Finding new life for wine-grape residue
Chardonnay pomace may be rich in health-enhancing compounds
2021-04-23
(Press-News.org) California produces nearly 4 million tons of world-class wine each year, but with that comes thousands of tons of residue like grape skins, seeds, stems and pulp. What if scientists could harness that viticultural waste to help promote human health?
Maybe they can, according to new research from food scientists at the University of California, Davis. In a study published in the journal LWT - Food Science and Technology, the team discovered a wealth of potentially health-enhancing compounds and sugar molecules called oligosaccharides within chardonnay wine-grape pomace.
Oligosaccharides are found in many plant and animal tissues, including human breast milk. Recent advances have revealed oligosaccharides' vast potential to support intestinal health.
"We were surprised by the diversity of the oligosaccharides in the chardonnay wine grapes, including the presence of structural elements found in mother's milk," said Amanda Sinrod, lead author and a master's candidate working with Professor Daniela Barile.
The UC Davis team analyzed the molecular composition of chardonnay residue provided by Jackson Family Wines and Sonomaceuticals, a company founded by two food industry businesswomen to develop new uses for viticulture waste. Wine-grape pomace, or marc, comprises about 30 percent of the original wine-grape material, and much of it is left to decompose in the sun.
Potential source for food or supplements
"It's all about sustainable wine production and finding a second life for wine grapes," Barile explained. "Up to this point, chardonnay marc has been regarded as a byproduct of winemaking with little or no value. Early results are encouraging that marc could be a valuable source for oligosaccharides and other compounds that support health and nutrition."
UC Davis researchers were among the first to decode the magic of oligosaccharides in mother's milk. The sugar molecules don't nourish the baby directly. Instead, they feed a strain of bacteria in the infant's intestines that helps build immunity against illness and disease. That discovery is helping scientists develop methods and products to improve human health.
Barile's lab innovates technologies for recovering health-enhancing compounds from various agricultural and industrial waste streams, such as whey, legumes and chickpeas. Her team previously discovered oligosaccharides in both red and white wine residue and is pleased with preliminary findings from the chardonnay analysis.
"There is more research to be done, but early results are promising that chardonnay marc can become a source for developing supplements and other food products to support health," Barile said.
Oligosaccharides appeared to be especially abundant in the wine-grape skins. In earlier research, scientists detected oligosaccharides in the finished wine product, but not in large concentrations. Researchers didn't include bottled wine in this study.
The chardonnay marc samples were also rich in flavonoids, healthy compounds found in many fruits and vegetables. Researchers are exploring whether the oligosaccharides work independently or synergistically with these bioactive compounds to support intestinal health. The team is studying how growing conditions, vintages and processing might affect the health potential of viticulture waste.
"We observed significant differences in the relative abundance and type of oligosaccharides in different parts of the marc, so further research is needed to maximize their potential in food product design," Sinrod said.
INFORMATION:
The UC Davis team included Cooperative Extension Specialist Selina Wang and Xuequi Li with the Olive Center, and Mrittika Bhattacharya and Bruna Paviani with the Department of Food Science and Technology.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-22
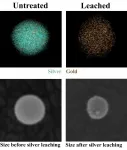
HOUSTON - (April 22, 2021) - There's gold in them thar nanoparticles, and there used to be a lot of silver, too. But much of the silver has leached away, and researchers want to know how.
Gold-silver alloys are useful catalysts that degrade environmental pollutants, facilitate the production of plastics and chemicals and kill bacteria on surfaces, among other applications. In nanoparticle form, these alloys could be useful as optical sensors or to catalyze hydrogen evolution reactions.
But there's an issue: Silver doesn't always stay put.
A new study by scientists at Rice University and the University ...
2021-04-22
RESEARCH TRIANGLE PARK, N.C. -- New photonics research paves the way for improved lasers, high-speed computing and optical communications for the Army.
Photonics has the potential to transform all manners of electronic devices by storing and transmitting information in the form of light, rather than electricity. Using light's speed and the way information can be layered in its various physical properties can increase the speed of communication while reducing wasted energy; however, light sources such as lasers need to be smaller, stronger and more stable to achieve that, researchers ...
2021-04-22
PHILADELPHIA-- Art appreciation is considered essential to human experience. While taste in art varies depending on the individual, cognitive neuroscience can provide clues about how viewing art affects our neural systems, and evaluate how these systems inform our valuation of art. For instance, one study shows that viewing art activates motor areas, both in clear representations of movement, like Adam and Eve in Michelangelo's Expulsion from Paradise, and in implied movement through brush strokes, like in Franz Kline's gestural paintings.
Altered neural functioning, like that experienced in patients with Parkinson's disease, changes the way ...
2021-04-22
University of Arkansas law professor Jordan Blair Woods challenges the conventional wisdom that only police can enforce traffic laws.
In "Traffic Without Police," to be published in Stanford Law Review, Woods articulates a new legal framework for traffic enforcement, one that separates it from critical police functions, such as preventing and deterring crime, conducting criminal investigations and responding to emergencies.
If not the police, who then would enforce traffic laws? As Woods explains, jurisdictions would delegate most traffic enforcement to newly created traffic agencies. These public offices would operate independently from ...
2021-04-22
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and McGill University have adapted an algorithm first developed to spot anomalies in data, like typos in patient information at hospitals or errant figures in accounting, to identify similarities across escort ads.
The algorithm scans and clusters similarities in text and could help law enforcement direct their investigations and better identify human traffickers and their victims, said Christos Faloutsos, the Fredkin Professor in Artificial Intelligence at CMU's School of Computer Science, who led the team.
"Our algorithm can put the millions of advertisements together and highlight the common parts," Faloutsos said. "If they have a lot of things in common, it's not guaranteed, but it's highly likely that it ...
2021-04-22
An international group of scientists from Italy, the USA, China and Russia have studied the relationship between collectivism, individualism and life satisfaction among young people aged 18-25 in four countries. They found that the higher the index of individualistic values at the country level, the higher the life satisfaction of young people's lives. At the individual level, however, collectivism was more significant for young people. In all countries, young people found a positive association between collectivism, particularly with regard to family ties, and life satisfaction. This somewhat contradicts and at the same time clarifies the results ...
2021-04-22
BOSTON - Exclusively using (or "vaping") e-cigarettes can help people quit smoking, but many people using e-cigarettes to quit smoking continue to smoke cigarettes. New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) reveals that respiratory symptoms--such as cough and wheeze--are more likely to develop when people use both e-cigarettes and tobacco cigarettes together compared with using either one alone. The findings are published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the flagship journal of the American Thoracic Society.
The ...
2021-04-22
A new study by Simon Fraser University historical ecologists finds that Indigenous-managed forests--cared for as "forest gardens"--contain more biologically and functionally diverse species than surrounding conifer-dominated forests and create important habitat for animals and pollinators. The findings are published today in Ecology and Society.
According to researchers, ancient forests were once tended by Ts'msyen and Coast Salish peoples living along the north and south Pacific coast. These forest gardens continue to grow at remote archaeological villages on Canada's northwest coast and are composed ...
2021-04-22
In 2005, an ultramarathon runner ran continuously 560 kilometers (350 miles) in 80 hours, without sleeping or stopping. This distance was roughly 324,000 times the runner's body length. Yet this extreme feat pales in comparison to the relative distances that fruit flies can travel in a single flight, according to new research from Caltech.
Caltech scientists have now discovered that fruit flies can fly up to 15 kilometers (about 9 miles) in a single journey--6 million times their body length, or the equivalent of over 10,000 kilometers for the average human. In comparison to body length, this is further than many migratory species of birds can fly in a day. To discover this, the team conducted experiments in a dry lakebed ...
2021-04-22
In a worldwide study of 2,100 pregnant women, those who contracted COVID-19 during pregnancy were 20 times more likely to die than those who did not contract the virus.
UW Medicine and University of Oxford doctors led this first-of-its-kind study, published today in JAMA Pediatrics. The investigation involved more than 100 researchers and pregnant women from 43 maternity hospitals in 18 low-, middle- and high-income nations; 220 of the women received care in the United States, 40 at UW Medicine. The research was conducted between April and August of 2020.
The study is unique because each woman affected by COVID-19 was compared with two uninfected pregnant women who gave birth during the same span in the same hospital.
Aside ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Finding new life for wine-grape residue
Chardonnay pomace may be rich in health-enhancing compounds