(Press-News.org) Skoltech scientists in collaboration with researchers from the University of Arizona and the Los Alamos National Laboratory have developed an approach that allows power grids to return to stability fast after demand response perturbation. Their research at the crossroads of demand response, smart grids, and power grid control was published in the journal Applied Energy.
Power grids are complex systems that manage the generation, transmission and distribution of electrical power to consumers, also called loads. As it is not possible to store electrical energy along the transmission lines, grid operators must ensure, ideally at all times, the balance between production and consumption of electrical energy, i.e. the stability of power grids. While it is essential to guarantee the provision of electricity to consumers and meet their needs, random events, such as electric faults, fluctuations due to renewables penetration or a sudden excessive demand, may perturb the grid stability, possibly leading to brownouts or worse, blackouts. An illustrative real-life situation is when the electricity demand for air conditioning is high in case of heat waves, and cannot be met. If the electrical power reserve is insufficient, rolling blackouts may be implemented on a part or the whole of the distribution network; this management strategy, or worse, failures that lead to non-controlled blackouts profoundly affect the customers' comfort and well-being, as well as the utility companies' operation and profitability.
Careful scheduling by electricity providers is crucial to manage peaks of demands. To avoid contingencies, solutions exist: generator reserves, ancillary services, and demand response. The latter solution involves the customers who may reduce or shift their electricity consumption at suitable times for the company in exchange for lower prices. Companies may also leverage direct load control programs acting on, e.g., air-conditioners' and water heaters' switches.
"Demand response is a low-cost and flexible solution that relies on the customers' tolerance to a temporary perturbation of their comfort, but it may also cause problems such as the parasitic synchronization of individual devices. Put simply, after some demand response operation like turning all devices on, the devices will all be in the same state, consuming energy; then after some time they will all be off, and then on again almost simultaneously, and so on and so forth, if no action is taken to avoid such a kind of collective behavior. In other words, if all devices become synchronized, the power grid has to bear the stress of consumption oscillations possibly causing instability, and certainly delaying the ensemble's availability for a subsequent demand response period," professor Henni Ouerdane comments.
In the new study, the scientists analyzed the relaxation of the energy consumption dynamics of an ensemble of thermostatically controlled loads (air conditioners) after a demand response perturbation. Relaxation must occur rapidly enough to ensure energy efficiency, grid stability, and return to the consumers' "comfort zone".
"The focus was on a discrete model that captures the actual discrete dynamics of the system as information and control signals are sent over discrete time intervals. While it was shown previously using a continuous in-time model that relaxation may be accelerated through mean-field control, it is essential for practical load management to rather rely on discretized control models. The study demonstrates that super-relaxation is a genuine feature of discretized models, but also how these models based on a few control parameters provide energy systems operators with an efficient way to effectively manage the consumption dynamics of aggregated loads", adds lead author of the study and Skoltech PhD student Ilia Luchnikov.
"Our work essentially deals with the optimal use of energy resources and the sustainability of power systems, but the scope of demand response extends beyond power systems management, as it may be applied in other settings like the water sector, the oil industry, and waste management," professor Ouerdane concludes.
INFORMATION:
Skoltech is a private international university located in Russia. Established in 2011 in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Skoltech is cultivating a new generation of leaders in the fields of science, technology and business, is conducting research in breakthrough fields, and is promoting technological innovation with the goal of solving critical problems that face Russia and the world. Skoltech is focusing on six priority areas: data science and artificial intelligence, life sciences, advanced materials and modern design methods, energy efficiency, photonics and quantum technologies, and advanced research. Web: https://www.skoltech.ru/.
A test which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to measure proteins present in some patients with advanced bowel cancer could hold the key to more targeted treatment, according to research published today.
A team at the University of Leeds collaborated with researchers at Roche Diagnostics to develop the technique, which will help doctors and patients to decide on the best treatment options.
They used samples from a previous trial funded by Cancer Research UK to look at the levels of two proteins, known as AREG and EREG, which are produced by some colorectal cancers.
Algorithms driven by AI enabled the researchers to show that patients with higher levels of these proteins received significant benefit from a treatment which inhibits a different protein involved ...
Key takeaways
Tourniquet use has been consistently increasing in Los Angeles County since 2015 and is significantly associated with improved patient survival.
Tourniquet use is safe and does not lead to increased risk of amputation with proper surgical care after arriving at the hospital.
Findings are specific to Los Angeles County, where patients who had a tourniquet placed were able to be transported quickly to a trauma center for further life-saving care.
CHICAGO (April 22, 2021): Uncontrolled bleeding continues to be one of the most common causes of preventable ...
Insect decline is one of the greatest challenges facing our society. As a result of the destruction of many natural habitats, bees, bumblebees, butterflies, beetles and the like find less and less food. As a consequence, they are barely able to fulfil their role as pollinators of wild and cultivated plants. This trend is increasingly noticeable in agricultural regions in particular.
Researchers at the University of Münster have now taken a more detailed look at how the choice of seeds in restoration measures - i.e. the restoration of natural habitats at degraded land - affects how insects benefit from these measures. Here, not only the plant ...
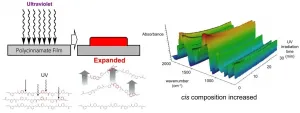
A phenomenon of "photoexpansion" in hard plastic films with a high glass transition temperature in the dry state was established, which was essentially different from very soft actuators, such as elastomers or gels. The photoexpanding hard actuators were expected to apply in the wide fields because they do not contain vaporable matters such as solvents and were much more thermoresistant than conventional ones.
Ishikawa, April 22, 2021 - Polymers that exhibit their functions by light have been studied for a few decades because they enable device miniaturization, energy saving, and precise signal control. Polymers based on azobenzene, diarylethene, etc. are the pioneers, ...
Patients with chronic kidney dysfunction frequently develop thickening of the heart muscle, so-called left ventricular hypertrophy. This is particularly pronounced in patients who are in the late stage of renal dysfunction, that is to say those requiring renal replacement therapy such as haemodialysis. The danger of this cardiac hypertrophy lies in the considerable associated increase in risk of acute cardiovascular disease, such as sudden cardiac death, for example. Haemodialysis patients have a number of risk factors for developing this form of cardiac hypertrophy. One of those is elevated levels of the protein Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23), ...
- Recent discoveries focused on manipulation of atomically-thin 2D materials, while the new breakthrough can be used to stack technologically-relevant 3D materials at a twist angle
- Method allows continuous, systematic control of optical emission intensity and energy, and can produce ultraviolet emissions at room temperature for bulk systems
- The discovery can be significant for applications in medicine, environmental or information technologies.
Singapore, 22 April 2021 - Researchers from the Low Energy Electronic Systems (LEES) Interdisciplinary Research ...
The citric acid cycle is an important metabolic pathway that enables living organisms to generate energy by degrading organic compounds into carbon dioxide (CO?). The first step in the cycle is usually performed by the enzyme citrate synthase, which builds citrate. But, in the absence of oxygen (under anaerobic conditions), some bacteria can perform the reverse cycle: They can build up biomass from CO?. In this so-called reversed citric acid cycle, citrate synthase is replaced by ATP-citrate lyase, which consumes cells' universal energy carrier ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to cleave citrate instead of forming it. However, a few years ago, a research team led by Ivan Berg (University of Münster) and Wolfgang Eisenreich (Technical University of Munich) discovered that instead of ...
A new study from the University of Surrey has found that among people aged 55 to 75 more frequent use of the internet was beneficial for mental health and quality of life under lockdown. Those who used the internet more, particularly for staying in touch with friends and family, were at lower risk of depression and reported a higher quality of life.
Loneliness and social isolation have been major problems for many under lockdown, and for older people in particular. Loneliness raises risk of depression and other negative health outcomes. In a paper published in the journal Healthcare, researchers from Surrey investigated ...
Australia's unique and highly endemic flora and fauna are threatened by rapid losses in biodiversity and ecosystem health, caused by human influence and environmental challenges. To monitor and respond to these trends, scientists and policy-makers need reliable data.
Biodiversity researchers and managers often don't have the necessary information, or access to it, to tackle some of the greatest environmental challenges facing society, such as biodiversity loss or climate change. Data can be a powerful tool for the development of science and decision-making, which is where the END ...
Rain is a common phenomenon on Earth. There is a similar phenomenon on the Sun, called coronal rain. It is related to the coronal heating and magnetic field, and plays a fundamental role in the mass cycle between the hot, tenuous corona and the cool, dense chromosphere.
Coronal rain usually takes place in post-flare loops and the non-flaring active region coronal loops. It is generally classified into two categories: flare-driven and quiescent coronal rain, depending on its relation to the flare. Both kinds of coronal rain form along structures that are magnetically ...