(Press-News.org) It's been hailed as a wonder drug and it's certainly creating wonder profits. By some estimates, the Cannabidiol (or CBD) market could be worth $20 billion dollars by 2024. While users tout its effectiveness in pain relief, up until now there's been limited experimental human research on the actual effectiveness of the drug. However, a new study led by researchers at Syracuse University sheds light on the ability of CBD to reduce pain along with the impact that the so-called placebo effect may have on pain outcomes.
"For science and the public at large the question remained, is the pain relief that CBD users claim to experience due to pharmacological effects or placebo effects," asked Martin De Vita, a researcher in the psychology department at Syracuse University's College of Arts and Sciences. "That's a fair question because we know that simply telling someone that a substance has the ability to relieve their pain can actually cause robust changes in their pain sensitivity. These are called expectancy effects." De Vita, along with Syracuse Emeritus Psychology Professor Stephen Maisto, were uniquely prepared to answer that exact question. The pair, along with fellow lab member and doctoral candidate Dezarie Moskal, previously conducted the first systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental research examining the effects cannabinoid drugs on pain. As the first experimental pain trial to examine CBD, their study yielded consistent and noteworthy results. Among other findings, the data showed that CBD and expectancies for receiving CBD do not appear to reduce experimental pain intensity, but do make the pain feel less unpleasant.
De Vita and Maisto used sophisticated equipment that safely induces experimental heat pain, allowing them to measure how the recipient's nervous system reacts and responds to it. "Then we administer a drug, like pure CBD, or a placebo and then re-assess their pain responses and see how they change based on which substance was administered," said De Vita. Researchers then took it a step farther by manipulating the information given to participants about which substances they received. In some cases, participants were told that they got CBD when they actually received a placebo, or told they would be getting a placebo when they actually got CBD. "That way we could parse out whether it was the drug that relieved the pain, or whether it was the expectation that they had received the drug that reduced their pain," according to De Vita. "We hypothesized that we would primarily detect expectancy-induced placebo analgesia (pain relief). What we found though after measuring several different pain outcomes is that it's actually a little bit of both. That is, we found improvements in pain measures caused by the pharmacological effects of CBD and the psychological effects of just expecting that they had gotten CBD. It was pretty remarkable and surprising."
"The data is exciting but pretty complex in that different pain measures responded differently to the drug effect, to the expectancy, or both the drug and expectancy combined--so we're still trying to figure out what is behind the differential data with different kinds of pain measures," said Maisto. "The next step is studying the mechanisms underlying these findings and figuring out why giving instructions or CBD itself causes certain reactions to a pain stimulus."
Most people think of pain as an on and off switch, you either have it or you don't. But pain, as De Vita describes it, is a complex phenomenon with several dimensions influenced by psychological and biological factors. For example, whereas pain intensity reflects a "sensory" dimension of pain, unpleasantness represents an "affective," or emotional, aspect of pain. "If you think of pain as the noxious noise coming from a radio the volume can represent the intensity of the pain, while the station can represent the quality," said De Vita. Results from his previous study showed that while cannabinoid drugs weren't reducing the volume of pain, they were "changing the channel making it a little less unpleasant." According to De Vita, "It's not sunshine and rainbows pleasant, but something slightly less bothersome. We replicated that in this study and found that CBD and expectancies didn't significantly reduce the volume of the pain, but they did make it less unpleasant--it didn't bother them as much." As part of the study De Vita and Maisto developed advanced experimental pain measurement protocols "to pop the hood and start looking at some of these other mechanistic pain processes," said De Vita. "It's not just pain, yes or no, but there are these other dimensions of pain, and it would be interesting to see which ones are being targeted. We found that sometimes pharmacological effects of CBD brought down some of those, but the expectancies did not. Sometimes they both did it. Sometimes it was just the expectancy. And so, we were going into this thinking we were going to primarily detect the expectancy-induced pain relief but what we found out was way more complex than that and that's exciting."
One important note to also consider is the source of the CBD. "What we used in our study was pure CBD isolate oil," said De Vita. "Commercially available CBD products differ in their content and purity, so results might be different for different CBD products, depending on what other compounds they may or may not contain."
INFORMATION:
Martin De Vita is currently completing a clinical psychology internship at Brooke Army Medical Center, JBSA, TX. The view(s) expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not reflect the official policy or position of Brooke Army Medical Center, the U.S. Army Medical Department, the U.S. Army Office of the Surgeon General, the Department of the Army, the Department of the Air Force and Department of Defense or the U.S. Government.
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have discovered that some skeletal defects associated with a lack of movement in the womb during early development may still be ameliorated after such periods of immobility if movement resumes.
The researchers' discovery was made using chicken embryos, which develop similarly to their human equivalents and which can be easily viewed as development takes place - raising hopes that the finding may also apply to humans and thus have important implications for therapeutic interventions.
The research has just been published in leading international journal, Disease Models and Mechanisms.
Why babies need to move in the womb
Foetal movement in the uterus is a normal part of a healthy ...
The new alloys created by NUST MISIS scientists in cooperation with LG Electronics will help reduce the weight of radiators and heat removal systems in electric vehicles and consumer electronics by one third. The research results are published in the Journal of Magnesium and Alloys.
According to experts, with the development of electronics the problem of efficient heat removal is becoming more and more acute -- with an increase in the productivity of equipment, heat generation also grows. Reducing the temperature directly affects the prolongation of the devices' life cycle. This is especially important for household appliances, electric vehicles, LED panels.
Scientists from NUST MISIS, in collaboration with LG Electronics, ...
"Jack and Jill went up the hill to fetch a pail of water." It's a silly rhyme, but one that highlights a simple fact: Humans have long relied on wells -- such as the one on the hill visited by Jack and Jill -- for their primary drinking water supply.
Although the number of people who draw their water by pail is declining as pumps become ever more widespread, groundwater wells still supply drinking water to more than half of the world's population and sustain over 40% of irrigated agriculture. But this vital resource underfoot often gets overlooked.
UC Santa Barbara assistant professors Debra Perrone and Scott Jasechko have compiled the most comprehensive assay of groundwater wells to date, spanning 40 countries that collectively account for half of all global groundwater ...
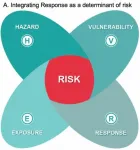
A team of researchers from the Africa Climate and Development Initiative (ACDI) led a global team of 21 climate risk scholars to better understand and inform decision making around climate change risks in Africa and globally by examining how the drivers of risk interact.
Their work extends on existing risk frameworks with the hope that this research could help decision makers, managers and researchers understand the inherent complexity of climate change.
"Understanding the interactions among risks holds potential to change the way we respond to the risks. This is important because policy makers may worry about the risk of implementing a response as much, or more so, than the risk ...
A Southern California high school junior has built a low-cost seismometer device that delivers earthquake early warnings for homes and businesses. Costing less than $100 for her to make today, the seismometer could someday be a regular household safety device akin to a smart smoke detector, says its inventor Vivien He.
About the size of a Rubik's cube and encased in clear acrylic, the seismometer has a sleek, consumer-ready look. The device's geophone detects incoming ground motion, while onboard hardware and software translate the geophone's electrical signals into a digital waveform. The device has detected all earthquakes over magnitude 3.0 around Los Angeles since September 2020.
When ...
At the Seismological Society of America's 2021 Annual Meeting, researchers shared how they are using fiber optic cable to detect the small earthquakes that occur in ice in Antarctica.
The results could be used to better understand the movement and deformation of the ice under changing climate conditions, as well as improve future monitoring of carbon capture and storage projects, said Anna Stork, a geophysicist at Silixa Ltd.
Stork discussed how she and her colleagues are refining their methods of distributed acoustic sensing, or DAS, for microseismicity--earthquakes too small to be felt. DAS works by using the tiny internal flaws within an optical fiber as thousands of seismic ...
A deep spatiotemporal neural network trained on more than 36,000 earthquakes offers a new way of quickly predicting ground shaking intensity once an earthquake is underway, researchers report at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)'s 2021 Annual Meeting.
DeepShake analyzes seismic signals in real time and issues advanced warning of strong shaking based on the characteristics of the earliest detected waves from an earthquake.
DeepShake was developed by Daniel J. Wu, Avoy Datta, Weiqiang Zhu and William Ellsworth at Stanford University.
The earthquake data used to train ...
The SEIS seismometer package from the Mars InSight lander has collected its first continuous Martian year of data, revealing some surprises among the more than 500 marsquakes detected so far.
At the Seismological Society of America (SSA)'s 2021 Annual Meeting, Savas Ceylan of ETH Zürich discussed some of the findings from The Marsquake Service, the part of the InSight ground team that detects marsquakes and curates the planet's seismicity catalog.
Marsquakes differ from earthquakes in a number of ways, Ceylan explained. To begin with, they ...
How can I prepare myself for something I do not yet know? Scientists from the Fritz Haber Institute in Berlin and from the Technical University of Munich have addressed this almost philosophical question in the context of machine learning. Learning is no more than drawing on prior experience. In order to deal with a new situation, one needs to have dealt with roughly similar situations before. In machine learning, this correspondingly means that a learning algorithm needs to have been exposed to roughly similar data. But what can we do if there is a nearly infinite amount of possibilities so that it is simply impossible to generate data ...
Cardiovascular disease, the most common cause of death, is the result of oxygen deprivation as blood perfusion to affected tissue is prevented. To halt the development of the disease and to promote healing, re-establishment of blood flow is crucial. Researchers at Uppsala University have now discovered that one of the most common immune cells in the human body, macrophages, play an important role in re-establishing and controlling blood flow, something that can be used to develop new drugs.
The classic function of immune cells is to defend the body against attacks from microorganisms and tumour cells. Macrophages are immune cells specialised in killing and consuming microorganisms but they have ...