(Press-News.org) New research suggests a simple step could help millions of people reduce their risk of heart disease: make sure to get enough vitamin D. Elucidating linkages between skin pigmentation, vitamin D and indicators of cardiovascular health, the new study, combined with evidence from previous research, suggests vitamin D deficiency could contribute to the high rate of heart disease among African Americans.
"More darkly-pigmented individuals may be at greater risk of vitamin D deficiency, particularly in areas of relatively low sun exposure or high seasonality of sun exposure," said S. Tony Wolf, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Pennsylvania State University and the study's lead author. "These findings may help to explain some of the differences that we see in the risk for developing blood vessel dysfunction, hypertension and overt cardiovascular disease between ethnic groups in the United States. Although there are many factors that contribute to the development of hypertension and cardiovascular disease, vitamin D supplementation may provide a simple and cost-effective strategy to reduce those disparities."
Wolf noted that the need for vitamin D supplementation depends on a variety of factors, including where you live, how much time you spend in the sun, your skin pigmentation and your age.
Wolf will present the research at the END
Taking vitamin D could lower heart disease risk for people with dark skin
Racial disparities in heart disease may be linked to vitamin D deficiency
2021-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
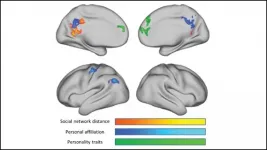
How the brain encodes social network structure
2021-04-26
The brain encodes information about our relationships and the relationships between our friends using areas involved in spatial processing, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Humans maintain hundreds of social relationships, requiring the brain to catalogue countless details about each person and their connections to other people. But it is not known how exactly the brain stores all of this information.
To uncover how the brain encodes social network structure, Peer et al. used Facebook data to map out participants' social connections. Then the researchers measured their brain activity with fMRI as they thought about people from their network. Thinking about a connection generated ...
Research result reporting set for boost under new system
2021-04-26
A new guideline for reporting research results has been developed to improve reproducibility, replication, and transparency in life sciences.
The new Research Materials, Design, Analysis and Reporting (MDAR) Framework will harmonise the recording of outcomes across several major journals, its developers say.
Existing guidelines address specific parts of biomedical research, such as ARRIVE - which relates to animal research - and CONSORT, associated with clinical trial reporting.
The MDAR Framework - developed by a team from the University of Edinburgh, the Centre for Open Science and six major journal publishers - complements these by establishing basic minimum reporting requirements and best practice recommendations.
The Framework ...
Spike in severe pediatric type 2 diabetes complication during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-04-26
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), children generally appear to be less severely impacted by COVID-19 than adults. But a new study from Children's Hospital Los Angeles shows that the pandemic could be affecting children's health in unexpected ways. The study reveals a surge of patients presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis, a severe complication of type 2 diabetes. Published today in Diabetes Care, these data offer additional insights into how the pandemic may be impacting the nation's children.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA, is life-threatening. "DKA happens when insulin levels in the blood drop too low for too long," says Lily Chao, MD, MS, ...
Supervisors focused on others' needs get 'benefit of the doubt' from employees
2021-04-26
Like beauty, fairness is in the eye of the beholder.
In the workplace, whether or not we believe that a supervisor has treated us fairly depends on a number of factors, including motive, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
Employees evaluate the fairness of an interaction with an authority figure based on what researcher Cindy Muir (Zapata), associate professor of management at Notre Dame's Mendoza College of Business, describes as justice criteria or rules. These include relying on decision-making processes that grant employees voice and are consistent among employees, ethical and free of bias; treating team members with dignity, respect and ...
Mayo Clinic researchers question effectiveness of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines for solid organ transplant
2021-04-26
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. -- A small study from Mayo Clinic researchers raises the concern that some transplant patients may have a limited immune response after being vaccinated for COVID-19 with an mRNA vaccine. Their findings are published as a letter to the editor in the American Journal of Transplantation.
The letter covers seven organ transplant recipients diagnosed with COVID-19 at Mayo Clinic in Florida six to 44 days after receiving either of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines that have been authorized for emergency use by the Food and Drug Administration. Two patients had received one dose, and five patients had received both doses.
COVID-19 infection was confirmed in all patients with a polymerase chain reaction nasal swab test. The study team, led by Hani Wadei, M.D., ...
Hydrocracking our way to recycling plastic waste
2021-04-26
Millions of tons of plastic end up in landfills every year. It's a big societal problem and an even larger environmental threat.
In the United States, less than 9% of plastic waste is recycled. Instead, more than 75% of plastics waste ends up in landfills and up to 16% is burned, a process that releases toxic gases into the atmosphere.
Researchers from the University of Delaware's Center for Plastics Innovation (CPI) have developed a direct method to convert single-use plastic waste -- plastic bags, yogurt containers, plastic bottles and bottle caps, packaging and more -- to ready-to-use molecules for jet fuels, diesel and lubricants.
The work, reported in a paper in Science ...
Asteroid that hit Botswana in 2018 likely came from Vesta
2021-04-26
April 23, 2021, Mountain View, CA -- An international team of researchers searched for pieces of a small asteroid tracked in space and then observed to impact Botswana on June 2, 2018. Guided by SETI Institute meteor astronomer Peter Jenniskens, they found 23 meteorites deep inside the Central Kalahari Game Reserve and now have published their findings online in the journal Meteoritics and Planetary Science.
"Combining the observations of the small asteroid in space with information gleaned from the meteorites shows it likely came from Vesta, second largest asteroid in our Solar System and target of NASA's ...
Study finds increased risk of serious opioid events in mothers, regardless of dose
2021-04-26
A new study from Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers finds that new mothers who receive opioids after uncomplicated vaginal births face an increased risk of serious opioid-related events regardless of the opioid dosage, a finding that could significantly impact care delivery.
Andrew Wiese, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of Health Policy in the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology, authored the paper published online April 15 in Women's Health Issues, with Sarah Osmundson, MD, MPH, associate professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, and other researchers in the departments of Biostatistics and Health Policy.
The study examined roughly 147,000 women enrolled in TennCare -- Tennessee's Medicaid program -- between ...
Genomic study points to new treatment approaches for advanced small-cell lung cancer
2021-04-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new study of advanced small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC - James) has identified molecular patterns linked to patients developing resistance to certain therapies.
This study, published in the journal JTO Clinical and Research Reports, examined more than 60 tumors from five patients. OSUCCC - James researchers identified distinct mutational and molecular changes in four SCLC subtypes. The findings provide new insights into the patterns treatment resistance and could offer new targets for the development of more effective ...
Drug derived from Kentucky-grown plant shows promise for ovarian cancer treatment
2021-04-26
LEXINGTON, Ky. (April 20, 2021) - A new study from University of Kentucky Markey Cancer researchers shows that Artemisia annua, a plant that has been traditionally used for its anti-malaria components, shows promise in treating ovarian cancer.
The study, recently published in Diagnostics, demonstrates that artesunate, a drug synthesized from Artemisia annua, kills ovarian cancer cells in multiple preclinical model systems.
Despite accounting for only 1.3% of all new cancer cases, 2.3% of cancer deaths in 2021 are predicted to be caused by ovarian cancer. The current ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Taking vitamin D could lower heart disease risk for people with dark skinRacial disparities in heart disease may be linked to vitamin D deficiency