(Press-News.org) Scientists have made a promising step towards developing a new drug for treating acute myeloid leukaemia, a rare blood disorder. In a study published today in Nature, Cambridge researchers report a new approach to cancer treatment that targets enzymes which play a key role in translating DNA into proteins and which could lead to a new class of cancer drugs.
Our genetic code is written in DNA, but in order to generate proteins - molecules that are vital to the function of living organisms - DNA first needs to be converted into RNA. The production of proteins is controlled by enzymes, which make chemical changes to RNA. Occasionally these enzymes become mis-regulated, being produced in over-abundance.
In a study published in 2017, a team led by Professor Tony Kouzarides from the Milner Therapeutics Institute and the Gurdon Institute at the University of Cambridge showed how one such enzyme, METTL3, plays a key role in the development and maintenance of acute myeloid leukaemia. The enzyme becomes over-expressed - that is, over-produced - in certain cell types, leading to the disease.
Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a cancer of the blood in which bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells known as myeloid cells, which normally protect the body against infection and against the spread of tissue damage. AML proceeds rapidly and aggressively, usually requiring immediate treatment, and affects both children and adults. Around 3,100 people are diagnosed with the condition every year in the UK, the majority of whom are over 65 years of age.
Now, Professor Kouzarides and colleagues at STORM Therapeutics, a Cambridge spinout associated with his team, and the Wellcome Sanger Institute, have identified a drug-like molecule, STM2457, that can inhibit the action of METTL3. In tissue cultured from individuals with AML and in mouse models of the disease, the team showed that the drug was able to block the cancerous effect caused by over-expression of the enzyme.
Professor Kouzarides said: "Proteins are essential for our bodies to function and are produced by a process that involves translating our DNA into RNA using enzymes. Sometimes, this process can go awry with potentially devastating consequences for human health. Until now, no one has targeted this essential process as a way of fighting cancer. This is the beginning of a new era for cancer therapeutics."
To investigate the anti-leukaemic potential of STM2457, the researchers tested the drug on cell lines derived from patients with AML and found that the drug significantly reduced the growth and proliferation of these cells. It also induced apoptosis - 'cell death' - killing off the cancerous cells.
The researchers transplanted cells from patients with AML into immunocompromised mice to model the disease. When they treated the mice with STM2457, they found that it impaired the proliferation and expansion of the transplanted cells and significantly prolonged the lifespan of the mice. It reduced the number of leukaemic cells in the mouse bone marrow and spleen, while showing no toxic side effects, including no effect on body weight.
Dr Konstantinos Tzelepis from the Milner Therapeutics Institute at the University of Cambridge and the Wellcome Sanger Institute added: "This is a brand-new field of research for cancer and the first drug-like molecule of its type to be developed. Its success at killing leukaemia cells and prolonging the lifespans of our mice is very promising and we hope to begin clinical trials to test successor molecules in patients as early as next year.
"We also believe that this approach - of targeting these enzymes - could be used to treat a wide range of cancers, potentially offering us a new weapon in our arsenal against these terrible diseases."
Michelle Mitchell, Chief Executive of Cancer Research UK, said: "This work is yet another example of how our researchers strive to get new cancer treatments into the clinic and improve outcomes for cancer patients.
"Acute myeloid leukaemia is an aggressive form of cancer which grows rapidly. Treatment is required as soon as possible after diagnosis, which means research like this can't come soon enough.
"We look forward to seeing the outcomes of the phase 1 trial and the benefits it may have for AML sufferers and their families in the future."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by Cancer Research UK, the European Research Council, Wellcome, the Kay Kendall Leukaemia Fund, and Leukaemia UK.
STORM Therapeutics is a University of Cambridge spin-out, supported by Cambridge Enterprise. It specialises in translating research in RNA epigenetics into the discovery of first-in-class drugs in oncology and other diseases.
DURHAM, N.C. - Engineers at Duke University have developed the world's first fully recyclable printed electronics. By demonstrating a crucial and relatively complex computer component -- the transistor -- created with three carbon-based inks, the researchers hope to inspire a new generation of recyclable electronics to help fight the growing global epidemic of electronic waste.
The work appears online April 26 in the journal Nature Electronics.
"Silicon-based computer components are probably never going away, and we don't expect easily recyclable electronics like ours to replace the technology and devices that are already widely used," ...
A new way to identify tumours that could be sensitive to particular immunotherapies has been developed using data from thousands of NHS cancer patient samples sequenced through the 100,000 Genomes Project. The MMRDetect clinical algorithm makes it possible to identify tumours that have 'mismatch repair deficiencies' and then improve the personalisation of cancer therapies to exploit those weaknesses.
The study, led by researchers from the University of Cambridge's Department of Medical Genetics and MRC Cancer Unit, identified nine DNA repair genes that are critical guardians of the human genome from damage caused by oxygen and water, as well as errors during cell division.
The team used ...
Australian scientists have unlocked another mystery of the class of microorganisms believed to be among Earth's oldest of life forms, throwing new light on the study of cell division and the evolution of life.
In a newly published paper in Nature Microbiology a research team from the iThree Institute at the University of Technology Sydney describes the cell division process used by the microorganism Haloferax volcanii from the archaea realm of single-celled life, which is distinct from bacteria.
Archaea make up the third major grouping, or domain, of life on the planet, alongside eukaryotes (including all plants and animals) and bacteria, but were only recognised ...
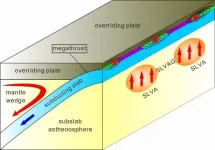
Earthquakes and volcanoes in subduction zones may cause great human catastrophe. Previous studies on subduction zone structure and causal mechanisms of giant megathrust earthquakes (M ≥ 9.0) have mainly focused on aspects like subducting plates and plate interfaces.
In contrast, the oceanic asthenosphere structure beneath the subducting slab (at depths of 100-250 km) and its influence on the nucleation of giant megathrust earthquakes have not been well studied.
Recently, Dr. FAN Jianke from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) and Prof. ZHAO Dapeng from Tohoku University ...
Weight loss surgery is more effective than dieting to reduce brain pressure that can cause blindness in patients with a neurological condition, finds a study led by the University of Birmingham and University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust (UHB).
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) is a debilitating condition that raises pressure in the brain and can lead to chronic headaches and even permanent sight loss. The illness, which often leaves patients with a reduced quality of life, predominately affects women aged 25 to 36 and weight gain is a major risk factor of developing IIH and relapses of the disease.
Weight ...
Sponges: They are considered to be one of the most primitive forms of animal life, because they have neither locomotion organs nor a nervous system. A team around deep-sea scientist Antje Boetius has now discovered that sponges leave trails on the sea floor in the Arctic deep sea. They conclude that the animals might move actively - even if only a few centimetres per year. They are now publishing these unique findings in the journal Current Biology.
The surprise was great when researchers looked at high-resolution images of the sea floor of the Arctic deep sea in detail: Path-like tracks across the sediments ended where sponges were located. These trails were observed to run in all directions, ...
Monday, 26 April 2021: A national study of 20,000 patients conducted by RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and the HSE Health Protection Surveillance Centre (HPSC) has identified the underlying conditions that are associated with more severe outcomes from COVID-19 in an Irish setting.
The research, which has been published in The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, will help inform national public health policies and assist in future treatment and prevention strategies for people at most risk from the virus.
The study, which took place during the first wave of the pandemic between March and July 2020, is the first national surveillance study in Ireland that captures data from both hospital ...
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/26/2021) -- A new study by five doctoral students in neuroscience at the University of Minnesota Medical School calls attention to a lack of regulation and unknown long-term health effects of tear gas. Based on their research, the group recommends changing the protocols around the use of tear gas as a crowd control measure at both the local and national level.
"Following the murder of George Floyd and the protests in our city, we felt compelled to dig into the police force used during those protests. We are trained to look at data and ...
A NUST MISIS professor was part of an international research team that has found evidence for the existence of the Zeeman spin-orbit coupling in antiferromagnetic conductors. This work may pave the way for the next generation of electronics. The study was published in npj Quantum Materials.
The electron possesses two fundamental properties: charge and spin. Conventional electronic devices use only the charge of electron for information processing. In recent years, an enormous research effort has been focused on building fundamentally new electronic devices (often called "spintronic devices") that would specifically exploit spin properties in addition to charge degrees of freedom. Transfer from conventional electronics to spintronics technology opens the possibilities to construct devices ...
BROOKLYN, New York, Thursday, April 22, 2021 - Rising sea levels and more powerful cyclonic storms, phenomena driven by the warming of oceans due to climate change, puts at immediate or potential risk an estimated 680 million people living in low-lying coastal zones (a number projected to reach more than one billion by 2050). In nations like Bangladesh these populations are already moving to escape sea-level rise.
In a new study, "Modeling human migration under environmental change: a case study of the effect of sea level rise in Bangladesh," researchers led by Maurizio Porfiri, an engineer at ...