(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, April 26, 2021 - Fast turnaround of COVID-19 test results for healthcare workers is critical. Investigators have now developed a COVID-19 testing strategy that maximizes the proportion of negative results after a single round of testing, allowing prompt notification of results. The method also reduces the need for increasingly limited test reagents, as fewer additional tests are required. Their strategy is described in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
There is an urgent need to reduce the spread of COVID-19 transmission in hospitals and care facilities and to maintain adequate levels of staffing. Group testing strategies with pooled samples have been proposed to increase capacity; however, the currently used strategies are slow.
"One of the main hurdles to initiating a comprehensive hospital staff testing program is the large number of staff requiring testing and the rapid turnaround times that would be required to make any screening strategy successful," explained lead investigators Graeme Black, DPhil, and John Henry McDermott, MD, both from the Division of Evolution and Genomic Sciences, School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK. "Using the method we have developed, any laboratory could adapt their testing scheme based on the current throughput and the current prevalence of infection in the population, facilitating a data-driven testing strategy."
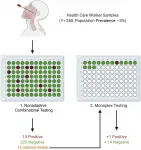
Traditional Dorfman sequential (DS) pooling combines multiple samples and, if a pool test returns positive, all of the constituent samples undergo further testing. In a healthcare setting, this means that even individuals who ultimately test negative for COVID-19 will have to isolate. The investigators developed a nonadaptive combinatorial (NAC) pooling approach that tests the same sample in several simultaneously assayed pools. The algorithm assumes initially that each sample is positive. It then attempts to disprove this assumption by finding a well in which the sample has been placed that has tested as negative. Then another algorithm is used to find positive wells that contain a single sample on the list of the remaining potentially positive samples. Indeterminate samples are retested.
To establish a suitable limit of detection for pooling, nasopharyngeal samples of known SARS-CoV-2 status were placed in two pools, each containing 14 SARS-CoV-2 negative samples and one SARS-CoV-2 positive sample, with the positive samples at differing viral loads. Pooling matrices were generated for 700, 350, and 250 samples, with each sample assigned to 2, 4, and 5 wells, respectively. The samples were also tested in a DS testing scheme. The efficacy of each matrix was tested under different SARS-CoV-2 prevalence levels of 0.1 percent, 3 percent, 7 percent, and 10 percent of the population.
All NAC matrices performed well at low prevalence levels, with an average of 585 tests saved per assay in the 700 sample matrix. In simulations of low-to-medium prevalence levels (0.1 percent - 3 percent), which is the prevalence expected in an asymptomatic healthcare worker population, all the NAC matrices required fewer retests than the DS testing scheme. However, as the population prevalence increased, the performance of each matrix deteriorated.
"Pooling becomes increasingly useful as the population prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 decreases," Prof. Black and Dr. McDermott observed. "Initially the most conservative matrix, 250 samples, should be used to determine the prevalence level. As the prevalence falls, the use of less tolerant but higher throughput assays could be used, such as the 700 sample pool."
The matrices and system to decode the results are freely available (http://www.samplepooling.com) and laboratories can choose the matrix that best suits their current population prevalence and sample size, facilitating a context-specific, relatively low cost data-driven testing approach.
"Many high-throughput testing schemes for SARS-CoV-2 detection have been developed over the past year. We illustrate the potential power that adaptable automated, innovative mathematical approaches have to increase COVID-19 diagnostic capability in a safe manner. Such an approach could reach far greater numbers, save lives, and be delivered in a sustainable way. Undoubtedly, this has considerable relevance to other future population-based screening approaches," Prof. Black and Dr. McDermott concluded.
INFORMATION:
Buyer beware: single-family homes in floodplains - almost 4 million U.S. homes - are overvalued by nearly $44 billion collectively or $11,526 per house on average, according to a new Stanford University-led study. The study, published in Proceedings of the National Academies of Science, suggests that unaware buyers and inadequate disclosure laws drive up financial risks that could destabilize the real estate market. The threat is likely to grow as climate change drives more frequent extreme weather. (WATCH VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n18s5kcE0So)
"The overvaluation we find is really concerning, ...
Results of a study co-authored by MGH Institute of Health Professions researcher Teresa Kimberley, PhD, PT, have the potential to be one of the most impressive advances in decades to help improve the lives of patients who have had a stroke with resulting arm weakness.
In an article published April 22 in The Lancet, "Vagus Nerve Stimulation Paired with Rehabilitation for Upper Limb Motor Function After Ischaemic Stroke (VNS-REHAB): A Randomised, Blinded, Pivotal, Device Trial," the study reports that patients who incorporated vagus nerve stimulation during physical or occupational therapy showed 2 to 3 times the improvement in arm and hand function compared to those who received intense rehabilitation with sham stimulation.
"How ...
With climate change looming, what must people hear to convince them to change their ways to stop harming the environment? A new Johns Hopkins University study finds stories to be significantly more motivating than scientific facts-- at least for some people.
After hearing a compelling pollution-related story in which a man died, the average person paid more for green products than after having heard scientific facts about water pollution. But the average person in the study was a Democrat. Republicans paid less after hearing the story rather than the simple facts.
The findings, published this week in the journal ...
Humans have been breeding plants for their economic value for thousands of years. Traditionally, plant breeding techniques included cumbersome and time-consuming techniques like grafting and hybridization to enhance traits of economic value like disease resistance and high nutrition content. Now, with the ability to edit plant DNA using revolutionary gene-editing tools, particularly the CRISPR-Cas9 system, it is possible to enhance traits of economic value in plants easily and more efficiently than by using traditional techniques. But for that, it is necessary to sequence whole ...
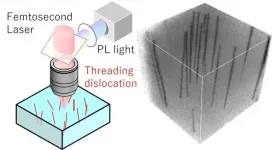
Osaka - Gallium nitride (GaN) is a semiconductor material whose wide band gap may one day lead to it superseding silicon in electronics applications. It is therefore important to have GaN characterization techniques that are able to support the development of GaN devices. Researchers at Osaka University have reported a nondestructive method for characterizing the crystalline quality of GaN. Their findings were published in Applied Physics Express.
GaN power switching devices offer numerous advantages including high-speed switching, high-power operation, low on-resistance, and high breakdown voltage. To take advantage of these properties, the defect density of GaN crystals must be low.
Threading dislocations ...
The various methods that Netflix employs when premiering its content favour the international success of original local productions and, at the same time, act as a safety net for these films in an audiovisual industry in constant evolution.
A study conducted by Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) researchers Antoni Roig, Judith Clares and Jordi Sánchez, published in the open access journal Communication & Society, has analysed the various systems and schedules implemented by the American entertainment platform in recent years in relation to its original feature films, which have allowed it to become the leader in the distribution of on-demand audiovisual content.
According to the authors, the approaches adopted by Netflix form part of a global expansion plan to consolidate ...
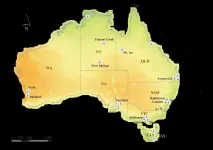
A new study has found Australia's government-owned airports could produce enough electricity to power 136,000 homes, if they had large-scale rooftop solar systems installed.
Researchers at RMIT University compared electricity generated by residential solar panels in a regional Australian city to the potential green energy production of 21 leased federal airports.
They found if large-scale solar panels were installed at the airports, they would generate 10 times more electricity than the city's 17,000 residential panels, while offsetting 151.6 kilotons of greenhouse gasses annually.
Researcher Dr Chayn Sun said the analysis showed the value ...
As a result of the work of five years of research, they have created the first trifocal corneal inlay that is also fully transparent. Such an inlay would allow good eyesight to presbyopic people of objects located at several distances: far, intermediate (computer, mobile devices) and near. Their work has been published in Nature group's Scientific Reports journal.
"This inlay could be an alternative for those suffering from presbyopia who would rather not use glasses or contact lenses. Furthermore, it would be fully compatible with laser refractive surgery in myopic and hyperopic patients, as well as possible subsequent cataract interventions. We are suggesting something totally new that is also not ...
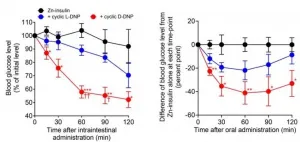
Researchers from Kumamoto University, Japan have found that DNP peptide, a small intestine-permeable cyclic peptide originally used as an insulin additive to improve absorption into the small intestinal, lowers blood glucose levels in mice. They also found that insulin can be administered orally by simply adding D-form DNP peptide (D-DNP) peptide to injectable insulin used in clinical practice. This study is expected to provide a basis for the development of oral insulin using DNP peptides.
Insulin therapy by self-injected insulin is currently the best way to control ...
Narcolepsy with cataplexy, or narcolepsy type 1 (NT1), is a rare and chronic neurological disease whose prevalence increased in children and adolescents after the administration of Pandemrix swine flu vaccine in 2009-2010. It is an autoimmune disease to which a specific inherited tissue type (HLA-DQB1*0602) predisposes people.
The disease mechanism of NT1 was investigated in a collaborative study carried out by PhD student Arja Vuorela and university researcher Dr. Tobias Freitag, working in the research groups of Prof. Outi Vaarala and Prof. Seppo Meri. The study analyzed the cell-mediated immune response targeting ...