenes have now been published in the renowned journal ACS Nano.
Like a stack of sheets of paper
Just ...
A new type of COVID-19 testing strategy could help streamline the process of identifying cases, tracking variants and detecting co-infecting viruses.
At present, separate assays and complex workflows are involved in each of these three diagnostic procedures, with analyses typically performed in highly specialized facilities. KAUST researchers have now combined all three kinds of tests into a single procedure that should allow for point-of-care tracking of COVID-19 and the many emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2.
"Our all-in-one test provides a promising integrated solution for rapid field-deployable detection and mutational surveillance of pandemic viruses," says stem cell biologist Mo Li, who led the study.
The test involves a portable ...
Scrobiculariaplana is a type of wedge clam widely found along the coasts and estuariesof northern Europe, the Mediterranean and West Africa. Like other mollusks, it is used as a bioindicator to study pollution in these types of ecosystems, for its ability to accumulate heavy metals and organic pollutants.
A new study has managed to identify the transcriptome and the associated proteome of this bivalve, a finding that could represent an important leap forward in the early detection of pollutants in coastal areas. While the genome is the DNA content comprising the genetic information essential for life, the transcriptome includes only the information on genes that are expressed, while the proteome is the totality of proteins expressed at a given time and under specific conditions. Therefore, ...
Frequent use of social media may not amount to the same as addiction, according to research at the University of Strathclyde.
The study invited 100 participants to locate specific social media apps on a simulated smartphone screen as quickly and accurately as possible, while ignoring other apps. The participants were varied in the extent and type of their social media use and engagement.
The exercise aimed to assess whether social media users who reported the greatest level of use were more likely to have their attention drawn to the apps through a process known as 'attentional bias,' ...
Researchers assessing the impact of solar energy development across Europe have come up with ten ways in which the expansion of solar can be shaped to ensure pollinators benefit.
Space-hungry solar photovoltaic (PV) is set to dominate future global electricity supply, but with careful decision making, efforts to secure clean energy need not come at the expense of biodiversity - particularly pollinators which are in sharp decline.
Bees, hoverflies, wasps, beetles, butterflies and moths play a key role in food production, with around 75% of the leading global food crops and 35% of global crop production relying on them to some extent.
Writing in the journal Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, a Lancaster-led team of environmental scientists systematically reviewed the available ...
KINGSTON, R.I., -- April 20, 2021 -- The Northwest Atlantic Shelf is one of the fastest-changing regions in the global ocean, and is currently experiencing marine heat waves, altered fisheries and a surge in sea level rise along the North American east coast. A END ...