(Press-News.org) What makes the human brain special? It's not the time it takes to mature, according to new research. Scientists report the human frontal cortex, the part of the brain involved in higher-level thinking and reasoning, follows a developmental trajectory similar to that of other primates including chimpanzees and macaques.
"We find no evidence that frontal cortex maturation is unusually extended in humans," said Christine Charvet, PhD, assistant professor at Delaware State University and the study's lead author. "Overall, our studies converge to demonstrate a surprising level of similarity in brain structure and development between humans and other studied primates."
Charvet will present the research at the END
Brain development is surprisingly similar between humans and other primates
Study offers first comprehensive view of brain maturation across species
2021-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using big data to save babies
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Although bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)--a chronic lung disease affecting newborns--is the most common complication of preterm birth, it remains difficult to diagnose and treat. Researchers from Fundación INFANT in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, hope to address these difficulties using machine learning to inform the clinical care of preemies with BPD. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
BPD affects between 20% and 40% of all infants with birthweight below 3 pounds, 4 ounces (1,500 grams). It usually subsides by age ...
Capsaicin analog could help treatment-resistant lung cancer
2021-04-27
A new study found that non-pungent synthetic analog of capsaicin -- the compound that makes chili peppers hot -- made small cell lung cancer cells more responsive to treatment. Small cell lung cancer is a very aggressive form of cancer with a low survival rate.
Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy is typically the first-line treatment for small cell lung cancer patients. Although patients initially respond very well to this chemotherapy, the tumor usually comes back within a year in a form that doesn't respond to treatments. Patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer have very few treatment options.
"Irinotecan is the only FDA approved second-line drug for small cell lung cancer, but less than 3% of patients respond to it," said research team leader Piyali Dasgupta, ...
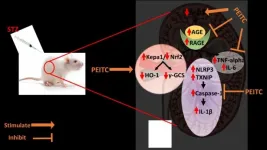
Compound found in some vegetables may reduce diabetes-related kidney damage
2021-04-27
New research conducted in rats suggests a compound that gives some cruciferous vegetables their pungent taste could help to reverse kidney problems associated with diabetes.
It is estimated that about one-quarter of people with diabetes will eventually develop diabetic nephropathy, a gradual loss of kidney function eventually requiring dialysis. The condition is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease in the U.S. and is also associated with a high risk of heart disease. There is currently no cure.
For the new study, researchers assessed the effects of phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) in rats with diabetic nephropathy. PEITC is found in several types of vegetables but is most concentrated ...
Could corals use sound to communicate?
2021-04-27
Corals are part of a highly complex ecosystem, but it remains a mystery if and how they might communicate within their biological community. In a new study, researchers found evidence of sound-related genes in corals, suggesting that the marine invertebrates could use sound to interact with their surroundings.
Coral reefs make up less than 1% of the ocean floor yet support more than 25% of all marine life. Around the world, coral reefs are being threatened by climate change, ocean acidification, diseases, overfishing and pollution. A better understanding of coral communication could help inform policies that aim to protect this critical ecosystem.
"A growing number of studies have shown that trees can communicate, and that this communication is important for ecosystems such ...
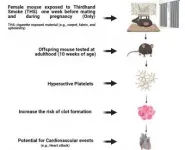
Depression medication could also protect against heart disease
2021-04-27
The antidepression drug duloxetine could be beneficial to patients with both depression and cardiovascular disease, according to new studies performed in human blood and in mice. Globally, more than 300 million people have depression, which comes with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
When a blood vessel is injured, the platelets in our blood respond by forming clots that stop blood bleeding. If this activation goes into overdrive, it can lead to thrombosis, a condition where blood clots form inside blood vessels and can dislodge to lead to a heart attack or stroke. In the new studies, researchers showed that duloxetine inhibited platelet function and protected ...
Five new insights in the fight against COVID-19
2021-04-27
Scientists from around the world are gathering to share the latest research at the forefront of biology during the END ...
Five studies point to dangers of environmental exposures
2021-04-27
Recent years have brought increased attention to the lasting effects of chemicals we unwittingly inhale, touch and ingest while going about our daily lives. The END ...
Gene changes might explain long-haul COVID-19 symptoms
2021-04-27
Results from a new cell study suggest that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein can bring about long-term gene expression changes. The findings could help explain why some COVID-19 patients -- referred to as COVID long-haulers -- experience symptoms such as shortness of breath and dizziness long after clearing the infection.
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is covered in tiny spike proteins. During infection, the spike proteins bind with receptors on cells in our body, starting a process that allows the virus to release its genetic material into the inside of the healthy cell.
"We found that exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alone was enough to change ...
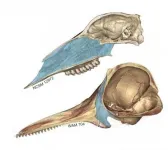
How does a nose evolve into a blowhole? Study suggests there's more than one way
2021-04-27
The two major types of cetaceans appear to have evolved their characteristic blowholes through different anatomical transformations, according to a study being presented at the END ...
Plant compound shows promise against triple-negative breast cancer
2021-04-27
Findings from a new cell study suggest that the natural plant compound sanguinarine could be a promising tool for targeting triple-negative breast cancer cells. The researchers also found that breast cancer cells derived from people with African American ancestry were more sensitive to sanguinarine than those of European origin.
"Triple negative breast cancer is especially aggressive in African American women, who are also more likely to develop this type of breast cancer than women of European descent," said Samia Messeha, PhD, a research associate in the College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Science at Florida Agricultural and Mechanical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Brain development is surprisingly similar between humans and other primatesStudy offers first comprehensive view of brain maturation across species