Newly discovered immune cell function vital to healing
2021-04-23
(Press-News.org) Cardiovascular disease, the most common cause of death, is the result of oxygen deprivation as blood perfusion to affected tissue is prevented. To halt the development of the disease and to promote healing, re-establishment of blood flow is crucial. Researchers at Uppsala University have now discovered that one of the most common immune cells in the human body, macrophages, play an important role in re-establishing and controlling blood flow, something that can be used to develop new drugs.
The classic function of immune cells is to defend the body against attacks from microorganisms and tumour cells. Macrophages are immune cells specialised in killing and consuming microorganisms but they have also been shown to be involved in wound healing and building blood vessels.
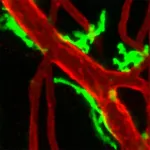
A new study published by researchers at Uppsala University demonstrates that macrophages accumulate around blood vessels in damaged tissue in mice, but also in humans after a myocardial infarction or peripheral ischemia. In mice, these macrophages could be seen to regulate blood flow, performing a necessary damage-control function. In healthy tissue, this task is carried out by blood vessel cells.
This discovery led the research group to investigate whether their findings could be developed into a new treatment to increase blood flow to damaged leg muscles, thus stimulating healing and improving function. By increasing the local concentration of certain signal substances that bind to macrophages in the damaged muscle, the research group was able to demonstrate that more macrophages accumulated around the blood vessels, improving their ability to regulate blood flow. This in turn resulted in improved healing and that the mice were able use the injured leg to a far greater extent.
"This is an entirely new function for the cells in our immune system and might mean that in future we can use immunotherapies to treat not only cancer but also cardiovascular diseases," says Mia Phillipson, leader of the research group behind the discovery.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-23
How primates get from A to B gives vital information about their cognitive evolution, say researchers in a new study looking at the travel paths of animals in the wild. Using data from 164 wild primate populations, the global survey examines the mental abilities that primates, including ourselves, use to know where and when to travel in the most efficient way.
A birds eye view
Co-author Miguel de Guinea, expert in Evolutionary Anthropology at Oxford Brookes University commented: "Imagine looking down on a huge outdoor market from high in the sky, perhaps from a drone hovering quietly above. The people below move in different ways. Some wander haphazardly among the stalls: they are learning what's available but are clearly not busy. Others take bee-line routes ...
2021-04-23
In celebration of the 31st anniversary of the launching of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers aimed the renowned observatory at a brilliant "celebrity star," one of the brightest stars seen in our galaxy, surrounded by a glowing halo of gas and dust.
The price for the monster star's opulence is "living on the edge." The star, called AG Carinae, is waging a tug-of-war between gravity and radiation to avoid self-destruction.
The expanding shell of gas and dust that surrounds the star is about five light-years wide, which equals the distance from here to the nearest star beyond the Sun, Proxima Centauri.
The huge ...
2021-04-23
Now that teens and young adults across the country account for an increasing share of COVID-19 cases, and many have become eligible for vaccination, several recently published studies based on polls of this age group provide insights into the kinds of messaging that might work best for both preventing transmission and vaccine uptake.
Using data from text-message polls of people between the ages of 14 and 24 taken at several points in 2020, researchers from the University of Michigan find a clear theme: that most young people are taking COVID-19 seriously and trying to follow public health guidance, and that many of them they are motivated by the desire to protect ...
2021-04-23
ABERDEEN PROVING GROUND, Md. -- Army and Arizona State University researchers identified a set of approaches to help scientists assess how well autonomous systems and humans communicate.
These approaches build on transformational scientific research efforts led by the Army's Robotics Collaborative Technology Alliance, which evolved the state of robots from tools to teammates and laid the foundation for much of the service's existing research into how humans and robots can work together effectively.
As ideas for autonomous systems evolve, and the possibilities ...
2021-04-23
Researchers from the Faraday Institution's SOLBAT project have made a significant step in understanding how and why solid-state batteries (SSBs) fail. A paper, published in Nature Materials on 22 April, provides answers to one important piece of the scientific puzzle.
To make step changes in electric vehicle (EV) battery range and safety at a lower cost, new battery chemistries that are "beyond lithium ion" must be developed. SSBs are one such promising technology, but mass market adoption has been held back by several key technical challenges that cause the battery to fail when charged and discharged.
SSBs can short circuit after repeating charging and discharging. One well-recognised cause of battery failure is the growth of dendrites, branching networks of lithium that ...
2021-04-23
An evolutionary biologist from the University of Bonn brought a new octopus species to light from depths of more than 4,000 meters in the North Pacific Ocean. The sensational discovery made waves in the media a few years ago. Researchers in Bonn have now published the species description and named the animal "Emperor dumbo" (Grimpoteuthis imperator). Just as unusual as the organism is the researchers' approach: in order to describe the new species, they did not dissect the rare creature, but instead used non-destructive imaging techniques. The results have now been published in the prestigious journal BMC Biology.
In the summer of 2016, Dr. Alexander ...
2021-04-23
A continental-scale network of conservation sites is likely to remain effective under future climate change scenarios, despite a predicted shift in key species distributions.
New research, led by Durham University and published in the journal Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, investigates the impacts of potential climate change scenarios on the network of Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas (IBAs) across the Caribbean, and Central and South America.
The research was carried out in collaboration with Senckenberg Biodiversity and Climate Research Centre, BirdLife International and the National Audubon Society.
IBAs are sites identified as being internationally important for the conservation of bird populations, with over 13,000 ...
2021-04-23
There are many different types of cancer, but they all have one thing in common: errors in the signals that control normal cell behaviour can cause uncontrolled cell growth and cell division, leading to a tumour. An enzyme called SHP2 plays a key role in this regard. SHP2 is a signalling molecule that in its activated state stimulates cell proliferation. In a normal healthy body, the rates of cell proliferation and cell death are balanced and tumours do not develop. However, if SHP2 becomes too active, the number of cells being created outweighs the number that die, which can lead to the formation of dangerous tumours. Enhanced SHP2 activity resulting from genetic ...
2021-04-23
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati say a regulatory protein found in skeletal muscle fiber may play an important role in the body's fight or flight response when encountering stressful situations.
The protein, fast skeletal myosin binding protein-C (fMyBP-C), plays a foundational role in the proper regulation of contractile structure and function in the body's fast twitch muscles -- these muscles produce sudden bursts of power to sprint into action, jump or lift heavy objects. Fast skeletal myosin binding protein-C modulates the speed and force of fast skeletal muscle contraction.
"This response ...
2021-04-23
People with type 2 diabetes tend to have poorer muscle function than others. Now a research team at Lund University in Sweden has discovered that in type 2 diabetes, a specific gene is of great importance for the ability of muscle stem cells to create new mature muscle cells. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
"In people with type 2 diabetes, the VPS39 gene is significantly less active in the muscle cells than it is in other people, and the stem cells with less activity of the gene do not form new muscle cells to the same degree. The gene is important when muscle cells absorb sugar from blood and build new muscle. Our study is the first ever to link this gene to type 2 diabetes", says Charlotte Ling, professor of epigenetics at Lund University who led ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Newly discovered immune cell function vital to healing







