INFORMATION:
Experimental proof for Zeeman spin-orbit coupling in antiferromagnetics
2021-04-26
(Press-News.org) A NUST MISIS professor was part of an international research team that has found evidence for the existence of the Zeeman spin-orbit coupling in antiferromagnetic conductors. This work may pave the way for the next generation of electronics. The study was published in npj Quantum Materials.
The electron possesses two fundamental properties: charge and spin. Conventional electronic devices use only the charge of electron for information processing. In recent years, an enormous research effort has been focused on building fundamentally new electronic devices (often called "spintronic devices") that would specifically exploit spin properties in addition to charge degrees of freedom. Transfer from conventional electronics to spintronics technology opens the possibilities to construct devices with high storage density and fast operation. The two-component nature of spin-based systems makes them potentially applicable for quantum computing.
Current effort in designing spintronic devices is focusing on understanding and making use of spin-orbit coupling, an interaction between the orbital angular momentum and the spin angular momentum of an individual particle, such as an electron. However, spin-orbit coupling occurring in many compounds is often weak or its emergence requires the use of heavy components. One way to overcome spin-orbit coupling related challenges could be the use of antiferromagnetics. A spin-orbit coupling of an unusual nature, termed Zeeman spin-orbit coupling is expected to manifest itself in a wide range of ferromagnetic conductors. Being proportional to the applied magnetic field, the coupling is tunable. Yet, experimental proof of this phenomenon has been lacking.
The collaboration of a NUST MISIS physicist with colleagues from Germany, France and Japan produced, for the first time, experimental evidence of Zeeman spin-orbit coupling in two very different layered conductors: an organic antiferromagnetic superconductor, and a prominent electron-doped superconductor that belongs to the family of high-temperature cuprate superconducting materials. Obtained on two very different materials, the results of this work demonstrate the generic nature of the Zeeman spin--orbit coupling. In addition to its fundamental importance, the Zeeman spin-orbit coupling opens new possibilities for spin manipulation, much sought after in the current effort to harness electron spin for future spintronic applications.
"The Zeeman spin-orbit coupling can be significantly stronger than other known kinds of spin-orbit coupling, thus providing new avenues for the development of fundamentally new electronic devices", noted Pavel Grigoriev, Professor at the NUST MISIS Department of Theoretical Physics and Quantum Technologies, senior researcher at Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Implications are global in new study predicting Human exodus in Bangladesh
2021-04-26
BROOKLYN, New York, Thursday, April 22, 2021 - Rising sea levels and more powerful cyclonic storms, phenomena driven by the warming of oceans due to climate change, puts at immediate or potential risk an estimated 680 million people living in low-lying coastal zones (a number projected to reach more than one billion by 2050). In nations like Bangladesh these populations are already moving to escape sea-level rise.
In a new study, "Modeling human migration under environmental change: a case study of the effect of sea level rise in Bangladesh," researchers led by Maurizio Porfiri, an engineer at ...
Blood transfusions in cats: A precious resource requiring a considered approach
2021-04-26
Blood transfusions are a common procedure in medical practice in which donated blood is used to replace blood lost to injury or surgery or to treat serious medical conditions. The procedure is not performed as routinely in the treatment of pet cats - but, as in people, can be lifesaving. The availability of donors has been a limitation in primary care veterinary practice, but with the growth of blood banks providing greater access to feline blood, the procedure is likely to become more commonplace.
To address the need for authoritative guidance, not only on best practice but also some important considerations beyond the clinical procedure itself, the International Society of Feline Medicine (ISFM) has today published consensus guidelines in the Journal ...
Plastic electronics: Ushering in the next generation of technology
2021-04-26
From Cat's-Whisker detectors in the early 1900s to electronic circuit chips in modern-day mobile phones, electronic devices have been modified in myriad creative ways to adapt to the needs of humankind. Apart from increasing the efficiency of conventionally used semiconductors such as silicon, recent research has focused on exploring more cost effective semiconductor materials. In tune with these requirements, a new publication in Nature Materials has successfully tweaked low cost semiconducting materials, quite similar to the composition of plastic, into conducting electricity more efficiently than before.
Solar cells have the property to convert ...
Study shows 2% of asymptomatic pediatric dental patients test positive for COVID-19
2021-04-26
A study by a University of Illinois Chicago pediatric dentist has shown a novel way to track potential COVID-19 cases -- testing children who visit the dentist. The study also showed an over 2% positivity rate for the asymptomatic children tested.
Dr. Flavia Lamberghini, UIC clinical assistant professor in the department of pediatric dentistry, has co-authored the article, "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in asymptomatic pediatric dental patients," in the April 2021 issue of the Journal of the American Dental Association. Co-authors are Dr. Fernando Testai, UIC professor ...
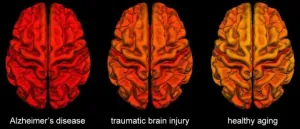
Brain changes following traumatic brain injury share similarities with Alzheimer's disease
2021-04-26
Brain changes in people with Alzheimer's disease and in those with mild traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) have significant similarities, a new USC study shows, suggesting new ways to identify patients at high risk for Alzheimer's. The findings appear this week in GeroScience.
TBIs, which affect over 1.7 million Americans every year, are often followed by changes in brain structure and function and by cognitive problems such as memory deficits, impaired social function and difficulty with decision-making. Although mild TBI -- also known as concussion -- is a known risk factor for Alzheimer's disease, ...
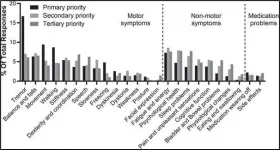
Which Parkinson's symptoms do patients most want to see improved by treatment?
2021-04-26
Amsterdam, April 26, 2021 - Individuals with Parkinson's disease (PD) face a wide range of symptoms and challenges. A team from Parkinson's UK, including several Patient and Public Involvement (PPI) contributors, surveyed patients to find out which PD symptoms troubled them most and how priorities may change with condition duration. Their goal was to identify where improved treatments and strategies are most needed to help maintain independence and quality of life. They report their findings in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease.
"While PD has some common features such as tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia, the disease is highly varied, with each individual experiencing their own unique blend of symptoms ...
New study shows microbes trap massive amounts of carbon
2021-04-26
Violent continental collisions and volcanic eruptions are not things normally associated with comfortable conditions for life. However, a new study, involving University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Associate Professor of Microbiology Karen Lloyd, unveils a large microbial ecosystem living deep within the earth that is fueled by chemicals produced during these tectonic cataclysms.
When oceanic and continental plates collide, one plate is pushed down, or subducted, into the mantle and the other plate is pushed up and studded with volcanoes. This is the main process by which chemical elements are moved between Earth's surface and interior and eventually recycled back to ...
A new way of rapidly counting and identifying viruses
2021-04-26
A Lancaster University professor has introduced a new concept for rapidly analysing for the presence of a virus from colds to coronaviruses.
Based on analysing chemical elements the methodology, which has been adapted from an analytical technique used to identify metallic nanoparticles, is able to detect the presence of viruses within just 20 seconds.
Although the tests would need to be performed in a lab, it could be used to quickly identify whether people admitted to hospitals have been infected by a virus - enabling clinicians to decide treatments and also whether to admit patients into isolation wards.
The ...
Researchers say prescribing opioids for pain relief after knee surgery is unnecessary
2021-04-26
DETROIT (April 26, 2021) - A new study by Henry Ford Health System published in Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery may signal a first step toward eliminating the use of opioids to relieve pain after knee surgery.
A novel multimodal pain management protocol developed at Henry Ford can bring about immediate pain relief for knee injury patients without using powerful opioids like morphine, codeine, and oxycodone.
"Orthopedic surgeons can now perform meniscal knee surgery without the need for prescribing opioids whatsoever," said Toufic Jildeh, M.D., chief resident at Henry Ford's Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and the study's lead researcher. "We believe this non-opioid approach can be replicated for other types of orthopedic ...
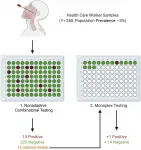
New testing strategy can speed up COVID-19 test results for healthcare workers
2021-04-26
Philadelphia, April 26, 2021 - Fast turnaround of COVID-19 test results for healthcare workers is critical. Investigators have now developed a COVID-19 testing strategy that maximizes the proportion of negative results after a single round of testing, allowing prompt notification of results. The method also reduces the need for increasingly limited test reagents, as fewer additional tests are required. Their strategy is described in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
There is an urgent need to reduce the spread of COVID-19 transmission in hospitals and care facilities and to maintain adequate levels of staffing. Group testing strategies with pooled samples have been proposed to increase capacity; however, the currently used strategies ...