Scientists reveal origin of neuronal diversity in hypothalamus
2021-04-21
(Press-News.org) A mechanistic understanding of brain development requires a systematic survey of neural progenitor cell types, their lineage specification and maturation of postmitotic neurons. Cumulative evidences based on single-cell transcriptomic analysis have revealed the heterogeneity of cortical neural progenitors, their temporal patterning and the developmental trajectories of excitatory and inhibitory neurons in the developing neocortex. Nevertheless, the developmental hierarchy of the hypothalamus, which contains an astounding diversity of neurons that regulate endocrine, autonomic and behavioral functions, has not been well understood.
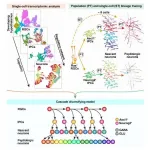
Recently, however, Prof. WU Qingfeng's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) conducted a study focusing on the origin of this neuronal diversity. For their work, they profiled the transcriptome of 43,261 hypothalamic neural cells to map the developmental landscape of the mouse hypothalamus and mapped the trajectory of radial glial cells (RGCs), intermediate progeny+++tor cells (IPCs), nascent neurons and peptidergic neurons.
The researchers found that RGCs adopt a conserved strategy for multipotential differentiation, but generate both Ascl1+ and Neurog2+ IPCs. Ascl1+ IPCs differ from their telencephalic counterpart by displaying fate bifurcation whereby they can differentiate into both glutamatergic (excitatory) and GABAergic (inhibitory) neurons. Postmitotic nascent neurons derived from IPCs further resolve into multiple peptidergic neuronal subtypes. Clonal analysis also demonstrates that single RGCs can produce multiple neuronal subtypes.
This finding reveals that multiple cell types along the lineage hierarchy contribute to the fate diversification of hypothalamic neurons in a stepwise fashion, thus uncovering an effective strategy for neural progenitors to generate extreme neuronal diversity.
Furthermore, this study provides a developmental perspective for understanding hypothalamus plasticity and gaining valuable insights into hypothalamic diseases such as anorexia, narcolepsy and insomnia.
This work, entitled "Cascade diversification directs generation of neuronal diversity in the hypothalamus," was published in Cell Stem Cell on April 21.
INFORMATION:
It was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS and the Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-21
WHO Peter Libby, MD, cardiovascular medicine specialist at Brigham and Women's Hospital and the Mallinckrodt Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School; author of a new review paper published in Nature.
WHAT Atherosclerosis -- hardening of the arteries -- is now involved in the majority of deaths worldwide, and advances in our understanding of the biology of the disease are changing traditional views and opening up new avenues for treatment.
The picture of who may be at risk for a heart attack has evolved considerably in recent decades. At one time, a heart attack might have conjured up the image of a middle-aged white man with high cholesterol and high blood pressure who smoked cigarettes. Today, traditional concepts of what contributes to risk have changed. These ...
2021-04-21
In 2016, an inflatable arch wreaked havoc at the Tour de France bicycle race when it deflated and collapsed on a cyclist, throwing him from his bike and delaying the race while officials scrambled to clear the debris from the road. Officials blamed a passing spectator's wayward belt buckle for the arch's collapse, but the real culprit was physics.
Today's inflatable structures, used for everything from field hospitals to sporting complexes, are monostable, meaning they need a constant input of pressure in order to maintain their inflated state. Lose that pressure and the structure ...
2021-04-21
What is the cost of 1 ton of a greenhouse gas? When a climate-warming gas such as carbon dioxide or methane is emitted into the atmosphere, its impacts may be felt years and even decades into the future - in the form of rising sea levels, changes in agricultural productivity, or more extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and heat waves. Those impacts are quantified in a metric called the "social cost of carbon," considered a vital tool for making sound and efficient climate policies.
Now a new study by a team including researchers from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) ...
2021-04-21
Despite our efforts to sort and recycle, less than 9% of plastic gets recycled in the U.S., and most ends up in landfill or the environment.
Biodegradable plastic bags and containers could help, but if they're not properly sorted, they can contaminate otherwise recyclable #1 and #2 plastics. What's worse, most biodegradable plastics take months to break down, and when they finally do, they form microplastics - tiny bits of plastic that can end up in our oceans, fish, and even our bodies.
Now, as reported in the journal Nature, scientists at the Department ...
2021-04-21
A study that appeared today on Current Biology sheds new light on the continental migrations which shaped the genetic background of all present Europeans. The research generates new ancient DNA evidence and direct dating from a fragmentary fossil mandible belonging to an individual who lived ~17,000 years ago in northeastern Italy (Riparo Tagliente, Verona). The results backdate by about 3,000 years the diffusion in Southern Europe of a genetic component linked to Eastern Europe/Western Asia previously believed to have spread westwards during later major warming shifts.
"By looking into the past of this particular individual, ...
2021-04-21
Astronomers using data from NASA and the ESA (European Space Agency) telescopes have released a new all-sky map of the outermost region of our galaxy. Known as the galactic halo, this area lies outside the swirling spiral arms that form the Milky Way's recognizable central disk and is sparsely populated with stars. Though the halo may appear mostly empty, it is also predicted to contain a massive reservoir of dark matter, a mysterious and invisible substance thought to make up the bulk of all the mass in the universe.
The data for the new map comes from ESA's Gaia mission and NASA's Near Earth Object Wide Field Infrared Survey Explorer, or NEOWISE, which operated from 2009 to 2013 under the moniker WISE. The study, led by astronomers at the Center for ...
2021-04-21
Substantial cuts in global greenhouse gas emissions could be achieved by raising water levels in agricultural peatlands, according to a new study in the journal Nature.
Peatlands occupy just three per cent of the world's land surface area but store a similar amount of carbon to all terrestrial vegetation, as well as supporting unique biodiversity.
In their natural state, they can mitigate climate change by continuously removing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it securely under waterlogged conditions for thousands of years.
But many peatland areas have been substantially modified by human activity, including drainage for agriculture and forest plantations. This results in the ...
2021-04-21
Scientists have found fragments of titanium blasting out of a famous supernova. This discovery, made with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, could be a major step in pinpointing exactly how some giant stars explode.
This work is based on Chandra observations of the remains of a supernova called Cassiopeia A (Cas A), located in our galaxy about 11,000 light-years from Earth. This is one of the youngest known supernova remnants, with an age of about 350 years.
For years, scientists have struggled to understand how massive stars - those with masses over about 10 times that of the Sun - explode when they run ...
2021-04-21
The diagnosis of diseases like cancer almost always needs a biopsy - a procedure where a clinician removes a piece of suspect tissue from the body to examine it, typically under a microscope. Many areas of diagnostic medicine, especially cancer management, have seen huge advances in technology, with genetic sequencing, molecular biology and artificial intelligence all rapidly increasing doctors' ability to work out what's wrong with a patient. However the technology of medical needles hasn't changed dramatically in 150 years, and - in the context of cancer management - needles are struggling to provide adequate tissue samples for new diagnostic techniques. Now researchers have shown that modifying the biopsy needle to vibrate rapidly ...
2021-04-21
PHILADELPHIA--Piperlongumine, a chemical compound found in the Indian Long Pepper plant (Piper longum), is known to kill cancerous cells in many tumor types, including brain tumors. Now an international team including researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has illuminated one way in which the piperlongumine works in animal models -- and has confirmed its strong activity against glioblastoma, one of the least treatable types of brain cancer.
The researchers, whose findings were published this month in END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists reveal origin of neuronal diversity in hypothalamus