URI oceanographers reveal links between migrating Gulf Stream and warming ocean waters
2021-04-20
(Press-News.org) KINGSTON, R.I., -- April 20, 2021 -- The Northwest Atlantic Shelf is one of the fastest-changing regions in the global ocean, and is currently experiencing marine heat waves, altered fisheries and a surge in sea level rise along the North American east coast. A END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How the language you speak aligns to your genetic origins and may impact research on your health
2021-04-20
Almost 80% of South Africans speak one of the SEB family languages as their first language. Their origins can be traced to farmers of West-Central Africa whose descendants over the past two millennia spread south of the equator and finally into Southern Africa.
Since then, varying degrees of sedentism [the practice of living in one place for a long time], population movements and interaction with Khoe and San communities, as well as people speaking other SEB languages, ultimately generated what are today distinct Southern African languages such as isiZulu, isiXhosa and Sesotho.
Despite these linguistic differences, ...
Biologists discover a new type of placental structure in animals
2021-04-20
The Cyclostomata is an ancient group of aquatic colonial suspension-feeders from the phylum Bryozoa. The fact that they have unique placentae has been discovered by researchers at St Petersburg University and the University of Vienna. The coenocytes, i.e. large multinucleate cell structures, originate via nuclear multiplication and cytoplasmic growth among the cells surrounding the early embryo. Interestingly, the coenocytes are commonly found among fungi and plants, yet are quite rare in animals. It is the first time coenocytes have been discovered in placenta.
Biologists are well aware that the cells of the living organisms are incredibly different in the way that they behave. They may happen to form a ...
New study reveal targeted therapy working in early breast cancer
2021-04-20
Targeted therapy in early stages of breast cancer can pave the way for a notable higher success rate, shows a study from the University of Bergen, Norway (UiB).
PARP (Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase) inhibitors represent an established targeted therapy for multiple cancer types, including cancers of the prostate, ovary and rare cases of breast cancer.
PARP inhibitors take advantage of defects in a central mechanism of DNA damage repair, observed in these cancers. While such compounds have been successfully applied in ovarian and prostate cancers, to this end only a small minority of patients with breast ...
Chickens and pigs with integrated genetic scissors
2021-04-20
Researchers at the TUM have demonstrated a way to efficiently study molecular mechanisms of disease resistance or biomedical issues in farm animals. Researchers are now able to introduce specific gene mutations into a desired organ or even correct existing genes without creating new animal models for each target gene. This reduces the number of animals required for research..
CRISPR/Cas9 enables desired gene manipulations
CRISPR/Cas9 is a tool to rewrite DNA information. Genes can be inactivated or specifically modified using this method. The CRISPR/Cas9 system consists of two components.
The gRNA (guide RNA) is a short sequence that binds specifically to the ...
A study finds gender bias in music recommendation algorithms
2021-04-20
Although the problem of gender discrimination is already found in the music industry, music recommendation algorithms would be increasing the gender gap. Andrés Ferraro and Xavier Serra, researchers of the Music Technology research group (MTG) of the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), with Christine Bauer, of the University of Utrecht (Netherlands), have recently published a paper on gender balance in music recommendation systems in which they ask themselves how the system should work to avoid gender bias.
At the outset, the authors identified that gender justice was one of the artists' main concerns
Initially, the work by Ferraro, Serra and Bauer ...
New findings suggest organ tissues become increasingly immune throughout life
2021-04-20
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/20/2021) -- University of Minnesota Medical School researchers have offered new ways to think about the immune system thanks to a recent study published in END ...
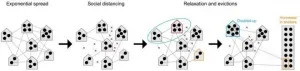
Preventing evictions remains critical to controlling COVID-19, study finds
2021-04-20
PHILADELPHIA - Renter protection policies that have curbed mass evictions during the COVID-19 pandemic have played a key role in preventing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in U.S. cities, according to a new study published in Nature Communications.
Using an epidemiological model to predict how evictions and eviction moratoria would impact the epidemic, the researchers found, for instance, that in a city of 1 million in which 1 percent of households experience eviction monthly, this could lead to up to 49,000 excess COVID-19 infections. In Philadelphia alone, a fivefold increase in ...
Overgrowth of gut yeast in newborns may increase asthma risk
2021-04-20
An overgrowth of yeast in the gut within the first few months of life may cause changes to the immune system that increase the risk of asthma later on, shows a study published today in eLife.
Asthma is a common and sometimes difficult-to-manage, life-long lung condition that affects one in 10 children in developed countries. The findings explain a possible cause of asthma and may help scientists develop new strategies to prevent or treat the condition.
The period just after birth is a critical window for the development of a healthy immune system and gut microbiome. ...
Specialized technique captures unique protein structures in neuropathy disorders
2021-04-20
Charcot Marie Tooth and Dejerine-Sottas syndrome are groups of diseases that involve the breakdown of the myelin sheath covering nerve axons.
As this myelin sheath breaks down, people who have these disorders suffer nerve damage in the arms and legs--those with Dejerine-Sottas disease may never walk or may lose the ability to walk by the time they are teenagers.
Researchers have known that a protein called PMP22, which is important for nerve myelin, is likely involved in the disease. But because the protein is so small and part of the cell membrane, ...
Study reveals roadmap of muscle decline with age
2021-04-20
Scientists have produced a comprehensive roadmap of muscle aging in mice that could be used to find treatments that prevent decline in muscle mobility and function, according to a report published today in eLife.
The study reveals which molecules in the muscle are most significantly altered at different life stages, and shows that a molecule called Klotho, when administered to mice in old, but not very old, age, was able to improve muscle strength.
Age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass and function - called sarcopenia - is associated with loss of mobility and increased risk of falls. Yet, although scientists know how sarcopenia affects the appearance and behaviour of muscle tissues, the underlying molecular mechanisms for sarcopenia remain poorly understood. Current treatments ...