(Press-News.org) Rising levels of dementia is putting pressure on residential aged care facilities, including in rural and regional centres where nursing homes and staff are already under pressure.
Now a pilot program of personalised interventions, including residents' favourite songs, has been shown to make a big difference to dementia behaviours, drug use and carers' wellbeing.
Harmony in the Bush, a study led by Flinders University in five nursing homes in Queensland and South Australia, developed a multimodal person-centred non-pharmacological intervention program incorporating individual music selections to reduce, resulting in a significant reduction in resident agitation and staff stress levels.
The focus on resident-centred therapies, rather than drug interventions, led to less dysfunctional behaviours and psychological symptoms in the trial group of 74 people living with dementia and reduced stress reported by the 87 staff in aged care homes who took part in the study.
More than one-third of the residents reported mild-severe pain and mild-severe sadness before the intervention.
"The Harmony in the Bush model is effective in reducing agitation among dementia residents with the important spinoff of significant reduction in staff stress levels in nursing homes in rural Australia," says researcher Dr Vivian Isaac, lead author on a new article in BMC Geriatrics.
The Flinders Rural and Remote Health team also found a reduction in the use of psychotropic medications and inappropriate medications when comparing residents' medication charts data covering three months pre- and post- the Harmony in the Bush intervention, as published recently in BMC Psychiatry.
In Australia, 60-70% of the people residing in nursing homes have dementia and about 70-90% of residents with dementia suffer from psychiatric or behavioral symptoms.
"The study found that the model gives staff with a structure to learn person-centred practice over about one month to reduce the impact of behavioural and psychiatric symptoms of dementia.
"The results show a statistically significant decline in aggressive behaviours, physically non-aggressive behaviours, and inappropriate verbal behaviour, hiding or hoarding - with a similar reduction in staff stress and resident safety when resources for specialised dementia care may be limited."
The study provides promising evidence on the potential of this novel model in low-resourced settings, researchers says.
Further studies will look at the cost-effectiveness and reliability of the model, which researchers have based on the Progressively Lowered Stress Threshold principles and person-centred music in nursing homes (using personal devices during rest time) to reduce agitation and other stressful behaviours.
Music has proved helpful in dementia to raise mood, stimulate memories and provide a soothing effect.
These behaviours include agitation, mood dysregulation, and disturbed thoughts and perceptions, which pose a major challenge for the residents with dementia and nursing home staff.
INFORMATION:
The paper, The outcomes of a person-centered, non-pharmacological intervention in reducing agitation in residents with dementia in Australian rural nursing homes (2021) by Vivian Isaac, Abraham Kuot, Mohammad Hamiduzzaman, Edward Strivens (James Cook University) and Jennene Greenhill (2021) by was published in BMC Geriatrics DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-38968/v2
Also Person-centered non-pharmacological intervention in reducing psychotropic medications use among residents with dementia in Australian rural aged care homes (2021) by DR Parajuli, A Kuot, M Hamiduzzaman, J Gladman and V Isaac in T DOI 10.1186/s12888-020-03033-w
Funding for the project was provided by the Department of Health under the National Aged Care Services Fund project (4-4ZOHI8C).
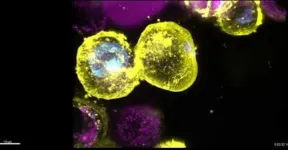
A new molecular 'freeze frame' technique has allowed WEHI researchers to see key steps in how the protein MLKL kills cells.
Small proteins called 'monobodies' were used to freeze MLKL at different stages as it moved from a dormant to an activated state, a key process that enables an inflammatory form of cell death called necroptosis. The team were able to map how the three-dimensional structure of MLKL changed, revealing potential target sites that might be targets for drugs - a potential new approach to blocking necroptosis as a treatment for inflammatory diseases.
The research, which ...
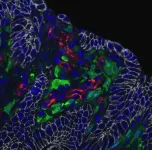
IL-11 is known to promote the development of colorectal cancer in humans and mice, but when and where IL-11 is expressed during cancer development is unknown. "To address these questions experimentally, we generated reporter mice that express the green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene in interleukin 11 (IL-11)-producing (IL11+) cells in vivo. We found IL-11+ cells in the colons of this murine colitis-associated colorectal cancer model," said Dr. Nishina, the lead author of a study published April 16 in Nature Communications. "The IL-11+ cells were absent from the colon under normal conditions but rapidly appeared in the tissues of mice with colitis and colorectal cancer."
In the study, Dr. Nishina and colleagues characterized the IL-11+ cells by flow cytometry and found that ...
The human immune defense is based on the ability of white blood cells to accurately identify disease-causing pathogens and to initiate a defense reaction against them. The immune defense is able to recall the pathogens it has encountered previously, on which, for example, the effectiveness of vaccines is based. Thus, the immune defense the most accurate patient record system that carries a history of all pathogens an individual has faced. This information however has previously been difficult to obtain from patient samples.
The learning immune system can be roughly divided into two parts, of which B cells are responsible for producing antibodies against pathogens, while T cells are responsible for destroying their targets. The measurement of antibodies by traditional laboratory ...
The study was published by the team from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB), the Max Planck Institutes of Biochemistry and Biophysics, the Center for Synthetic Microbiology (SYNMIKRO) and the Chemistry Department at Philipps Universität Marburg, the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, USA, and Université Paris-Saclay, France, online on 12 April 2021 in the journal Nature Plants.
Catalyst of life
Photosystem II (PS II) is of fundamental importance for life, as it is able to catalyse the splitting of water. The oxygen released in this reaction allows us to breathe. In addition, PS II converts light energy ...
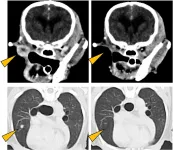
Scientists have shown that the biological molecule PD-L1 is a potential target for the treatment of metastasized oral malignant melanoma in dogs.
There are a number of cancers that affect dogs, but there are far fewer diagnosis and treatment options for these canine cancers. However, as dogs and humans are both mammals, it is likely that strategies and treatments for cancers in humans can be used for canine cancer, with minor modifications.
A team of scientists, including Associate Professor Satoru Konnai from the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at Hokkaido University, have demonstrated that an anti-cancer therapy that targets the cancer marker PD-L1--a target that has shown great promise for treating cancer in humans--is ...
Notch proteins are key regulators of growth and differentiation of both normal and cancer cells. Researchers in Turku, Finland, have now demonstrated that the activities of distinct Notch family members are modified differently by phosphorylation. These results can be used in the development of new cancer treatments, especially for hormone-dependent breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women in Finland and other Western countries. Due to the availability of hormonal therapies, the estrogen-responsive breast cancer cases have a relatively good prognosis as compared to other breast cancer subtypes. However, some of them can also develop into an aggressive, metastatic disease, for which new types ...
New research by the University of New England's Palaeoscience Research Centre suggests juvenile tyrannosaurs were slenderer and relatively faster for their body size compared to their multi-tonne parents.
The research, published in the END ...
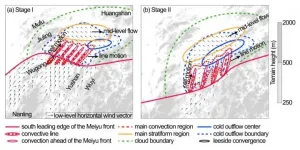
Thunderstorm development is not always dependent on atmospheric physics alone. Often, the surrounding landscape can influence convection, especially in regions with dramatic elevation changes. The Yangtze river basin in China's Jiangxi Province, which is surrounded by the Nanling Mountains, often experiences mesoscale convective systems (MCS) or squall line thunderstorms during the summer. These MCSs develop along the persistent mei-yu front, and often exhibit quickly developing parallel back-building, or training thunderstorms, resulting in torrential flooding. A research team led by Dr. Zhemin Tan, Professor at the School of Atmospheric Sciences of Nanjing University, analyzed the influences of the regional landscape that lead to consistent MCS back-building ...
SINGAPORE, 22 April 2021 - A multidisciplinary team of researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) in Singapore discovered a new mitochondrial peptide called MOCCI that plays an important role in regulating inflammation of blood vessel and immunity. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, revealed how one gene encoded two molecules that provide two-pronged protection following viral infection.
Chronic and excessive inflammation of the blood vessels, known as vascular inflammation, can lead to tissue damage and cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and fibrosis. Although some therapies have shown promising results in clinical trials, they have considerable side effects, such as immunosuppression ...
An increasing number of young women are at increased risk of having children born with impaired neurological conditions, due to poor iodine intake.
Dietary changes, including a growing trend towards the avoidance of bread and iodised salt, as well as a reduced intake of animal products containing iodine can contribute to low iodine levels.
A small pilot study undertaken by the University of South Australia (UniSA) comparing iodine levels between 31 vegan/plant-based participants and 26 omnivores has flagged the potential health risk.
Urine samples showed iodine readings of 44 ug/L in the plant-based group, compared to the meat eaters' 64 ug/L ...