Star light, star bright...as explained by math
2021-04-26
(Press-News.org) Not all stars shine brightly all the time. Some have a brightness that changes rhythmically due to cyclical phenomena like passing planets or the tug of other stars. Others show a slow change in this periodicity over time that can be difficult to discern or capture mathematically. KAUST's Soumya Das and Marc Genton have now developed a method to bring this evolving periodicity within the framework of mathematically "cyclostationary" processes.
"It can be difficult to explain the variations of the brightness of variable stars unless they follow a regular pattern over time," says Das. "In this study we created methods that can explain the evolution of the brightness of a variable star, even if it departs from strict periodicity or constant amplitude."
Classic cyclostationary processes have an easily definable variation over time, like the sweep of a lighthouse beam or the annual variation in solar irradiance at a given location. Here, "stationary" refers to the constant nature of the periodicity over time and describes highly predictable processes like a rotating shaft or a lighthouse beam. However, when the period or amplitude changes slowly over many cycles, the mathematics for cyclostationary processes fails.
"We call such a process an evolving period and amplitude cyclostationary, or EPACS, process," says Das. "Since EPACS processes are more flexible than cyclostationary processes, they can be used to model a wide variety of real-life scenarios."
Das and Genton modeled the nonstationary period and amplitude by defining them as functions that vary over time. In doing this, they expanded the definition of a cyclostationary process to better describe the relationship among variables, such as the brightness and periodic cycle for a variable star. They then used an iterative approach to refine key parameters in order to fit the model to the observed process.
"We applied our method to model the light emitted from the variable star R Hydrae, which exhibited a slowing of its period from 420 to 380 days between 1900 and 1950," says Das. "Our approach showed that R Hydrae has an evolving period and amplitude correlation structure that was not captured in previous work."
Importantly, because this approach links EPACS processes back to classical cyclostationary theory, then fitting an EPACS process makes it possible to use existing methods for cyclostationary processes.
"Our method can also be applied to similar phenomena other than variable stars, such as climatology and environmetrics, and particularly for solar irradiance, which could be useful for predicting energy harvesting in Saudi Arabia," Das says.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-26
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in ski wax have been receiving a lot of attention recently, but waxes constitute only a limited part of the problem of the PFAS group of toxicants.
PFAS are a large group of man-made fluorocarbon toxicants, and you are most likely full of them. The toxic substances don't break down and instead accumulate, both in nature and in your body.
"Due to their extensive use, humans and animals all over the world are continuously exposed to PFAS," says Håkon Austad Langberg, a PhD candidate at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) who has studied several of them in the last few years.
PFAS are used in many different products beyond the fluorinated ski wax that ends up in the ground on ski slopes and on trails, ...
2021-04-26
The corona pandemic has made us all focus on new ways of organizing our work. More and more companies and organizations around the world are considering how to meet their employees' demand for flexibility while at the same time reducing their office space and expensive rents.
There are advantages and disadvantages to working from home, and many factors that affect the peoples' experience of it, such as their job function, age and seniority, whether they have children, whether they are a manager or employee, etc.
Researchers from DTU Management have identified six main areas that company managers should focus on when developing strategies for remote work in future.
Associate Professor at DTU Management Christine ...
2021-04-26
People who take a commonly-prescribed drug for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) should not assume they are protected after a first dose of COVID-19 vaccine, after a large-scale study found many had poor antibody responses.
The research measured antibody responses after vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech or the Oxford/AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine in 865 people treated with infliximab, an anti-tumour necrosis factor (anti-TNF) biologic drug, prescribed to around two million people worldwide. Anti-TNF drugs are effective treatments for immune-mediated inflammatory ...
2021-04-26
The Chauvet Cave, which lies by the entrance to the Gorges of the Ardèche, is home to the world's oldest cave paintings, dating back 36,000 years. Their state of preservation and aesthetic qualities earned them a spot on the World Heritage List in 2014, 20 years after their discovery. The location of the cavern--surrounded by a remarkable landscape, next to the Pont d'Arc natural archway--raises the question of whether the people who executed these artworks looked and walked out upon the same landscape as today. Did they see the same natural archway? Scientists from the CNRS, Université Savoie Mont Blanc, and the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle1 ...
2021-04-26
Researchers from Skoltech (Russia) and their colleagues from SINTEF (Norway) have developed a mathematical model of freezing water droplets moving in cold air. This model is a part of a joint RFBR-supported Russian-Norway research project. The project is focused on predicting ice accretion on ships and other offshore structures operated in Arctic climate, which may interfere with their proper functioning and endanger crew members and cargo. The paper was published in the journal Energies.
Ships travel in cold northern waters under constant bombardment by tiny water droplets populating the chilly air. ...
2021-04-26
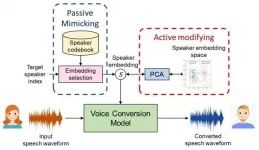
Ishikawa, Japan - Robots today have come a long way from their early inception as insentient beings meant primarily for mechanical assistance to humans. Today, they can assist us intellectually and even emotionally, getting ever better at mimicking conscious humans. An integral part of this ability is the use of speech to communicate with the user (smart assistants such as Google Home and Amazon Echo are notable examples). Despite these remarkable developments, they still do not sound very "human".
This is where voice conversion (VC) comes in. A technology used to ...
2021-04-26
Just one third of people in the UK managed to access the hospital care they needed at the peak of the first wave of the Covid-19 pandemic - according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today looks at the extent to which people managed to access NHS healthcare in April 2020, and as lockdown restrictions eased.
The researchers found that, despite high levels of unmet need, there was equal access to NHS hospital care for people at different levels of income. And the NHS principle of equal treatment for equal need was upheld.
However, people on higher incomes had better access to GP consultations, prescriptions and medical helplines at ...
2021-04-26
Steroids should not be used to treat smell loss caused by Covid-19 according to an international group of smell experts, including Prof Carl Philpott from the University of East Anglia.
Smell loss is a prominent symptom of Covid-19, and the pandemic is leaving many people with long-term smell loss.
But a new study published today shows that corticosteroids - a class of drug that lowers inflammation in the body - are not recommended to treat smell loss due to Covid-19.
Instead, the team recommend 'smell training' - a process that involves sniffing at least four different odours twice a day for several months.
Smell loss expert Prof Carl Philpott from UEA's Norwich Medical School, said: "The huge rise in smell loss caused by Covid-19 has created an unprecedented worldwide demand for ...
2021-04-26
According to the Motorik-Modul-Längsschnittstudie (MoMo, Motor Module Longitudinal Study) of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Karlsruhe University of Education (PHKA), mental health of children and adolescents decreased during the first lockdown. For children aged between 4 and 10 years and for girls irrespective of their age, mental health was found to promote physical activity during Covid-induced lockdown in spring 2020. This is reported in Children (DOI: 10.3390/children8020098).
"The impacts of the lockdown on children and adolescents is discussed widely," ...
2021-04-26
Deaths of people who suffered strokes increased during the first lockdown compared to the three previous years, new data analysis has found. Despite the pandemic, health care quality was maintained at a high level.
In their paper, published today in Stroke American Heart Association, research teams from King's College London, Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation and the Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme (SSNAP) analysed the data of 184,017 patients admitted to hospital with confirmed stroke during October-April periods across four consecutive years. This patient data were collected from 114 hospital trusts in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
Starting from the third week of February 2020 there was ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Star light, star bright...as explained by math