New research data on the regulation of hormone-dependent breast cancer
2021-04-22
(Press-News.org) Notch proteins are key regulators of growth and differentiation of both normal and cancer cells. Researchers in Turku, Finland, have now demonstrated that the activities of distinct Notch family members are modified differently by phosphorylation. These results can be used in the development of new cancer treatments, especially for hormone-dependent breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women in Finland and other Western countries. Due to the availability of hormonal therapies, the estrogen-responsive breast cancer cases have a relatively good prognosis as compared to other breast cancer subtypes. However, some of them can also develop into an aggressive, metastatic disease, for which new types of therapeutic ideas are needed.
Research groups led by Dr Päivi Koskinen from the University of Turku and Professor Cecilia Sahlgren from Åbo Akademi University have been investigating the interactions of PIM and Notch proteins in cancer cells. The PIM kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate other proteins, whereas Notch proteins are transmembrane receptors, the intracellular part of which can be released and translocated to the nucleus to regulate the expression of Notch target genes.
While overexpression of PIM kinases has been shown to support survival and metastatic motility of cancer cells, the roles of distinct Notch family members have remained less clear in the development of cancer.
"We have now shown that PIM kinases phosphorylate the intracellular domains of both Notch1 and Notch3 proteins. To our surprise, phosphorylation is targeted to distinct sites of these structurally highly similar proteins," tells University Teacher Niina Santio from the University of Turku.
"Phosphorylation stimulates the transcriptional activity of Notch1 but has the opposite effects on Notch3. Yet, both act as oncogenes when they are phosphorylated, which is also surprising," states Postdoctoral Researcher Sebastian Landor from Åbo Akademi University.
In addition to experiments carried out with cultured cells and chick embryo xenografts, patient databases were analysed. This analysis revealed that the overexpression of both PIM1 and Notch3 is connected to poor prognosis in advanced cases of estrogen-responsive breast cancer.
"The clinical data together with our experimental observations suggest that drugs targeting PIM or Notch proteins might be able to provide new treatment options especially for the most difficult cases of breast cancer," says Niina Santio.
INFORMATION:
The research article is in press in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-22
New research by the University of New England's Palaeoscience Research Centre suggests juvenile tyrannosaurs were slenderer and relatively faster for their body size compared to their multi-tonne parents.
The research, published in the END ...
2021-04-22
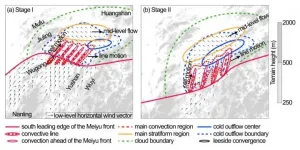
Thunderstorm development is not always dependent on atmospheric physics alone. Often, the surrounding landscape can influence convection, especially in regions with dramatic elevation changes. The Yangtze river basin in China's Jiangxi Province, which is surrounded by the Nanling Mountains, often experiences mesoscale convective systems (MCS) or squall line thunderstorms during the summer. These MCSs develop along the persistent mei-yu front, and often exhibit quickly developing parallel back-building, or training thunderstorms, resulting in torrential flooding. A research team led by Dr. Zhemin Tan, Professor at the School of Atmospheric Sciences of Nanjing University, analyzed the influences of the regional landscape that lead to consistent MCS back-building ...
2021-04-22
SINGAPORE, 22 April 2021 - A multidisciplinary team of researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) in Singapore discovered a new mitochondrial peptide called MOCCI that plays an important role in regulating inflammation of blood vessel and immunity. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, revealed how one gene encoded two molecules that provide two-pronged protection following viral infection.
Chronic and excessive inflammation of the blood vessels, known as vascular inflammation, can lead to tissue damage and cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and fibrosis. Although some therapies have shown promising results in clinical trials, they have considerable side effects, such as immunosuppression ...
2021-04-22
An increasing number of young women are at increased risk of having children born with impaired neurological conditions, due to poor iodine intake.
Dietary changes, including a growing trend towards the avoidance of bread and iodised salt, as well as a reduced intake of animal products containing iodine can contribute to low iodine levels.
A small pilot study undertaken by the University of South Australia (UniSA) comparing iodine levels between 31 vegan/plant-based participants and 26 omnivores has flagged the potential health risk.
Urine samples showed iodine readings of 44 ug/L in the plant-based group, compared to the meat eaters' 64 ug/L ...
2021-04-22
The week of Thanksgiving last year, a postcard arrived in mailboxes in Christiansburg. A link to a survey was on the back. On the front, there was a picture that was, by then, very familiar to the residents of a town that made history in 2019 as the first place in the U.S. to have a residential drone delivery service: a yellow-winged drone with a small cardboard box tucked underneath it.
The survey's 20 questions were designed to measure how Christiansburg's 22,000 residents felt about drone delivery -- the first time that this question had ever been posed to a community that had actually experienced the service. The survey was developed and conducted by researchers from the Virginia ...
2021-04-22
DALLAS, April 22, 2021 -- People with abdominal obesity and excess fat around the body's mid-section and organs have an increased risk of heart disease even if their body mass index (BMI) measurement is within a healthy weight range, according to a new Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association published today in the Association's flagship journal, Circulation.
"This scientific statement provides the most recent research and information on the relationship between obesity and obesity treatment in coronary heart disease, heart failure and arrhythmias," said Tiffany M. Powell-Wiley, M.D., ...
2021-04-22
When it comes to friendships and rivalries, male dolphins know who the good team players are. New findings, published in Nature Communications by University of Bristol researchers, reveal that male dolphins form a social concept of team membership based on cooperative investment in the team.
The Bristol researchers, with colleagues from the University of Zurich and University of Massachusetts, used 30 years of observational data from a dolphin population in Shark Bay, Western Australia, and sound playback experiments to assess how male dolphins responded to the calls of other males from their alliance network.
Dr Stephanie ...
2021-04-22
By cracking open a cellular membrane, Northwestern University synthetic biologists have discovered a new way to increase production yields of protein-based vaccines by five-fold, significantly broadening access to potentially lifesaving medicines.
In February, the researchers introduced a new biomanufacturing platform that can quickly make shelf-stable vaccines at the point of care, ensuring they will not go to waste due to errors in transportation or storage. In its new study, the team discovered that enriching cell-free extracts with cellular membranes -- the components needed to made conjugate vaccines -- vastly increased yields of its freeze-dried platform.
The work sets the stage to rapidly make medicines that address rising antibiotic-resistant bacteria as well as new viruses ...
2021-04-22
BOSTON -- Radiation therapy is used as a treatment for more than half of all cancer patients and can be highly effective at shrinking tumors and killing cancer cells. But radiation treatment can also damage healthy tissue, including tissue in the mouth and gastrointestinal tract. This tissue injury can lead to oral mucositis, esophagitis, and proctitis -- painful and sometimes debilitating tissue damage. It's estimated that these injuries occur in over 200,000 patients in the U.S. each year. In a new paper published in Advanced Science, investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital and ...
2021-04-22
Bottom Line: When given a choice, most individuals with an average risk of colorectal cancer said they would prefer a stool-based screening test for colorectal cancer over colonoscopy, the method most often recommended by health care providers.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Prevention Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Xuan Zhu, PhD, senior health services analyst at the Mayo Clinic Robert D. and Patricia E. Kern Center for the Science of Health Care Delivery
Background: Although colorectal cancer is the second most frequent cause of cancer-related death in the United States, about one-third of eligible American adults have never completed a colorectal cancer screening test, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New research data on the regulation of hormone-dependent breast cancer