'Planar and curved' pyrrole-fused azacoronenes
Effect of 3D sructures on π-electron functions
2021-04-23
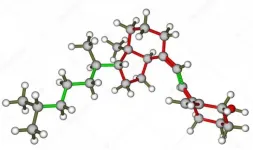
(Press-News.org) Recently study on synthetic approaches toward polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) as graphene with a well-defined structure has attracted much attention. A research group in Ehime University has been studying the synthesis and fundamental properties of pyrrole-fused azacoronene (HPHAC), a nitrogen-containing PAH. HPHACs are composed of electron-rich pyrroles, which are easily oxidized, and their dicationic species in particular exhibit unique features such as global aromaticity based on macrocyclic π-conjugation. However, all the compounds reported so far have bulky substituents at the periphery of the HPHAC skeleton, and thus the characterization of the physical properties of the pristine HPHAC itself or the π-electron function based on π-π interactions has not been possible.
In this study, the group has synthesized two new derivatives, one with alkyl groups at the periphery of the HPHAC skeleton and the other with concave π-planes above and below the HPHAC skeleton. The HPHAC with alkyl groups was found to be more readily oxidized than the compounds previously reported and to exhibit stable redox properties. In addition, reflecting its planar structure, the HPHAC forms an alternating stacked column structure with electron-deficient π-electron compounds. On the other hand, the HPHAC with an extended π-electron system exhibits an unusual π-electron function with a double concave surface. Reflecting its shape, this electron-rich HPHAC strongly interacts with spherical fullerene, which is an electron-deficient π-electron compound. A comparison of the global aromaticities of the two dicationic species reveals that the double-concave HPHAC possesses weaker aromaticity.
Recent research on π-electron materials has led to the synthesis of three-dimensional structures, such as bowl- and saddle-shaped compounds, instead of the conventional planar ones. However, there have been few studies focusing on the π-electron function of the 3D structure, except for clarifying its structural features using single crystal X-ray structure analysis. By elucidating the detailed structure-property relationships between analogues that share the same skeleton but have different 3D structures, new design guidelines can be obtained for organic electronics and spintronics materials involving π-electron functions.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-23
An interdisciplinary group of Spanish scientists, bringing together biologists and chemists from the Universities of Seville, Huelva, the Autonomous University of Madrid and the Institute of Marine Sciences of Andalusia of the CSIC in Cadiz, have just published the results of their pioneering research studying the management of marinas. The group of scientists, led by the US professor José Manuel Guerra García, studied in detail the sediments in Andalusia's marinas and has proposed a new index, the MEPI (Marinas Environmental Pollution Index) to quantify the level of contamination in these ports.
There has been a proliferation of marinas in recent ...
2021-04-23
The giant star featured in this latest Hubble Space Telescope anniversary image is waging a tug-of-war between gravity and radiation to avoid self-destruction. The star, called AG Carinae, is surrounded by an expanding shell of gas and dust -- a nebula -- that is shaped by the powerful winds of the star. The nebula is about five light-years wide, which equals the distance from here to our nearest star, Alpha Centauri.
The huge structure was created from one or more giant eruptions several thousand years ago. The star's outer layers were blown into space, the expelled material ...
2021-04-23
How do the billions of cells communicate in order to perform tasks? The cells exert force on their environment through movement - and in doing so, they communicate. They work as a group in order to infiltrate their environment, perform wound healing and the like. They sense the stiffness or softness of their surroundings and this helps them connect and organize their collective effort. But when the connection between cells is distrubeddisturbed, a situation just like when cancer is initiated, can appear.
Assistant Professor Amin Doostmohammadi at the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen has investigated the mechanics of cell movement and connection ...
2021-04-23
Etrasimod 2 mg treatment group achieved statistical significance in the percentage change in weekly peak pruritis (PP-NRS), in the change in Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), and in the change in Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM)
Etrasimod 2 mg was generally well tolerated, consistent with data in previous trials
Park City, Utah, April 23, 2021 - Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Nasdaq: ARNA) today announced data at a late-breaking session at the American Academy of Dermatology VMX Experience. Etrasimod, a novel investigational drug candidate to treat moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD), demonstrated statistical significance in both clinician and patient reported outcomes in the ADVISE Phase 2b clinical trial. Etrasimod is a highly selective, once-daily, oral sphingosine ...
2021-04-23
Paper Title: Safety of Tranexamic Acid in Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in High-risk Patients
Journal: Anesthesiology
Authors: Jashvant Poeran MD, PhD, Director of the Center for Clinical and Outcomes Research, and Associate Professor of Population Health Science & Policy and Orthopedics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; Calin S. Moucha, MD, Chief of Adult Reconstruction & Joint Replacement Surgery at Mount Sinai Hospital, and Associate Professor of Orthopedics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; and other coauthors.
Bottom Line: The use of the drug tranexamic acid is commonplace in patients undergoing hip or knee replacement surgery to reduce blood loss. However, this drug works by promoting clotting and safety concerns exist when used in certain high-risk ...
2021-04-23
By Karina Toledo | Agência FAPESP – Can a high dose of vitamin D administered on admission to hospital improve the condition of patients with moderate or severe COVID-19? The answer is no, according to a Brazilian study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
The article reports a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, the kind of study considered the gold standard to evaluate drug efficacy. It was conducted with FAPESP’s support by researchers at the University of São Paulo’s ...
2021-04-23
DURHAM, N.H.-- Corals and sponges are important foundations in ocean ecosystems providing structure and habitats that shelter a high number of species like fish, crabs and other creatures, particularly in the seamounts and canyons of the deep sea. Researchers at the University of New Hampshire have discovered that when it comes to climate change not all deep-sea corals and sponges are affected the same and some could be threatened if average ocean temperatures continue to increase in the deep sea of the Northwest Atlantic.
"These deep-sea corals and sponges are ecologically important because they are foundational ...
2021-04-23
ITHACA, N.Y. - House finches are locked in a deadly cycle of immunity and new strains of bacterial infection in battling an eye disease that halved their population when it first emerged 25 years ago, according to new research from the Cornell Lab of Ornithology.
House finch eye disease causes red, swollen, watery or crusty eyes. Afflicted birds can recover, but may die because they cannot see well enough to find food or avoid predators. The latest analyses, based on the observations of Project FeederWatch participants from eight Northeast states, addresses the long-term ...
2021-04-23
A recently published article in the Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions journal provides new evidence that pathogens are hijacking the plant immune system to cause disease while providing insights into a newly discovered mechanism.
A large variety of pathogens infect plants and cause different diseases, which can lead to reduced crop yields. During infection, pathogens secrete effector proteins into the plant cell. Some of these proteins target plant proteasomal degradation machinery, which is responsible for recycling proteins to regulate cell processes. Some E1, E2 and E3-ligase proteins have been identified as playing a role in plant susceptibility ...
2021-04-23
PHILADELPHIA, PA - The first National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Cancer Institute (NCI)-funded clinical study examining stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in the treatment of oligometastatic breast, prostate, and non-small cell lung (NSCLC) cancers displayed evidence that SBRT can be safely used to treat patients who have multiple metastases. These results were recently published in JAMA Oncology.
The results of the Phase I NRG-BR001 trial, conducted by the NCI National Clinical Trials Network group NRG Oncology, indicate that SBRT treatment in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Planar and curved' pyrrole-fused azacoronenes
Effect of 3D sructures on π-electron functions