Persuading consumers to go green
Study identifies more effective messaging for businesses to increase customers' eco-friendly tactics
2021-04-27
(Press-News.org) Shopping habits and escalating consumption of many consumers are inflicting a heavy environmental toll, and while the majority of customers seem hesitant to act "green" on their own, companies are increasingly expected to implement effective eco-friendly tactics. But efforts to increase towel reuse at hotels, paperless adoption in the banking industry or "ugly" food consumption at grocery stores have been challenging.
As a result, millions of tons of cosmetically imperfect produce are wasted every year in the United States while about one billion trees worth of paper are thrown away. Electricity consumption is impacted when those plain nonverbal stickers used in hotel bathrooms fail to significantly alter towel usage habits.
So, what's missing in the messaging? Persuasive language that combines peer pressure with what the consumer, or broader world, can gain by lightening carbon footprints. Humanize the earth with a smiling face or give the visually unappealing potato a name, and the persuasive green impact is further amplified, according to a study led by the University of Houston Conrad N. Hilton College of Hotel and Restaurant Management.
Researchers presented hypothetical scenarios to 776 experimental respondents across the hotel, banking and retail industries to identify low-cost and useful means to facilitate pro-environmental appeals. The work is published in Psychology & Marketing.
"Gain language is messaging that says 'you can save this amount of water if you reuse your towel or save this amount of electricity.' Highlight the positive benefit of the proposed action," said study co-author Priyanko Guchait, associate professor at UH's Hilton College. "Combine that strategy with peer pressure, or what's called normative influence, and convey that 75% of customers reuse towels, for example. Then customers will be more likely to do the same because of that established social norm."
Guchait collaborated on the research with visiting scholar The Khoa Do and Chen-Ya Wang from National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan.
Gain language does not work in all social situations, just those defined as "low risk," such as green behavior, according to Guchait. "It's low risk because no one is going to die if you don't reuse a towel," he said. Loss language, or highlighting negative possible outcomes, is more effective in "high risk" situations where lives could be at stake, such as calls to practice physical distancing during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to his previous research.
The study also uncovered that by adding anthropomorphism to the messaging, or giving objects human characteristics, green compliance increased. The researchers suggest that hoteliers should add a happy facial expression of the earth to their green signs in bathrooms to encourage the reuse of towels as well as discourage the excessive use of water and toilet paper.
"Retailers such as supermarkets can give a name to their ugly food promotion programs (e.g., Mr. Potato) to better entice customers' engagement in their green campaigns. Similarly, restaurant managers who want to sell foods made of ugly vegetables can create a menu with an anthropomorphized character," the authors wrote. "Banking managers who want to promote paperless behavior may also think of assigning a first-person pronoun to their green paperless initiatives."
Not only could these efforts positively impact the environment, the researchers suggest that by shifting customers' behaviors to be greener, businesses can save money while increasing their reputation.
"Businesses could reduce their losses and generate more revenue all while showing their customers they care about the environment," said Guchait. "That's a win-win situation."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-27
An international, multidisciplinary team that includes faculty members from The University of Texas at Arlington has published a paper in the journal Philosophical Psychology that wades into the debate about whether fish feel pain.
Their conclusion: while fish lack certain regions of the brain typically associated in humans with processing the unpleasantness of pain, this does not offer definitive proof that fish don't experience painful events.
There is a divide among contemporary scientists and philosophers on the issue of animal suffering, particularly in fish. Following the discovery of pain receptors in fish in the early 21st century, scientists developed behavioral experiments that seemed to show that fish ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Deep heat creams widely used by athletes to soothe sore muscles may also boost performance when applied before exercise, according to new research presented virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Researchers at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore studied a small group of male volunteers to determine the effects of deep heat cream on exercise endurance. Each volunteer participated in two trials--one where he applied a thin layer of a commercially available ...
2021-04-27
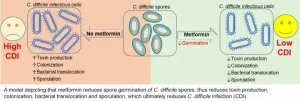
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Researchers from Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina have demonstrated that a common diabetes drug inhibits the spread of Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff--a potentially life-threatening infection commonly acquired during hospital stays. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
C. diff is the most common hospital-acquired infection in the U.S. It starts in the intestines, often after a course of antibiotics. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention categorizes the bacteria C. diff as a public health threat that "require[s] urgent and aggressive action." In 2017, ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--The popular herbicide Roundup® has been in the news because of concerns its main ingredient, glyphosate, might cause cancer. Now researchers from Florida Atlantic University (FAU) are evaluating the pesticide for potential neurological impacts. This week, the scientists will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is a microscopic worm that lives in soil and feeds on bacteria. Scientists have studied it extensively since the 1960s to better understand fundamental physiological processes of the animal kingdom. Because roughly 38% of its genes have counterparts in humans, findings ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--High-intensity cycling in very short bursts can lead to performance and health benefits in just 10 minutes a day, according to a new study to be presented virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Young adult volunteers participated in high-intensity cycling three times a week for eight weeks. They cycled at maximum effort for four seconds and rested for 15 to 30 seconds before beginning another four-second sprint. Each sprint-rest bout was repeated up to 30 times in a single workout session, for a total of 10 minutes.
By the end of the trial ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--A new study by researchers at the VA Portland Health Care System in Oregon found that augmenting traditional treatment for traumatic brain injury (TBI) with morning bright light therapy (MBLT) improved physical and mental symptoms for participants. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
According to the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), over 185,000 veterans have been diagnosed with at least one TBI. TBI is both a common and complex injury. Because of the circumstances surrounding the brain injury, TBI frequently coincides with posttraumatic stress disorder ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Fatty acid supplements may protect children with high cholesterol from heart disease later in life by increasing their blood levels of healthy omega-3 fatty acids, according to a new study. Researchers from the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Maryland, will present their work virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Previous research has shown that high blood levels of beneficial fatty acids, including omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) found in seafood, are associated with a lower risk of coronary artery disease and a higher likelihood of healthy aging. "Since coronary artery ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--A new study reveals that renin-angiotensin system (RAS) genes within the amygdala--the brain region important for traumatic memory processing--express differently when the brain develops fearful memories, such as when people undergo traumatic stress. Researchers have found that medication may potentially be used as a pharmacological blockade of the angiotensin type 1 receptor, thereby improving components of fear memory as assessed by freezing behavior. The research team from George Washington University in Washington, D.C., will present their findings virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a strong predictor ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Exposure to extreme heat (95 degrees Fahrenheit and above) and humidity for eight hours raises the core body temperature and causes dehydration, resulting in an increased risk of acute kidney injury, according to a new study. The researchers, from the Indiana University School of Public Health-Bloomington and University at Buffalo Center for Research and Education in Special Environments in New York, will present their findings virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Acute kidney injury, ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--New research to be presented this week virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021 explores the positive and negative effects of lifespan-extending drugs on mitochondrial function and age-related osteoarthritis (OA).
Decreased function of mitochondria--the energy centers of the cells--is a hallmark characteristic of aging. Maintaining mitochondrial function during the aging process while delaying age-related diseases, such as OA, could be a key to extending lifespan. Previous research has found that metformin, primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes, and rapamycin, a drug used to prevent organ transplant rejection, can extend lifespan and maintain physiological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Persuading consumers to go green
Study identifies more effective messaging for businesses to increase customers' eco-friendly tactics