Researchers solve puzzle of origin and formation of specialized body plan in flatfishes
2021-04-26
(Press-News.org) The colonization of the seafloor is one of the most important events in evolutionary history, leading to an explosive radiation and large-scale morphological diversification of marine phyla. Flatfishes are one of the most successful groups of seafloor colonizers and have evolved the most specialized body plan (i.e., flat and asymmetrical) among the teleosts. However, the origin and formation mechanism of the peculiar morphology of flatfishes had long been unclear.
Now, researchers from the Kunming Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology of CAS, the Institute of Hydrobiology of CAS, Zhejiang Ocean University and Northwestern Polytechnical University, have unraveled the evolutionary and genetic origins of the specialized body plan of flatfishes through comparative genomic analysis. The study was published in Nature Genetics.
By analyzing ten de novo-assembled genomes and eight already-published genome sequences from teleost species, the researchers found that Pleuronectoidei and Psettodoidei (the only two suborders of Pleuronectiformes) do not form a monophyletic group, indicating that they each descended independently from their percoid ancestors.
Several genes related to visual perception, immune response, hypoxia tolerance and cardiac function were found to have experienced significant alteration in flatfishes, possibly suggesting a similar remodeling of their visual, immune, respiratory and circulatory systems in benthic adaptation to seafloor colonization.
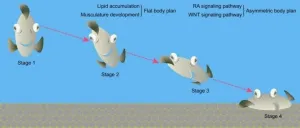
Genes associated with musculature development and lipid accumulation were also found to have experienced marked changes. Experiments on one fat-related gene showed fast lipid oxidization and decreased fat accumulation in flatfish and thus may correlate with the evolutionary origin and development of flatfishes' flat body plan.
Wnt and retinoic acid (RA) signal pathways have been found to play key roles in normal body axis development. The researchers also found that multiple genes from these pathways have undergone remarkable genetic alteration in flatfishes, suggesting they play a role in the evolution of an asymmetric body plan.
To find gene evolution and expression evidence, the researchers studied Paralichthys olivaceus as a representative species. They found that multiple genes in both RA and Wnt signaling pathways exhibited obvious transient expression fluctuations during metamorphosis, which include marked left-right asymmetrical expression beginning with the pre-metamorphic stage, climbing to an asymmetrical climax during the pro-metamorphic and metamorphic climax stage and then recovering to symmetry in the post-metamorphic stage.
The findings of this study substantially clarify the long-standing controversy (i.e., monophyletic origin vs. non-monophyletic origin) over the phylogeny of flatfishes. At the same time, the genes highlighted in this study offer a blueprint for future functional characterization of the molecular mechanisms underlying the unusual body plan of flatfishes.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-26
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this mini review article the authors Meiyu Qiu and Pei Li from Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Republic of Korea summarize CRISPR/Cas-based Diagnostics and Gene Therapy.
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) technology, an easy, rapid, cost-effective, and precise gene-editing technique, has revolutionized diagnostics and gene therapy. Fast and accurate diagnosis of diseases is essential for point-of-care-testing (POCT) and specialized medical institutes. The CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins system shed light on the new diagnostics methods at point-of-care (POC) owning to its advantages. In addition, CRISPR/Cas-based gene-editing ...
2021-04-26
People's ability to perceive speech sounds has been deeply studied, specially during someone's first year of life, but what happens during the first hours after birth? Are babies born with innate abilities to perceive speech sounds, or do neural encoding processes need to age for some time?
Researchers from the Institute of Neurosciences of the University of Barcelona (UBNeuro) and the Sant Joan de Déu Research Institute (IRSJD) have created a new methodology to try to answer this basic question on human development.
The results, published in the Nature's open-access journal Scientific Reports, ...
2021-04-26
Not all stars shine brightly all the time. Some have a brightness that changes rhythmically due to cyclical phenomena like passing planets or the tug of other stars. Others show a slow change in this periodicity over time that can be difficult to discern or capture mathematically. KAUST's Soumya Das and Marc Genton have now developed a method to bring this evolving periodicity within the framework of mathematically "cyclostationary" processes.
"It can be difficult to explain the variations of the brightness of variable stars unless they follow a regular pattern over time," says Das. "In this study we created methods that can explain the evolution of the brightness of a variable star, even if it ...
2021-04-26
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in ski wax have been receiving a lot of attention recently, but waxes constitute only a limited part of the problem of the PFAS group of toxicants.
PFAS are a large group of man-made fluorocarbon toxicants, and you are most likely full of them. The toxic substances don't break down and instead accumulate, both in nature and in your body.
"Due to their extensive use, humans and animals all over the world are continuously exposed to PFAS," says Håkon Austad Langberg, a PhD candidate at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) who has studied several of them in the last few years.
PFAS are used in many different products beyond the fluorinated ski wax that ends up in the ground on ski slopes and on trails, ...
2021-04-26
The corona pandemic has made us all focus on new ways of organizing our work. More and more companies and organizations around the world are considering how to meet their employees' demand for flexibility while at the same time reducing their office space and expensive rents.
There are advantages and disadvantages to working from home, and many factors that affect the peoples' experience of it, such as their job function, age and seniority, whether they have children, whether they are a manager or employee, etc.
Researchers from DTU Management have identified six main areas that company managers should focus on when developing strategies for remote work in future.
Associate Professor at DTU Management Christine ...
2021-04-26
People who take a commonly-prescribed drug for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) should not assume they are protected after a first dose of COVID-19 vaccine, after a large-scale study found many had poor antibody responses.
The research measured antibody responses after vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech or the Oxford/AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine in 865 people treated with infliximab, an anti-tumour necrosis factor (anti-TNF) biologic drug, prescribed to around two million people worldwide. Anti-TNF drugs are effective treatments for immune-mediated inflammatory ...
2021-04-26
The Chauvet Cave, which lies by the entrance to the Gorges of the Ardèche, is home to the world's oldest cave paintings, dating back 36,000 years. Their state of preservation and aesthetic qualities earned them a spot on the World Heritage List in 2014, 20 years after their discovery. The location of the cavern--surrounded by a remarkable landscape, next to the Pont d'Arc natural archway--raises the question of whether the people who executed these artworks looked and walked out upon the same landscape as today. Did they see the same natural archway? Scientists from the CNRS, Université Savoie Mont Blanc, and the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle1 ...
2021-04-26
Researchers from Skoltech (Russia) and their colleagues from SINTEF (Norway) have developed a mathematical model of freezing water droplets moving in cold air. This model is a part of a joint RFBR-supported Russian-Norway research project. The project is focused on predicting ice accretion on ships and other offshore structures operated in Arctic climate, which may interfere with their proper functioning and endanger crew members and cargo. The paper was published in the journal Energies.
Ships travel in cold northern waters under constant bombardment by tiny water droplets populating the chilly air. ...
2021-04-26
Ishikawa, Japan - Robots today have come a long way from their early inception as insentient beings meant primarily for mechanical assistance to humans. Today, they can assist us intellectually and even emotionally, getting ever better at mimicking conscious humans. An integral part of this ability is the use of speech to communicate with the user (smart assistants such as Google Home and Amazon Echo are notable examples). Despite these remarkable developments, they still do not sound very "human".
This is where voice conversion (VC) comes in. A technology used to ...
2021-04-26
Just one third of people in the UK managed to access the hospital care they needed at the peak of the first wave of the Covid-19 pandemic - according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today looks at the extent to which people managed to access NHS healthcare in April 2020, and as lockdown restrictions eased.
The researchers found that, despite high levels of unmet need, there was equal access to NHS hospital care for people at different levels of income. And the NHS principle of equal treatment for equal need was upheld.
However, people on higher incomes had better access to GP consultations, prescriptions and medical helplines at ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers solve puzzle of origin and formation of specialized body plan in flatfishes