New study shows microbes trap massive amounts of carbon
2021-04-26
(Press-News.org) Violent continental collisions and volcanic eruptions are not things normally associated with comfortable conditions for life. However, a new study, involving University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Associate Professor of Microbiology Karen Lloyd, unveils a large microbial ecosystem living deep within the earth that is fueled by chemicals produced during these tectonic cataclysms.
When oceanic and continental plates collide, one plate is pushed down, or subducted, into the mantle and the other plate is pushed up and studded with volcanoes. This is the main process by which chemical elements are moved between Earth's surface and interior and eventually recycled back to the surface.
"Subduction zones are fascinating environments--they produce volcanic mountains and serve as portals for carbon moving between the interior and exterior of Earth," said Maarten de Moor, associate professor at the National University of Costa Rica and coauthor of the study.
Normally this process is thought to occur outside the reach of life because of the extremely high pressures and temperatures involved. Although life almost certainly does not exist at the extreme conditions where Earth's mantle mixes with the crust to form lava, in recent decades scientists have learned that microbes extend far deeper into Earth's crust than previously thought.
This opens the possibility for discovering previously unknown types of biological interactions occurring with deep plate tectonic processes.
An interdisciplinary and international team of scientists has shown that a vast microbial ecosystem primarily eats the carbon, sulfur, and iron chemicals produced during the subduction of the oceanic plate beneath Costa Rica. The team obtained these results by sampling the deep subsurface microbial communities that are brought to the surface in natural hot springs, in work funded by the Deep Carbon Observatory and the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation.
The team found that this microbial ecosystem sequesters a large amount of carbon produced during subduction that would otherwise escape to the atmosphere. The process results in an estimated decrease of up to 22 percent in the amount of carbon being transported to the mantle.
"This work shows that carbon may be siphoned off to feed a large ecosystem that exists largely without input from the sun's energy. This means that biology might affect carbon fluxes in and out of the earth's mantle, which forces scientists to change how they think about the deep carbon cycle over geologic time scales," said Peter Barry, assistant scientist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and a coauthor of the study.
The team found that these microbes--called chemolithoautotrophs--sequester so much carbon because of their unique diet, which allows them to make energy without sunlight.
"Chemolithoautotrophs are microbes that use chemical energy to build their bodies. So they're like trees, but instead of using sunlight they use chemicals," said Lloyd, a co-corresponding author of the study. "These microbes use chemicals from the subduction zone to form the base of an ecosystem that is large and filled with diverse primary and secondary producers. It's like a vast forest, but underground."
This new study suggests that the known qualitative relationship between geology and biology may have significant quantitative implications for our understanding of how carbon has changed through deep time. "We already know of many ways in which biology has influenced the habitability of our planet, leading to the rise in atmospheric oxygen, for example," said Donato Giovannelli, a professor at the University of Naples Federico II and co-corresponding author of the study. "Now our ongoing work is revealing another exciting way in which life and our planet coevolved."
INFORMATION:
CONTACT:
Amanda Womac (865-974-2992, awomac1@utk.edu)
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-26
A Lancaster University professor has introduced a new concept for rapidly analysing for the presence of a virus from colds to coronaviruses.
Based on analysing chemical elements the methodology, which has been adapted from an analytical technique used to identify metallic nanoparticles, is able to detect the presence of viruses within just 20 seconds.
Although the tests would need to be performed in a lab, it could be used to quickly identify whether people admitted to hospitals have been infected by a virus - enabling clinicians to decide treatments and also whether to admit patients into isolation wards.
The ...
2021-04-26
DETROIT (April 26, 2021) - A new study by Henry Ford Health System published in Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery may signal a first step toward eliminating the use of opioids to relieve pain after knee surgery.
A novel multimodal pain management protocol developed at Henry Ford can bring about immediate pain relief for knee injury patients without using powerful opioids like morphine, codeine, and oxycodone.
"Orthopedic surgeons can now perform meniscal knee surgery without the need for prescribing opioids whatsoever," said Toufic Jildeh, M.D., chief resident at Henry Ford's Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and the study's lead researcher. "We believe this non-opioid approach can be replicated for other types of orthopedic ...
2021-04-26
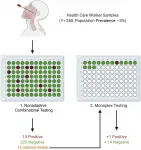
Philadelphia, April 26, 2021 - Fast turnaround of COVID-19 test results for healthcare workers is critical. Investigators have now developed a COVID-19 testing strategy that maximizes the proportion of negative results after a single round of testing, allowing prompt notification of results. The method also reduces the need for increasingly limited test reagents, as fewer additional tests are required. Their strategy is described in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
There is an urgent need to reduce the spread of COVID-19 transmission in hospitals and care facilities and to maintain adequate levels of staffing. Group testing strategies with pooled samples have been proposed to increase capacity; however, the currently used strategies ...
2021-04-26
Buyer beware: single-family homes in floodplains - almost 4 million U.S. homes - are overvalued by nearly $44 billion collectively or $11,526 per house on average, according to a new Stanford University-led study. The study, published in Proceedings of the National Academies of Science, suggests that unaware buyers and inadequate disclosure laws drive up financial risks that could destabilize the real estate market. The threat is likely to grow as climate change drives more frequent extreme weather. (WATCH VIDEO: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n18s5kcE0So)
"The overvaluation we find is really concerning, ...
2021-04-26
Results of a study co-authored by MGH Institute of Health Professions researcher Teresa Kimberley, PhD, PT, have the potential to be one of the most impressive advances in decades to help improve the lives of patients who have had a stroke with resulting arm weakness.
In an article published April 22 in The Lancet, "Vagus Nerve Stimulation Paired with Rehabilitation for Upper Limb Motor Function After Ischaemic Stroke (VNS-REHAB): A Randomised, Blinded, Pivotal, Device Trial," the study reports that patients who incorporated vagus nerve stimulation during physical or occupational therapy showed 2 to 3 times the improvement in arm and hand function compared to those who received intense rehabilitation with sham stimulation.
"How ...
2021-04-26
With climate change looming, what must people hear to convince them to change their ways to stop harming the environment? A new Johns Hopkins University study finds stories to be significantly more motivating than scientific facts-- at least for some people.
After hearing a compelling pollution-related story in which a man died, the average person paid more for green products than after having heard scientific facts about water pollution. But the average person in the study was a Democrat. Republicans paid less after hearing the story rather than the simple facts.
The findings, published this week in the journal ...
2021-04-26
Humans have been breeding plants for their economic value for thousands of years. Traditionally, plant breeding techniques included cumbersome and time-consuming techniques like grafting and hybridization to enhance traits of economic value like disease resistance and high nutrition content. Now, with the ability to edit plant DNA using revolutionary gene-editing tools, particularly the CRISPR-Cas9 system, it is possible to enhance traits of economic value in plants easily and more efficiently than by using traditional techniques. But for that, it is necessary to sequence whole ...
2021-04-26
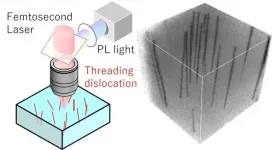
Osaka - Gallium nitride (GaN) is a semiconductor material whose wide band gap may one day lead to it superseding silicon in electronics applications. It is therefore important to have GaN characterization techniques that are able to support the development of GaN devices. Researchers at Osaka University have reported a nondestructive method for characterizing the crystalline quality of GaN. Their findings were published in Applied Physics Express.
GaN power switching devices offer numerous advantages including high-speed switching, high-power operation, low on-resistance, and high breakdown voltage. To take advantage of these properties, the defect density of GaN crystals must be low.
Threading dislocations ...
2021-04-26
The various methods that Netflix employs when premiering its content favour the international success of original local productions and, at the same time, act as a safety net for these films in an audiovisual industry in constant evolution.
A study conducted by Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) researchers Antoni Roig, Judith Clares and Jordi Sánchez, published in the open access journal Communication & Society, has analysed the various systems and schedules implemented by the American entertainment platform in recent years in relation to its original feature films, which have allowed it to become the leader in the distribution of on-demand audiovisual content.
According to the authors, the approaches adopted by Netflix form part of a global expansion plan to consolidate ...
2021-04-26
A new study has found Australia's government-owned airports could produce enough electricity to power 136,000 homes, if they had large-scale rooftop solar systems installed.
Researchers at RMIT University compared electricity generated by residential solar panels in a regional Australian city to the potential green energy production of 21 leased federal airports.
They found if large-scale solar panels were installed at the airports, they would generate 10 times more electricity than the city's 17,000 residential panels, while offsetting 151.6 kilotons of greenhouse gasses annually.
Researcher Dr Chayn Sun said the analysis showed the value ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study shows microbes trap massive amounts of carbon