(Press-News.org) A new study has found Australia's government-owned airports could produce enough electricity to power 136,000 homes, if they had large-scale rooftop solar systems installed.
Researchers at RMIT University compared electricity generated by residential solar panels in a regional Australian city to the potential green energy production of 21 leased federal airports.
They found if large-scale solar panels were installed at the airports, they would generate 10 times more electricity than the city's 17,000 residential panels, while offsetting 151.6 kilotons of greenhouse gasses annually.
Researcher Dr Chayn Sun said the analysis showed the value of focusing renewable energy efforts on large, centralised rooftop solar systems.
"We can't rely on small residential solar panels to get us to a zero-emission economy but installing large panels at locations like airports would get us a lot closer," she said.
"We hope our results will help guide energy policy, while informing future research in solar deployment for large buildings.
"There's so much potential to facilitate national economic development while contributing towards greenhouse gas emission reduction targets."
Sun, a geospatial scientist in RMIT's School of Science, said airports were ideal for solar panels but were not currently being used to their full potential - many Australian airports are without adequate solar systems.
"Airports get good sun exposure because they're not shaded by tall buildings or trees, making them a perfect spot to harness the sun's energy," she said.
"Australia is facing an energy crisis, yet our solar energy resources - such as airport rooftops - are being wasted.
"Harnessing this power source would avoid 63 kilotons of coal being burned in Australia each year, an important step towards a zero-carbon future."
For the study, published in the Journal of Building Engineering, geospatial researchers estimated the solar electricity generated from 17,000 residential solar panels in Bendigo, Victoria, over one year.
Lead author Athenee Teofilo, a Master of Geospatial Science student, then mapped the buildings in every leased federal airport - excluding unsuitable structures like dome and blister-type hangars - and identified 2.61km2 of usable rooftop space.
Researchers determined the optimum tilt angle for the solar arrays for each airport, to maximise efficiency.
Perth Airport had most energy-generating potential; placing solar panels there could produce almost twice the solar output of Bendigo, equal to the combined production from Adelaide, Sydney, Moorabbin and Townsville airports.
Even Melbourne Airport alone would outperform Bendigo's annual solar electricity production by almost 12 gigawatt hours a year.
Airport buildings less suited to solar panels could still be useful for ground-mounted solar systems, the study found.
Sun said the research underlined the necessity for energy policies to include a plan for installing solar panels at airports.
"Based on our solar radiation analysis, we know airports with decent solar systems could not only be self-sufficient but would generate enough electricity to send the excess back into the grid," she said.
"We mapped airports owned by the federal government, but Australia has more than 150 privately-owned airfields, which could also have panels installed.
"Australia receives so much solar radiation, so every airport in the country would benefit from having the right type of solar panels installed.
"The same could be said for many airports and large buildings located around the world."
Sun said reflections from the panels would not be a problem, as modern solar arrays absorb rather than reflect sunlight.
Previous studies have deemed airports as great solar generators but the RMIT research goes further by precisely modelling the use of large-scale systems.
The findings could also be extended to assess the solar potential of other sites, such as large commercial buildings, warehouses or distribution centres.
INFORMATION:
'Investigating potential rooftop solar energy generated by Leased Federal Airports in Australia: Framework and implications', with Athenee Teofilo, Dr Chayn Sun, Nenad Radosevic, Yaguang Tao, Jerome Iringan and Chengyang Liu, is published in the Journal of Building Engineering (DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102390).
As a result of the work of five years of research, they have created the first trifocal corneal inlay that is also fully transparent. Such an inlay would allow good eyesight to presbyopic people of objects located at several distances: far, intermediate (computer, mobile devices) and near. Their work has been published in Nature group's Scientific Reports journal.
"This inlay could be an alternative for those suffering from presbyopia who would rather not use glasses or contact lenses. Furthermore, it would be fully compatible with laser refractive surgery in myopic and hyperopic patients, as well as possible subsequent cataract interventions. We are suggesting something totally new that is also not ...
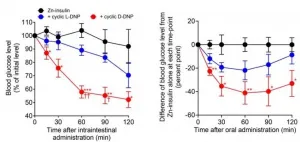
Researchers from Kumamoto University, Japan have found that DNP peptide, a small intestine-permeable cyclic peptide originally used as an insulin additive to improve absorption into the small intestinal, lowers blood glucose levels in mice. They also found that insulin can be administered orally by simply adding D-form DNP peptide (D-DNP) peptide to injectable insulin used in clinical practice. This study is expected to provide a basis for the development of oral insulin using DNP peptides.
Insulin therapy by self-injected insulin is currently the best way to control ...
Narcolepsy with cataplexy, or narcolepsy type 1 (NT1), is a rare and chronic neurological disease whose prevalence increased in children and adolescents after the administration of Pandemrix swine flu vaccine in 2009-2010. It is an autoimmune disease to which a specific inherited tissue type (HLA-DQB1*0602) predisposes people.
The disease mechanism of NT1 was investigated in a collaborative study carried out by PhD student Arja Vuorela and university researcher Dr. Tobias Freitag, working in the research groups of Prof. Outi Vaarala and Prof. Seppo Meri. The study analyzed the cell-mediated immune response targeting ...
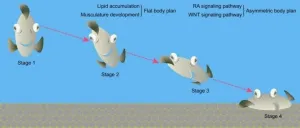
The colonization of the seafloor is one of the most important events in evolutionary history, leading to an explosive radiation and large-scale morphological diversification of marine phyla. Flatfishes are one of the most successful groups of seafloor colonizers and have evolved the most specialized body plan (i.e., flat and asymmetrical) among the teleosts. However, the origin and formation mechanism of the peculiar morphology of flatfishes had long been unclear.
Now, researchers from the Kunming Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences ...
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this mini review article the authors Meiyu Qiu and Pei Li from Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Republic of Korea summarize CRISPR/Cas-based Diagnostics and Gene Therapy.
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) technology, an easy, rapid, cost-effective, and precise gene-editing technique, has revolutionized diagnostics and gene therapy. Fast and accurate diagnosis of diseases is essential for point-of-care-testing (POCT) and specialized medical institutes. The CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins system shed light on the new diagnostics methods at point-of-care (POC) owning to its advantages. In addition, CRISPR/Cas-based gene-editing ...
People's ability to perceive speech sounds has been deeply studied, specially during someone's first year of life, but what happens during the first hours after birth? Are babies born with innate abilities to perceive speech sounds, or do neural encoding processes need to age for some time?
Researchers from the Institute of Neurosciences of the University of Barcelona (UBNeuro) and the Sant Joan de Déu Research Institute (IRSJD) have created a new methodology to try to answer this basic question on human development.
The results, published in the Nature's open-access journal Scientific Reports, ...
Not all stars shine brightly all the time. Some have a brightness that changes rhythmically due to cyclical phenomena like passing planets or the tug of other stars. Others show a slow change in this periodicity over time that can be difficult to discern or capture mathematically. KAUST's Soumya Das and Marc Genton have now developed a method to bring this evolving periodicity within the framework of mathematically "cyclostationary" processes.
"It can be difficult to explain the variations of the brightness of variable stars unless they follow a regular pattern over time," says Das. "In this study we created methods that can explain the evolution of the brightness of a variable star, even if it ...
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in ski wax have been receiving a lot of attention recently, but waxes constitute only a limited part of the problem of the PFAS group of toxicants.
PFAS are a large group of man-made fluorocarbon toxicants, and you are most likely full of them. The toxic substances don't break down and instead accumulate, both in nature and in your body.
"Due to their extensive use, humans and animals all over the world are continuously exposed to PFAS," says Håkon Austad Langberg, a PhD candidate at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) who has studied several of them in the last few years.
PFAS are used in many different products beyond the fluorinated ski wax that ends up in the ground on ski slopes and on trails, ...
The corona pandemic has made us all focus on new ways of organizing our work. More and more companies and organizations around the world are considering how to meet their employees' demand for flexibility while at the same time reducing their office space and expensive rents.
There are advantages and disadvantages to working from home, and many factors that affect the peoples' experience of it, such as their job function, age and seniority, whether they have children, whether they are a manager or employee, etc.
Researchers from DTU Management have identified six main areas that company managers should focus on when developing strategies for remote work in future.
Associate Professor at DTU Management Christine ...
People who take a commonly-prescribed drug for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) should not assume they are protected after a first dose of COVID-19 vaccine, after a large-scale study found many had poor antibody responses.
The research measured antibody responses after vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech or the Oxford/AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine in 865 people treated with infliximab, an anti-tumour necrosis factor (anti-TNF) biologic drug, prescribed to around two million people worldwide. Anti-TNF drugs are effective treatments for immune-mediated inflammatory ...