INFORMATION:
Circadian clock in the mouse placenta
2021-04-27
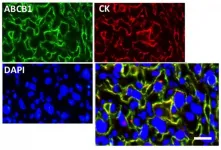
(Press-News.org) The placenta forms the interface between the maternal and foetal circulatory systems. As well as ensuring essential nutrients, endocrine and immunological signals get through to the foetus to support its development and growth, the placenta must also protect it from the accumulation of potentially toxic compounds. A study from Cécile Demarez, Mariana Astiz and colleagues at the University of Lübeck in Germany now reveals that the activity of a crucial placental gatekeeper in mice is regulated by the circadian clock, changing during the day-night cycle. The study, which has implications for the timing of maternal drug regimens, is published in the journal Development.
The circadian clock translates time-of-day information into physiological signals through rhythmic regulation of downstream genes. In this study, the researchers discover that in the labyrinth zone of the mouse placenta, a tissue functionally equivalent to the human chorionic villi, clock genes are expressed in a 24h rhythm. Importantly, they show that this placental clock is responsible for regulating the expression and activity of ABCB1, a drug efflux transporter with hundreds of known substrates.
An important prediction of this work is that the time-of-day of maternal treatment could be an important factor to consider to avoid non-desirable effects for the foetus during pregnancy.
"Pharmacological treatments are mostly avoided by pregnant women but in certain circumstances there is no other option," says Dr. Mariana Astiz. "An example would be maternal treatment with antiretrovirals (many of which are in fact substrates of ABCB1). So, choosing the correct time of day to take drugs like these might reduce the ammount of drug reaching the baby and hence the possible negative effects in the short and long-term."
Dr. Astiz hopes this study will provide a stimulus to design studies that specifically test hypotheses about the placental circadian clock in humans. "This is definitely a very exciting and rapidly advancing field of research."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study first to explore combined impacts of fishing and ocean warming on fish populations
2021-04-27
The combined effect of rapid ocean warming and the practice of targeting big fish is affecting the viability of wild populations and global fish stock says new research by the University of Melbourne and the University of Tasmania.
Unlike earlier studies that traditionally considered fishing and climate in isolation, the research found that ocean warming and fishing combined to impact on fish recruitment, and that this took four generations to manifest.
"We found a strong decline in recruitment (the process of getting new young fish into a population) in all populations that had been exposed to warming, and this effect was highest where all the largest individuals ...
SARS-CoV-2 curtails immune response in the gut
2021-04-27
In an effort to determine the potential for COVID-19 to begin in a person's gut, and to better understand how human cells respond to SARS-CoV-2, the scientists used human intestinal cells to create organoids - 3D tissue cultures derived from human cells, which mimic the tissue or organ from which the cells originate. Their conclusions, published in the journal Molecular Systems Biology, indicate the potential for infection to be harboured in a host's intestines and reveal intricacies in the immune response to SARS-CoV-2.
"Previous research had shown that SARS-CoV-2 can infect the gut," says Theodore Alexandrov, who leads one of the two EMBL groups involved. "However, it remained unclear how intestinal cells mount their immune response to the infection."
In fact, ...
Flood risk to new homes in England and Wales will increase in disadvantaged areas
2021-04-27
The building of new homes continues in flood-prone parts of England and Wales, and losses from flooding remain high. A new study, which looked at a recent decade of house building, concluded that a disproportionate number of homes built in struggling or declining neighbourhoods will end up in high flood-risk areas due to climate change.
The study, by Viktor Rözer and Swenja Surminski from the Grantham Research Institute, used property-level data for new homes and information on the socio-economic development of neighbourhoods to analyse spatial clusters ...
Ship traffic dropped during first months of Covid pandemic
2021-04-27
Ship movements on the world's oceans dropped in the first half of 2020 as Covid-19 restrictions came into force, a new study shows.
Researchers used a satellite vessel-tracking system to compare ship and boat traffic in January to June 2020 with the same period in 2019.
The study, led by the University of Exeter (UK) and involving the Balearic Islands Coastal Observing and Forecasting System and the Mediterranean Institute for Advanced Studies (both in Spain), found decreased movements in the waters off more than 70 per cent of countries.
Global ...
Extinct 'horned' crocodile gets new spot in the tree of life
2021-04-27
A study led by scientists at the American Museum of Natural History has resolved a long-standing controversy about an extinct "horned" crocodile that likely lived among humans in Madagascar. Based on ancient DNA, the research shows that the horned crocodile was closely related to "true" crocodiles, including the famous Nile crocodile, but on a separate branch of the crocodile family tree. The study, published today in the journal Communications Biology, contradicts the most recent scientific thinking about the horned crocodile's evolutionary relationships and also suggests that the ancestor of modern crocodiles likely originated in Africa.
"This crocodile was hiding out on the island of Madagascar during the time when people were building ...
Dietary amino acid determines the fate of cancer cells
2021-04-27
A research group at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research (BDR) has discovered molecular events that determine whether cancer cells live or die. With this knowledge, they found that reduced consumption of a specific protein building block prevents the growth of cells that become cancerous. These findings were published in the scientific journal eLife and open up the possibility of dietary therapy for cancer.
A tumor is a group of cancer cells that multiplies--or proliferates--uncontrollably. Tumors originate from single cells that become cancerous when genes that cause cells to proliferate are over-activated. However, because these genes, called oncogenes, often also cause cell death, activation of a single oncogene within a cell is not enough for it to become a cancer cell. ...
Pandemic significantly increases insomnia in health care workers
2021-04-27
The COVID pandemic appears to have triggered about a 44% increase in insomnia disorder among health care workers at a medical-school affiliated health system, with the highest rates surprisingly among those who spent less time in direct patient care, investigators say.
Another surprise was that about 10% of the group of 678 faculty physicians, nurses, advanced practice providers, like nurse practitioners and physician assistants, as well as residents and fellows, reported in a 17-question survey that their insomnia actually got better in the early months of the pandemic, says Dr. Vaughn McCall, chair of the Department of Psychiatry and Health Behavior at the Medical ...
Vertical turbines could be the future for wind farms
2021-04-27
The now-familiar sight of traditional propeller wind turbines could be replaced in the future with wind farms containing more compact and efficient vertical turbines. New research from Oxford Brookes University has found that the vertical turbine design is far more efficient than traditional turbines in large scale wind farms, and when set in pairs the vertical turbines increase each other's performance by up to 15%.
A research team from the School of Engineering, Computing and Mathematics (ECM) at Oxford Brookes led by Professor Iakovos Tzanakis conducted an in-depth study using more than 11,500 hours of computer simulation to ...
Texas Biomed shares critical work in development of Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine
2021-04-27
(Media note: Interviews with Texas Biomed researchers are available with advanced notice. Photos and video of rhesus macaques and the Biosafety Level 3 & 4 laboratories at Texas Biomed are available upon request.)
SAN ANTONIO (April 27, 2021) - When the world was coming to grips with an emerging global pandemic a year ago, scientists at Texas Biomedical Research Institute sprang into action. The rhesus macaques at the Southwest National Primate Research Center (SNPRC) at Texas Biomed were quickly validated as models for studying vaccines designed to protect humans ...
New prostate cancer urine test shows how aggressive disease is
2021-04-27
New prostate cancer urine test shows how aggressive disease is and could reduce invasive biopsies
Researchers from the University of East Anglia have developed a new urine test for prostate cancer which also shows how aggressive the disease is.
A new study published today shows how an experimental new test called 'ExoGrail' has the potential to revolutionise how patients with suspected prostate cancer are risk-assessed prior to an invasive biopsy.
The research team say their new test could reduce the number of unnecessary prostate cancer biopsies by 35 per ...