Research brief: Improving drug efficacy against prostate cancer and related bone growths
2021-04-21
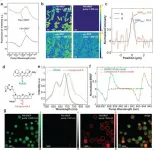
(Press-News.org) Published in the Advanced Functional Materials, University of Minnesota researcher Hongbo Pang led a cross-institutional study on improving the efficacy of nucleotide-based drugs against prostate cancer and bone metastasis.
In this study, Pang and his research team looked at whether liposomes, when integrated with the iRGD peptide, will help concentrate antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) into primary prostate tumors and its bone metastases. Liposomes are used as a drug carrier system, and ASOs are a type of nucleotide drug.
More importantly, they investigated whether this system helps more drugs across the vessel wall and deeply into the tumor tissue. This is critical because, although nucleotide drugs offer unique advantages in treating tumors and other diseases, they often suffer from a poor efficiency of crossing the blood vessels and entering the tumor tissue, where their targets reside. This problem greatly limits their clinical applicability and efficacy.
"Our system demonstrates a good ability to deliver more ASOs into both primary tumor tissue and bone metastases -- which is the primary site for prostate cancer metastasis," said Pang, an assistant professor in the College of Pharmacy and a member of the Masonic Cancer Center. "This further translates into a significant improvement of ASO efficacy to inhibit the growth of primary tumor and bone metastases. We expect this system to become a universal carrier system, to improve the clinical efficacy of ASOs and other nucleotide drugs."
The study found that:
iRGD-liposomes can increase the tumor accumulation and vascular/tissue penetration of ASOs against the disease-driving gene of prostate cancer;
the ability of ASOs to inhibit the growth of both primary tumors and bone metastases was significantly enhanced by iRGD-liposomes;
and, a long-term tumor inhibition study was also performed, showing that iRGD-liposomes significantly prolongs the AR-ASO suppression of primary tumor growth.
Pang and his team say that iRGD-liposomes are proven as a desirable delivery system for ASOs, and hold the promise to improve the clinical efficacy of nucleotide drugs in cancer therapies.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by the National Institute of Health and the State of Minnesota.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-21
DUARTE, Calif. -- Scientists at City of Hope, a world-renowned independent research and treatment center for cancer and diabetes, have developed a novel, noninvasive liquid biopsy test for detecting lymph node metastasis in individuals with high-risk T1 colorectal carcinoma. Research on the development of the blood test was reported in a END ...
2021-04-21
A new study is the first-ever to identify the genes for creativity in Homo sapiens that distinguish modern humans from chimpanzees and Neanderthals. The research identified 267 genes that are found only in modern humans and likely play an important role in the evolution of the behavioral characteristics that set apart Homo sapiens, including creativity, self-awareness, cooperativeness, and healthy longevity. The study, led by an international and interdisciplinary team of researchers from the American Museum of Natural History and Washington University among other institutions, is published today in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
"One of the most fundamental questions about ...
2021-04-21
It has been a long pursuit to develop super-resolution imaging techniques for Raman microscopy, which has intrinsic advantages of chemical specificity over the fluorescence counterpart. Despite the perceived importance and extensive research efforts, true super-resolution (defined as diffraction-unlimited) Raman imaging of biological systems in the optical far-field remains challenging due to the deficiency in sensitivity for conventional Raman scattering. Consequently, those reported super-resolution vibrational imaging methods have to base on excitation saturating, ...
2021-04-21
The Endangered dryas monkey (Cercopithecus dryas), endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, is one of Africa's most mysterious primates. The discovery of the dryas monkey killed by a hunter in the buffer zone of Lomami National Park in 2014 has prompted field research of this small species (5-7 pounds). However, they are difficult to detect because they live in dense vegetation in secondary forest thickets.
Using non-invasive research and no-flash camera traps from 2014 to 2019, scientists from Florida Atlantic University in collaboration with researchers from the FZS-Lomami Project, Democratic Republic of the Congo, now have picture-perfect details on this elusive species. They have confirmed ...
2021-04-21
Astronomers have discovered a pulsar--a dense and rapidly spinning neutron star sending radio waves into the cosmos--using a low-frequency radio telescope in outback Australia.
The pulsar was detected with the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) telescope, in Western Australia's remote Mid West region.
It's the first time scientists have discovered a pulsar with the MWA but they believe it will be the first of many.
The finding is a sign of things to come from the multi-billion-dollar Square Kilometre Array (SKA) telescope. The MWA is a precursor telescope for the SKA.
Nick Swainston, a PhD student at the Curtin University node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR), made the discovery while processing data collected as part ...
2021-04-21
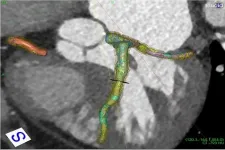
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common form of heart disease and is present in about END ...
2021-04-21
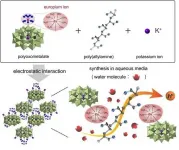
Protons are the next big thing when it comes to fuel cell technology. The subatomic exchange produces power on a scale that challenges contemporary solid-state fuel cell technology, used to help power space shuttles. To realize the proton-based technology sooner, an international team of researchers have developed a hybrid material that effectively transports protons at high temperatures and humidity -- two major challenges in past attempts.
The results were published on April 19 in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, a journal of the American Chemical Society.
The team, led by ...
2021-04-21
A new Portland State study challenges the idea that youth with cognitive disabilities are unable or lack potential to pursue a career in science, technology, engineering and mathematics.
In a study using national data on more than 15,000 adolescents, the researchers found that undergraduates with medicated ADHD or autism appear to be more likely to major in STEM than youth without cognitive disabilities, and youth with autism have the most positive STEM attitudes.
Dara Shifrer, the lead author and an associate professor of sociology at PSU, says that increasing access to STEM fields for youth with disabilities depends not only on encouraging them to pursue STEM majors but also to enroll in college because STEM occupations often require bachelor's degrees at ...
2021-04-21
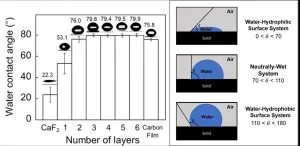
Graphene is a two-dimensional material in which carbon atoms are arranged in hexagonal structures, and it has unique physical and chemical properties such as sub-nanometer thickness, chemical stability, mechanical flexibility, electrical and thermal conductivity, optical transparency, and selective permeability to water. Due to these properties, various applications of graphene in transparent electrodes, desalination, electrical energy storage, and catalysts have been vigorously studied.
Because graphene is an extremely thin material, for practical uses, it has to be deposited on top of other materials that serve as substrate. One of the research subjects which is of great scientific ...
2021-04-21
Osaka, Japan - Catalysts lie at the heart of a greener and more sustainable future for chemical production. However, many of the catalysts currently in widespread use have limitations that affect their efficiency. Researchers from Osaka University have reported a stable and reusable nickel phosphide nanoalloy catalyst for the hydrogenation of maltose to maltitol that outperforms conventional catalysts. Their findings are published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Maltitol is a sugar alcohol that is widely used as a sweetener and food additive. It can be produced by hydrogenating maltose; however, the reaction must be selective to avoid generating ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research brief: Improving drug efficacy against prostate cancer and related bone growths