Diabetes drug could protect against dangerous infection
Metformin inhibited C. diff spread in three study models
2021-04-27
(Press-News.org) Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Researchers from Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina have demonstrated that a common diabetes drug inhibits the spread of Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff--a potentially life-threatening infection commonly acquired during hospital stays. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
C. diff is the most common hospital-acquired infection in the U.S. It starts in the intestines, often after a course of antibiotics. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention categorizes the bacteria C. diff as a public health threat that "require[s] urgent and aggressive action." In 2017, nearly 223,900 people required hospitalization for its treatment, and at least 12,800 died from it. Of those who recover, 1 in 6 people experience reinfection within eight weeks. Antibiotic-resistant strains are also a growing concern.
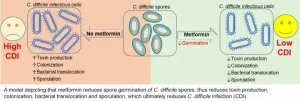
Metformin, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, is the fourth most prescribed drug in the U.S. Earlier studies have shown that metformin beneficially alters the microbiomes of people with diabetes and of the elderly. Inspired by these findings, Shaohua Wang, PhD, a researcher in the lab of Hariom Yadav, PhD, evaluated the effect of metformin on C. diff infection in three different models. She tested the treatment in cell cultures, mice and an ex vivo model of the human microbiota developed by the lab.
In all three systems, metformin had the desired effect. It reduced C. diff proliferation in the cell culture. In the ex vivo model, it both reduced the population of the pathogen and increased the growth of closely related nonpathogenic bacteria. Lastly, in the mouse model, it reduced C. diff in the colon a hundredfold and limited the pathogen's spread to organs outside the intestine.
Yadav, who now heads the University of South Florida Center for Microbiome Research, plans to move forward with future studies that "determine the mechanisms by which metformin inhibits C. difficile infections and clinical efficacy in patients with [C. difficile infection]."
INFORMATION:
NOTE TO JOURNALISTS: To schedule an interview with a member of the research team, or to request the abstract, "Metformin reduces Clostridium difficile infection," please contact the APS Communications Office or call 301.634.7314. Find more research highlights in the END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--The popular herbicide Roundup® has been in the news because of concerns its main ingredient, glyphosate, might cause cancer. Now researchers from Florida Atlantic University (FAU) are evaluating the pesticide for potential neurological impacts. This week, the scientists will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is a microscopic worm that lives in soil and feeds on bacteria. Scientists have studied it extensively since the 1960s to better understand fundamental physiological processes of the animal kingdom. Because roughly 38% of its genes have counterparts in humans, findings ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--High-intensity cycling in very short bursts can lead to performance and health benefits in just 10 minutes a day, according to a new study to be presented virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Young adult volunteers participated in high-intensity cycling three times a week for eight weeks. They cycled at maximum effort for four seconds and rested for 15 to 30 seconds before beginning another four-second sprint. Each sprint-rest bout was repeated up to 30 times in a single workout session, for a total of 10 minutes.
By the end of the trial ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--A new study by researchers at the VA Portland Health Care System in Oregon found that augmenting traditional treatment for traumatic brain injury (TBI) with morning bright light therapy (MBLT) improved physical and mental symptoms for participants. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
According to the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), over 185,000 veterans have been diagnosed with at least one TBI. TBI is both a common and complex injury. Because of the circumstances surrounding the brain injury, TBI frequently coincides with posttraumatic stress disorder ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Fatty acid supplements may protect children with high cholesterol from heart disease later in life by increasing their blood levels of healthy omega-3 fatty acids, according to a new study. Researchers from the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Maryland, will present their work virtually this week at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Previous research has shown that high blood levels of beneficial fatty acids, including omega-3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) found in seafood, are associated with a lower risk of coronary artery disease and a higher likelihood of healthy aging. "Since coronary artery ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--A new study reveals that renin-angiotensin system (RAS) genes within the amygdala--the brain region important for traumatic memory processing--express differently when the brain develops fearful memories, such as when people undergo traumatic stress. Researchers have found that medication may potentially be used as a pharmacological blockade of the angiotensin type 1 receptor, thereby improving components of fear memory as assessed by freezing behavior. The research team from George Washington University in Washington, D.C., will present their findings virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a strong predictor ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Exposure to extreme heat (95 degrees Fahrenheit and above) and humidity for eight hours raises the core body temperature and causes dehydration, resulting in an increased risk of acute kidney injury, according to a new study. The researchers, from the Indiana University School of Public Health-Bloomington and University at Buffalo Center for Research and Education in Special Environments in New York, will present their findings virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Acute kidney injury, ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--New research to be presented this week virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021 explores the positive and negative effects of lifespan-extending drugs on mitochondrial function and age-related osteoarthritis (OA).
Decreased function of mitochondria--the energy centers of the cells--is a hallmark characteristic of aging. Maintaining mitochondrial function during the aging process while delaying age-related diseases, such as OA, could be a key to extending lifespan. Previous research has found that metformin, primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes, and rapamycin, a drug used to prevent organ transplant rejection, can extend lifespan and maintain physiological ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--People who self-report daytime sleepiness were found to have shorter telomeres regardless of whether they had obstructive sleep apnea, according to a new study from researchers at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota. The findings will be presented virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Telomeres protect DNA from biological stressors, and shortened telomeres are associated with multiple cardiovascular diseases, according to the research team. This study found people reporting daytime sleepiness had similar telomere length compared to those without sleepiness; ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Urine analysis of COVID-19 patients revealed elevated levels of specific biomarkers of the immune system compared to those who were not infected with the coronavirus. In addition, levels of these inflammatory markers were higher in patients with comorbidities such as high blood pressure and diabetes, according to researchers from Wayne State University in Detroit. The findings will be presented virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Researchers said they undertook this study in hopes of determining whether biomarkers of COVID-19 could predict which individuals will develop "overly exuberant immune responses," ...
2021-04-27
What makes the human brain special? It's not the time it takes to mature, according to new research. Scientists report the human frontal cortex, the part of the brain involved in higher-level thinking and reasoning, follows a developmental trajectory similar to that of other primates including chimpanzees and macaques.
"We find no evidence that frontal cortex maturation is unusually extended in humans," said Christine Charvet, PhD, assistant professor at Delaware State University and the study's lead author. "Overall, our studies converge to demonstrate a surprising level of similarity in brain structure and development between humans and other studied primates."
Charvet will present the research at the END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Diabetes drug could protect against dangerous infection
Metformin inhibited C. diff spread in three study models






