INFORMATION:
This research was supported by funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Applied Research Collaborations (ARC) South London at King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and South West Peninsula, with support from the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre based at Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, the Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme (SNNAP) team and King's College London.
The Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme (SSNAP) is commissioned by the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership (HQIP).
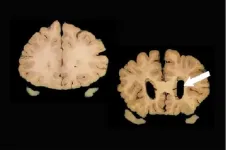
Increase in stroke mortality in people with COVID-19 during first lockdown
2021-04-26
(Press-News.org) Deaths of people who suffered strokes increased during the first lockdown compared to the three previous years, new data analysis has found. Despite the pandemic, health care quality was maintained at a high level.
In their paper, published today in Stroke American Heart Association, research teams from King's College London, Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation and the Sentinel Stroke National Audit Programme (SSNAP) analysed the data of 184,017 patients admitted to hospital with confirmed stroke during October-April periods across four consecutive years. This patient data were collected from 114 hospital trusts in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
Starting from the third week of February 2020 there was an increase in seven-day in-patient case fatality (people who died within seven days of being admitted to hospital) from 6.9% to 9.4%, compared to the same period in the three previous years.
This was significantly higher in stroke patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19, at 22.0% and 21.9% respectively, compared to 7.3% for patients with negative/unknown COVID-19 status.
In contrast, during the first lockdown the number of people admitted to hospital with a stroke remained stable until the second week of February 2020 when there was a steep decline. Between 23 March and 30 April 2020 there was a 12% reduction in stroke admissions compared to the same period in the three previous years (6,923 versus 7,902).
The team found that during the first lockdown stroke admissions fell more for:
Ischaemic stroke (blockage cutting off the blood supply to the brain) than haemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in or around the brain)
Older patients (aged over 65 years)
Patients with less severe strokes
No change was found in the proportion of patients discharged from hospital with good outcomes.
Quality of care was preserved for all measures and in some areas improved during lockdown, such as access to stroke unit care, speed of screening for dysphagia and access to rehabilitation therapies.
Dr Abdel Douiri, study lead from King's College London, said: "We know the immediate impact of the COVID-19 pandemic was to cause a reduction in the number of people presenting to hospital with stroke, an effect that was evident from early February and well before the imposition of population-level lockdown measures. This fall in admissions was predominantly for patients with mild symptoms and particularly in patients over the age of 85 years. Whether this was because there was a reluctance to refer patients to hospital due to their increased risk if they did contract coronavirus, in an attempt to reduce the burden on the health service or because the patients were not able to alert emergency services themselves or decided against referral is not known."
Dr Douiri added: "Despite maintaining high quality services, the seven-day case fatality rate for stroke increased significantly by 2.5% percentage points. It is not possible to determine if this higher mortality is explained by the high case fatality rates in patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 or as a result of fewer patients with milder stroke being admitted to hospital, or a combination of these effects."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study evaluates biomarker criteria for assessing Alzheimer's risk
2021-04-26
One of the biggest challenges in Alzheimer's research is to identify biomarkers that can identify people who are at risk of developing dementia. Biomarkers could be used to screen people so they might be helped before they develop dementia.
Researchers have focused primarily on three such biomarkers. Two are Alzheimer's-related proteins, amyloid and tau. Amyloid forms clumps in brains, and tau forms skeins of filaments called neurofibrillary tangles. Both can be detected in cerebral spinal fluid or by specialized positron emission tomography (PET) scans. The third marker, brain atrophy, can be seen with CT or MRI scans.
To guide researchers, the National Institute on Aging and the Alzheimer's Association ...
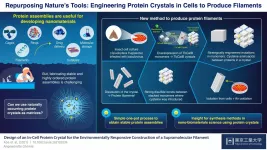
In-cell nano-3D printer: Synthesizing stable filaments from in-cell protein crystals
2021-04-26
Proteins are undoubtedly some of the most fascinating biomolecules, and they perform many of the functions that (in our eyes) separate life from inanimate matter. Multi-molecular protein assemblies even have large-scale structural functions, as evidenced by feathers, hair, and scales in animals. It should come as no surprise that, with progress in advanced nanotechnology and bioengineering, artificial protein assemblies have found applications in a variety of fields, including catalysis, molecular storage, and drug delivery systems.
However, producing ordered protein assemblies remains challenging. It is particularly difficult to get monomers, the building blocks of proteins, to assemble stably into the desired structures; this generally ...
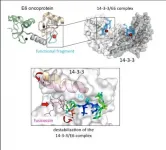
Biophysicists found an Achilles heel of a cancerogenic virus
2021-04-26
Although most oncological diseases are not infectious, some viruses can cause cancer. According to the World Health Organization, two HPV subtypes account for 70% of cervical cancer cases and pre-existing conditions. Moreover, HPV considerably increases the risks of other types of cancer. Within an infected cell, a viral protein called E6 binds with human proteins from the 14-3-3 family. 14-3-3 proteins are present in cells of all eukaryotic organisms and can interact with hundreds of other important players of intracellular processes to regulate cell division, gene activity, metabolism, cell death, and intracellular ...
Researchers identify the proteins that cause intestinal disease
2021-04-26
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have created an artificial intelligence platform that can identify the specific proteins that allow bacteria to infect the intestines - a method that paves the way for the creation of smart drugs that will neutralize the proteins and prevent disease, without the use of antibiotics. Participating in the study, which was published in the prestigious journal Science, were Ph.D. student Naama Wagner and Prof. Tal Pupko, head of the Shmunis School of Biomedicine and Cancer Research at the Faculty of Life Sciences and the new Center for Artificial Intelligence ...
Researchers complete high-precision time-frequency dissemination
2021-04-26
Prof. PAN Jianwei and his colleagues from the University of Science and Technology of China of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated the high-loss free space high-precision time-frequency dissemination experiment between remote locations, simulating the high-precision time-frequency high-orbit satellite-ground links in the channel loss, atmospheric noise, and transmission delay effects.
This link experiment exhibits that the instability of the time-frequency transfer via a satellite in middle-high earth orbits might reach E-18 at 10,000 s, enabling ...
Football Fitness gives an important boost to health in women treated for breast cancer
2021-04-26
The University of Southern Denmark (SDU), Rigshospitalet and the University of Copenhagen have come together to study the effects of Football Fitness on various health parameters and self-rated health following treatment for breast cancer.
The results of the project, called Football Fitness After Breast Cancer (ABC), have now been published in three scientific articles published in international sports medicine, cardiology and oncology journals.
"The main conclusion is that Football Fitness is an intense and good form of training for women treated for breast cancer, with beneficial effects on balance, muscle strength and bone density," says END ...
Pain patients and healthcare providers want CDC opioid guideline revoked
2021-04-26
The CDC's opioid prescribing guideline has failed to reduce addiction and overdoses, significantly worsened the quality of pain care in the United States and should be revoked, according to a large new survey of patients and healthcare providers by Pain News Network, an independent, non-profit news organization.
Nearly 4,200 patients and providers participated in the online survey, which was conducted as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention prepares to update and possibly expand its 2016 guideline, which discourages doctors from prescribing opioid ...
TBI: A new roadmap for advancing personalized treatment solutions
2021-04-26
NEW YORK, NY (April 26, 2021) -Brain research and advocacy nonprofit Cohen Veterans Bioscience (CVB) today announced the launch of a National TBI Precision Solutions Research Roadmap, with the advent of the first in a series of publications resulting from its Brain Trauma Blueprint framework program.
The Brain Trauma Blueprint is a framework that enables stakeholder groups across government, academia, foundations, and industry to advance precision diagnostics and treatments for brain trauma through a coordinated effort. The framework comprises a 12-step process to jointly identify unmet patient needs, associated research priorities, landscape state of the science, identify research gaps and barriers, and provide ...
Study looked at how nurses view touch as a form of care
2021-04-26
SPOKANE, Wash. - Touching patients while providing care is an important and unavoidable aspect of the nursing profession. Nurses can also transform touch into a useful therapeutic tool to improve patients'-- and their own--wellbeing.
That is the topic of a study, "'Permission to Touch': Nurses' Perspectives of Interpersonal Contact during Patient Care," published in the Western Journal of Nursing Research.The authors include two Washington State University College of Nursing faculty, Associate Professor Marian Wilson and Assistant Professor Tullamora Landis, former faculty member Michele Shaw, and lead author Enrico DeLuca, of Sapienza University of Rome, Italy, who visited WSU in 2018 to work with Wilson on the study.
Nurses touch patients frequently ...
Cell adaptation in critically ill could be difference between life and death
2021-04-26
Creating the best conditions for cells to make energy and survive critical illness is a challenge little understood in modern medicine. Now a new study led by scientists at the University of Plymouth, in collaboration with University College London and the Universities of Cambridge and Southampton, shows early signs that cells in some critically ill patients actually adapt to their conditions by producing energy more efficiently.
The research, published in the journal Redox Biology, took muscle and blood samples over seven days from 21 critically ill patients (ie those with two or more organs failing) in intensive care, and 12 healthy people, comparing cells' behaviour.
The study showed that all of the critically ill ...