Racial, ethnic differences in marijuana use in e-cigarettes among adolescents
2021-04-26
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: This survey study looked at how common is the use of marijuana in e-cigarettes among students in grades 6 to 12 and also changes in use by racial and ethnic groups from 2017 to 2020.
Authors: Christina V. Watson, Dr.P.H., M.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.0305)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.0305?guestAccessKey=07fe4718-2452-416d-9bb7-74ea71e75642&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=042621
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-26
WHAT:
A mobile app was successful at distinguishing toddlers diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) from typically developing toddlers based on their eye movements while watching videos, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. The findings suggest that the app could one day screen infants and toddlers for ASD and refer them for early intervention, when chances for treatment success are greatest.
The study appears in JAMA Pediatrics and was conducted by Geraldine Dawson, Ph.D., director of the NIH Autism Center of Excellence at Duke University, and colleagues. Funding was provided by NIH's Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) and National Institute of ...
2021-04-26
Scientists have made a promising step towards developing a new drug for treating acute myeloid leukaemia, a rare blood disorder. In a study published today in Nature, Cambridge researchers report a new approach to cancer treatment that targets enzymes which play a key role in translating DNA into proteins and which could lead to a new class of cancer drugs.
Our genetic code is written in DNA, but in order to generate proteins - molecules that are vital to the function of living organisms - DNA first needs to be converted into RNA. The production of proteins is controlled by enzymes, which make chemical changes to RNA. Occasionally these enzymes become mis-regulated, being produced in over-abundance.
In a study published in 2017, a team led by Professor Tony Kouzarides from the Milner ...
2021-04-26
DURHAM, N.C. - Engineers at Duke University have developed the world's first fully recyclable printed electronics. By demonstrating a crucial and relatively complex computer component -- the transistor -- created with three carbon-based inks, the researchers hope to inspire a new generation of recyclable electronics to help fight the growing global epidemic of electronic waste.
The work appears online April 26 in the journal Nature Electronics.
"Silicon-based computer components are probably never going away, and we don't expect easily recyclable electronics like ours to replace the technology and devices that are already widely used," ...
2021-04-26
A new way to identify tumours that could be sensitive to particular immunotherapies has been developed using data from thousands of NHS cancer patient samples sequenced through the 100,000 Genomes Project. The MMRDetect clinical algorithm makes it possible to identify tumours that have 'mismatch repair deficiencies' and then improve the personalisation of cancer therapies to exploit those weaknesses.
The study, led by researchers from the University of Cambridge's Department of Medical Genetics and MRC Cancer Unit, identified nine DNA repair genes that are critical guardians of the human genome from damage caused by oxygen and water, as well as errors during cell division.
The team used ...
2021-04-26
Australian scientists have unlocked another mystery of the class of microorganisms believed to be among Earth's oldest of life forms, throwing new light on the study of cell division and the evolution of life.
In a newly published paper in Nature Microbiology a research team from the iThree Institute at the University of Technology Sydney describes the cell division process used by the microorganism Haloferax volcanii from the archaea realm of single-celled life, which is distinct from bacteria.
Archaea make up the third major grouping, or domain, of life on the planet, alongside eukaryotes (including all plants and animals) and bacteria, but were only recognised ...
2021-04-26
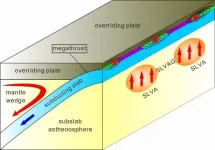
Earthquakes and volcanoes in subduction zones may cause great human catastrophe. Previous studies on subduction zone structure and causal mechanisms of giant megathrust earthquakes (M ≥ 9.0) have mainly focused on aspects like subducting plates and plate interfaces.
In contrast, the oceanic asthenosphere structure beneath the subducting slab (at depths of 100-250 km) and its influence on the nucleation of giant megathrust earthquakes have not been well studied.
Recently, Dr. FAN Jianke from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) and Prof. ZHAO Dapeng from Tohoku University ...
2021-04-26
Weight loss surgery is more effective than dieting to reduce brain pressure that can cause blindness in patients with a neurological condition, finds a study led by the University of Birmingham and University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust (UHB).
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) is a debilitating condition that raises pressure in the brain and can lead to chronic headaches and even permanent sight loss. The illness, which often leaves patients with a reduced quality of life, predominately affects women aged 25 to 36 and weight gain is a major risk factor of developing IIH and relapses of the disease.
Weight ...
2021-04-26
Sponges: They are considered to be one of the most primitive forms of animal life, because they have neither locomotion organs nor a nervous system. A team around deep-sea scientist Antje Boetius has now discovered that sponges leave trails on the sea floor in the Arctic deep sea. They conclude that the animals might move actively - even if only a few centimetres per year. They are now publishing these unique findings in the journal Current Biology.
The surprise was great when researchers looked at high-resolution images of the sea floor of the Arctic deep sea in detail: Path-like tracks across the sediments ended where sponges were located. These trails were observed to run in all directions, ...
2021-04-26
Monday, 26 April 2021: A national study of 20,000 patients conducted by RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences and the HSE Health Protection Surveillance Centre (HPSC) has identified the underlying conditions that are associated with more severe outcomes from COVID-19 in an Irish setting.
The research, which has been published in The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, will help inform national public health policies and assist in future treatment and prevention strategies for people at most risk from the virus.
The study, which took place during the first wave of the pandemic between March and July 2020, is the first national surveillance study in Ireland that captures data from both hospital ...
2021-04-26
MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (04/26/2021) -- A new study by five doctoral students in neuroscience at the University of Minnesota Medical School calls attention to a lack of regulation and unknown long-term health effects of tear gas. Based on their research, the group recommends changing the protocols around the use of tear gas as a crowd control measure at both the local and national level.
"Following the murder of George Floyd and the protests in our city, we felt compelled to dig into the police force used during those protests. We are trained to look at data and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Racial, ethnic differences in marijuana use in e-cigarettes among adolescents