Urine of COVID-19 patients could predict who will develop severe disease
Inflammatory markers were higher in people with high blood pressure and diabetes
2021-04-27
(Press-News.org) Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Urine analysis of COVID-19 patients revealed elevated levels of specific biomarkers of the immune system compared to those who were not infected with the coronavirus. In addition, levels of these inflammatory markers were higher in patients with comorbidities such as high blood pressure and diabetes, according to researchers from Wayne State University in Detroit. The findings will be presented virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
Researchers said they undertook this study in hopes of determining whether biomarkers of COVID-19 could predict which individuals will develop "overly exuberant immune responses," also called a cytokine storm. They chose to screen the urine of COVID-19 patients because of its non-invasive nature that doesn't require the use of needles or blood samples.
Scientists said they hope the results of this study will translate to a regular screening process for COVID-19 patients to predict who is more likely to develop severe disease and to aid in a successful treatment strategy.
INFORMATION:
NOTE TO JOURNALISTS: To schedule an interview with a member of the research team, and/or request the abstract, "Urine cytokines as biomarkers in COVID-19 patients," please contact the APS Communications Office or call 301.634.7314. Find more research highlights in the END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-27
What makes the human brain special? It's not the time it takes to mature, according to new research. Scientists report the human frontal cortex, the part of the brain involved in higher-level thinking and reasoning, follows a developmental trajectory similar to that of other primates including chimpanzees and macaques.
"We find no evidence that frontal cortex maturation is unusually extended in humans," said Christine Charvet, PhD, assistant professor at Delaware State University and the study's lead author. "Overall, our studies converge to demonstrate a surprising level of similarity in brain structure and development between humans and other studied primates."
Charvet will present the research at the END ...
2021-04-27
Rockville, Md. (April 27, 2021)--Although bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)--a chronic lung disease affecting newborns--is the most common complication of preterm birth, it remains difficult to diagnose and treat. Researchers from Fundación INFANT in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, hope to address these difficulties using machine learning to inform the clinical care of preemies with BPD. The team will present their work virtually at the American Physiological Society's (APS) annual meeting at Experimental Biology 2021.
BPD affects between 20% and 40% of all infants with birthweight below 3 pounds, 4 ounces (1,500 grams). It usually subsides by age ...
2021-04-27
A new study found that non-pungent synthetic analog of capsaicin -- the compound that makes chili peppers hot -- made small cell lung cancer cells more responsive to treatment. Small cell lung cancer is a very aggressive form of cancer with a low survival rate.
Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy is typically the first-line treatment for small cell lung cancer patients. Although patients initially respond very well to this chemotherapy, the tumor usually comes back within a year in a form that doesn't respond to treatments. Patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer have very few treatment options.
"Irinotecan is the only FDA approved second-line drug for small cell lung cancer, but less than 3% of patients respond to it," said research team leader Piyali Dasgupta, ...
2021-04-27
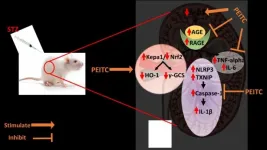
New research conducted in rats suggests a compound that gives some cruciferous vegetables their pungent taste could help to reverse kidney problems associated with diabetes.
It is estimated that about one-quarter of people with diabetes will eventually develop diabetic nephropathy, a gradual loss of kidney function eventually requiring dialysis. The condition is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease in the U.S. and is also associated with a high risk of heart disease. There is currently no cure.
For the new study, researchers assessed the effects of phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) in rats with diabetic nephropathy. PEITC is found in several types of vegetables but is most concentrated ...
2021-04-27
Corals are part of a highly complex ecosystem, but it remains a mystery if and how they might communicate within their biological community. In a new study, researchers found evidence of sound-related genes in corals, suggesting that the marine invertebrates could use sound to interact with their surroundings.
Coral reefs make up less than 1% of the ocean floor yet support more than 25% of all marine life. Around the world, coral reefs are being threatened by climate change, ocean acidification, diseases, overfishing and pollution. A better understanding of coral communication could help inform policies that aim to protect this critical ecosystem.
"A growing number of studies have shown that trees can communicate, and that this communication is important for ecosystems such ...
2021-04-27
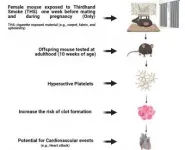
The antidepression drug duloxetine could be beneficial to patients with both depression and cardiovascular disease, according to new studies performed in human blood and in mice. Globally, more than 300 million people have depression, which comes with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
When a blood vessel is injured, the platelets in our blood respond by forming clots that stop blood bleeding. If this activation goes into overdrive, it can lead to thrombosis, a condition where blood clots form inside blood vessels and can dislodge to lead to a heart attack or stroke. In the new studies, researchers showed that duloxetine inhibited platelet function and protected ...
2021-04-27
Scientists from around the world are gathering to share the latest research at the forefront of biology during the END ...
2021-04-27
Recent years have brought increased attention to the lasting effects of chemicals we unwittingly inhale, touch and ingest while going about our daily lives. The END ...
2021-04-27
Results from a new cell study suggest that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein can bring about long-term gene expression changes. The findings could help explain why some COVID-19 patients -- referred to as COVID long-haulers -- experience symptoms such as shortness of breath and dizziness long after clearing the infection.
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is covered in tiny spike proteins. During infection, the spike proteins bind with receptors on cells in our body, starting a process that allows the virus to release its genetic material into the inside of the healthy cell.
"We found that exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alone was enough to change ...
2021-04-27
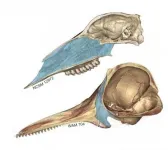
The two major types of cetaceans appear to have evolved their characteristic blowholes through different anatomical transformations, according to a study being presented at the END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Urine of COVID-19 patients could predict who will develop severe disease
Inflammatory markers were higher in people with high blood pressure and diabetes