(Press-News.org) Targeted therapy in early stages of breast cancer can pave the way for a notable higher success rate, shows a study from the University of Bergen, Norway (UiB).
PARP (Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase) inhibitors represent an established targeted therapy for multiple cancer types, including cancers of the prostate, ovary and rare cases of breast cancer.
PARP inhibitors take advantage of defects in a central mechanism of DNA damage repair, observed in these cancers. While such compounds have been successfully applied in ovarian and prostate cancers, to this end only a small minority of patients with breast cancer (2-3%), harboring germline mutations in the BReast CAncer type-1 and -2 (BRCA1/2) genes have benefitted, and a seminal study conducted 12 years ago reveled no benefit for patients with breast cancer not harboring such mutations.
Now, a national Norwegian study headed by professors Hans Petter Eikesdal, Stian Knappskog and Per Eystein Lønning at University of Bergen and Haukeland University Hospital for the first time reveals benefit of the PARP inhibitor Olaparib in patients with early breast cancer not harboring germline mutations.
Poor prognosis - considerable results
In the PETREMAC study, unselected patients with large (>4 cm diameter) so-called triple negative breast cancers were treated upfront with Olaparib.
Triple negative breast cancers is a breast cancer subgroup often affecting young patients and is a form of breast cancer associated with a poor prognosis.
Among 32 patients treated, 18 (56%) responded with tumor regression on Olaparib monotherapy. Most importantly, 16 out of the 18 responders revealed molecular markers predicting a likely benefit (gene mutations or so-called epigenetic modifications) of genes involved in the process of DNA repair contrasting only 4 out of 14 non-responders.
These findings allow identification of individual tumors likely to benefit from PARP inhibition. Five patients harbored germline mutations (i.e. patients that may potentially be treated with a PARP inhibitor prior to this study).
However, among patients not harboring such germline mutations (i.e. patients that would normally be excluded from PARP inhibitor therapy), 14/26 patients (54%) responded to therapy. Moreover, among these 14 patients, 12 could be identified upfront as likely responders based on analyzing their tumor tissue for mutations / epimutations affecting DNA repair.
Improved personalized treatment
In conclusion, the study challenges the previous dogma that PARP inhibition may not work for patients not harboring germline mutations. Most importantly, the authors found a strong correlation between response to therapy and molecular markers easily detectable in the tumor tissue.
"While the results need confirmation in independent studies, our results point toward improved personalized treatment for many patients diagnosed with triple negative breast cancer", says professor Lønning.
Finally, the study illuminates a concept gaining increasing support in oncology: While previous studies revealed no benefit from PARP inhibition in late-stage breast cancer, this study demonstrates a therapy which was ineffective in late cancer may potentially be of great benefit in the early setting.
INFORMATION:
Researchers at the TUM have demonstrated a way to efficiently study molecular mechanisms of disease resistance or biomedical issues in farm animals. Researchers are now able to introduce specific gene mutations into a desired organ or even correct existing genes without creating new animal models for each target gene. This reduces the number of animals required for research..
CRISPR/Cas9 enables desired gene manipulations
CRISPR/Cas9 is a tool to rewrite DNA information. Genes can be inactivated or specifically modified using this method. The CRISPR/Cas9 system consists of two components.
The gRNA (guide RNA) is a short sequence that binds specifically to the ...
Although the problem of gender discrimination is already found in the music industry, music recommendation algorithms would be increasing the gender gap. Andrés Ferraro and Xavier Serra, researchers of the Music Technology research group (MTG) of the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), with Christine Bauer, of the University of Utrecht (Netherlands), have recently published a paper on gender balance in music recommendation systems in which they ask themselves how the system should work to avoid gender bias.
At the outset, the authors identified that gender justice was one of the artists' main concerns
Initially, the work by Ferraro, Serra and Bauer ...
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/20/2021) -- University of Minnesota Medical School researchers have offered new ways to think about the immune system thanks to a recent study published in END ...
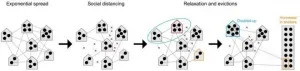
PHILADELPHIA - Renter protection policies that have curbed mass evictions during the COVID-19 pandemic have played a key role in preventing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in U.S. cities, according to a new study published in Nature Communications.
Using an epidemiological model to predict how evictions and eviction moratoria would impact the epidemic, the researchers found, for instance, that in a city of 1 million in which 1 percent of households experience eviction monthly, this could lead to up to 49,000 excess COVID-19 infections. In Philadelphia alone, a fivefold increase in ...
An overgrowth of yeast in the gut within the first few months of life may cause changes to the immune system that increase the risk of asthma later on, shows a study published today in eLife.
Asthma is a common and sometimes difficult-to-manage, life-long lung condition that affects one in 10 children in developed countries. The findings explain a possible cause of asthma and may help scientists develop new strategies to prevent or treat the condition.
The period just after birth is a critical window for the development of a healthy immune system and gut microbiome. ...
Charcot Marie Tooth and Dejerine-Sottas syndrome are groups of diseases that involve the breakdown of the myelin sheath covering nerve axons.
As this myelin sheath breaks down, people who have these disorders suffer nerve damage in the arms and legs--those with Dejerine-Sottas disease may never walk or may lose the ability to walk by the time they are teenagers.
Researchers have known that a protein called PMP22, which is important for nerve myelin, is likely involved in the disease. But because the protein is so small and part of the cell membrane, ...
Scientists have produced a comprehensive roadmap of muscle aging in mice that could be used to find treatments that prevent decline in muscle mobility and function, according to a report published today in eLife.
The study reveals which molecules in the muscle are most significantly altered at different life stages, and shows that a molecule called Klotho, when administered to mice in old, but not very old, age, was able to improve muscle strength.
Age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass and function - called sarcopenia - is associated with loss of mobility and increased risk of falls. Yet, although scientists know how sarcopenia affects the appearance and behaviour of muscle tissues, the underlying molecular mechanisms for sarcopenia remain poorly understood. Current treatments ...
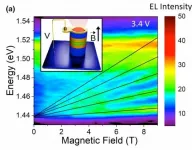
Diodes are widely used electronic devices that act as one-way switches for current. A well-known example is the LED (light-emitting diode), but there is a special class of diodes designed to make use of the phenomenon known as “quantum tunneling”. Called resonant-tunneling diodes (RTDs), they are among the fastest semiconductor devices and are used in countless practical applications, such as high-frequency oscillators in the terahertz band, wave emitters, wave detectors, and logic gates, to take only a few examples. RTDs are also sensitive to light and can be used as photodetectors or optically active elements in optoelectronic circuits.
Quantum tunneling (or the tunnel ...
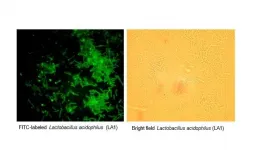
Philadelphia, April 20, 2021 - Intestinal epithelial tight junctions (TJs) act as a functional and structural barrier against harmful antigens that promote intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and other inflammatory conditions of the gut. A defective intestinal TJ barrier, sometimes known as "leaky gut," plays an important role in exacerbating and prolonging intestinal inflammation. New research reported in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, shows that the probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus) strain known as LA1 can generate a rapid and sustained enhancement of this defective intestinal barrier and effectively treat intestinal inflammation by preserving and restoring ...
Current national strategies for bridge maintenance favor replacement over maintenance. A fairly simple depreciation formula is used, resulting in overly conservative assessments of a bridge's long-term health. In a study published in the American Society of Civil Engineers' Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, researchers from UGA's College of Engineering propose a new model for the first time. This new approach considers the interaction of 60 to 80 bridge components in predicting long-term bridge performance and focuses on maintenance instead of replacement.
"Rather than considering a bridge as a monolithic structure, the bridge coactive model assesses a bridge as a system in which changes in the condition of each coactive element not only directly affects the ...