(Press-News.org) The tree of life just got a little bigger: A team of scientists from the U.S. and China has identified an entirely new group of microbes quietly living in hot springs, geothermal systems and hydrothermal sediments around the world. The microbes appear to be playing an important role in the global carbon cycle by helping break down decaying plants without producing the greenhouse gas methane.
"Climate scientists should take these new microbes into account in their models to more accurately understand how they will impact climate change," said END
Climate-friendly microbes chomp dead plants without releasing heat-trapping methane
2021-04-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New blood markers may reveal heart attack in chest pain patients
2021-04-23
A patient arrives at hospital with chest pain. Doctors suspect heart attack and rapid diagnosis is important, but the tests to confirm it can be invasive and it could easily be something else. Could a simple blood test help to non-invasively rule heart attack in or out? A new study in open access journal Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine certainly suggests so. The study identified telltale markers in the blood of heart attack patients that distinguished them from patients suffering chest pain with other causes. The researchers hope that the results will lead to new diagnostic tests for heart attacks.
If you have ever suffered chest pain, the possibility of a heart attack may have popped into your head. While chest pain is ...
Study uncovers human-to-cat transmission of the virus that causes COVID-19
2021-04-23
New research provides evidence that people have transmitted SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, to cats during the pandemic in the UK. The study, which is published in Veterinary Record, detected the virus last year in cats that developed mild or severe respiratory disease.
Investigators used a range of laboratory techniques to show that two domestic cats from households with suspected cases of COVID-19 were infected with SARS-CoV-2.
"These findings indicate that human-to-cat transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic in ...
Malaria vaccine becomes first to achieve WHO-specified 75% efficacy goal
2021-04-23
Researchers from the University of Oxford and their partners have today reported findings from a Phase IIb trial of a candidate malaria vaccine, R21/Matrix-M, which demonstrated high-level efficacy of 77% over 12-months of follow-up. In their findings (posted on SSRN/Preprints with The Lancet) they note that they are the first to meet the World Health Organization's Malaria Vaccine Technology Roadmap goal of a vaccine with at least 75% efficacy.
The authors report (in findings in press with The Lancet) from a Phase IIb randomised, controlled, double-blind trial conducted at the Clinical Research Unit of Nanoro (CRUN) / Institut de Recherche en Sciences de la Santé (IRSS), Burkina Faso. 450 participants, aged 5-17 months, were recruited from the catchment area of Nanoro, covering ...
Radar satellites can better protect against bushfires and floods
2021-04-23
New research led by Curtin University has revealed how radar satellites can improve the ability to detect, monitor, prepare for and withstand natural disasters in Australia including bushfires, floods and earthquakes.
The research used Synthetic Aperture Radar data obtained by the European Space Agency Sentinel-1 satellite, amongst others, to evaluate Australia-specific case studies.
Lead researcher Dr Amy Parker, an ARC Research Fellow from Curtin's School of Earth and Planetary Sciences, said the Sentinel-1 satellite mission provided the first complete global Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) dataset and the first opportunity to use this type of data to assess hazards in new locations, including Australia.
"What makes SAR so valuable is that it provides all-weather and night-and-day ...
Using spatial distance strategically with luxury and popular product displays
2021-04-23
Researchers from Nanjing University, National Sun Yat-sen University, and Northwestern University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that shows that the spatial distance between products and consumers can affect perceived value and willingness to pay.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Values Created from Far and Near: Influence of Spatial Distance on Brand Evaluation" and is authored by Xing-Yu (Marcos) Chu, Chun-Tuan Chang, and Angela Y. Lee.
No one ever questions why some retail products are on display in cabinets behind the sales counter, ...
New species of dumbo octopus identified using minimally invasive techniques
2021-04-23
A new species of deep-sea dwelling dumbo octopus called Grimpoteuthis imperator sp. nov. has been described using a combination of MRI, micro-CT and minimally invasive gene analysis rather than traditional dissection methods. The findings are presented in the open access journal BMC Biology.
The single specimen, which was identified as a mature male, was named G. imperator because it was discovered in the northern part of the Emperor Seamounts, an undersea mountain ridge in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. In addition to the scientific name in Latin, the authors suggest possible common names for this new species such as Emperor dumbo, Dumbo impérial (French), and Kaiserdumbo (German).
Finned or dumbo octopods, although considered rare organisms, form ...
Naturally GM: Crops steal genes from other species to accelerate evolution
2021-04-23
Grass crops are able to bend the rules of evolution by borrowing genes from their neighbours, giving them a competitive advantage, a new study has revealed.
Research, led by the University of Sheffield, is the first to show that grasses can incorporate DNA from other species into their genomes through a process known as lateral gene transfer.
The stolen genetic secrets give them an evolutionary advantage by allowing them to grow faster, bigger or stronger and adapt to new environments quicker. These findings could inform future work to create crops that are more resistant to the effects of climate change and help to tackle food security problems.
The Sheffield team studied grasses, which include some of the most economically and ecologically important plants, such as the most ...
Teaching pupils to 'think like Da Vinci' will help them to take on climate change
2021-04-23
A radically reformed approach to education, in which different subjects teach connected themes, like climate change or food security, is being proposed by researchers, who argue that it would better prepare children for future crises.
In a newly-published study, education researchers from the Universities of Cambridge and Edinburgh argue that there is a compelling case for a drastic shake-up of the school curriculum, so that subjects are no longer taught independently of one another. Instead, they argue that the arts and sciences should 'teach together' around real-world problems, and in a manner ...
Finding new life for wine-grape residue
2021-04-23
California produces nearly 4 million tons of world-class wine each year, but with that comes thousands of tons of residue like grape skins, seeds, stems and pulp. What if scientists could harness that viticultural waste to help promote human health?
Maybe they can, according to new research from food scientists at the University of California, Davis. In a study published in the journal LWT - Food Science and Technology, the team discovered a wealth of potentially health-enhancing compounds and sugar molecules called oligosaccharides within chardonnay wine-grape pomace.
Oligosaccharides are found in many plant and animal tissues, including human breast milk. Recent advances have revealed oligosaccharides' vast potential ...
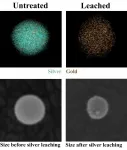
Silver ions hurry up, then wait as they disperse
2021-04-22
HOUSTON - (April 22, 2021) - There's gold in them thar nanoparticles, and there used to be a lot of silver, too. But much of the silver has leached away, and researchers want to know how.
Gold-silver alloys are useful catalysts that degrade environmental pollutants, facilitate the production of plastics and chemicals and kill bacteria on surfaces, among other applications. In nanoparticle form, these alloys could be useful as optical sensors or to catalyze hydrogen evolution reactions.
But there's an issue: Silver doesn't always stay put.
A new study by scientists at Rice University and the University ...