Nontoxic, flexible energy converters could power wearable devices
Nontoxic, nanotube-based thermoelectric generation converts uneven heat distribution from wearables to electrical energy for their next cycle of operation.
2021-04-27
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, April 27, 2021 -- A wide variety of portable and wearable electronics have become a large part of our daily lives, so a group of Stanford University researchers wondered if these could be powered by harvesting electricity from the waste heat that exists all around us.
Further inspiration came from a desire to ultimately fabricate energy converting devices from the same materials as the active devices themselves, so they can blend in as an integral part of the total system. Today, many biomedical nanodevices' power supplies come from several types of batteries that must be separated from the active portion of the systems, which is not ideal.
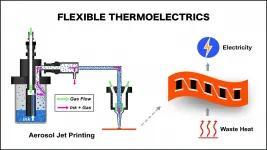
In Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing, the researchers report the design and fabrication of single-wall carbon nanotube thermoelectric devices on flexible polyimide substrates as a basis for wearable energy converters.
"Carbon nanotubes are one-dimensional materials, known for good thermoelectric properties, which mean developing a voltage across them in a temperature gradient," said Eric Pop, a professor of electrical engineering and materials science. "The challenge is that carbon nanotubes also have high thermal conductivity, meaning it's difficult to maintain a thermal gradient across them, and they have been hard to assemble them into thermoelectric generators at low cost."
The group uses printed carbon nanotube networks to tackle both challenges.
"For example, carbon nanotube spaghetti networks have much lower thermal conductivity than carbon nanotubes taken alone, due to the presence of junctions in the networks, which block heat flow," Pop said. "Also, direct printing such carbon nanotube networks can significantly reduce their cost when they are scaled up."
Thermoelectric devices generate electric power locally "by reusing waste heat from personal devices, appliances, vehicles, commercial and industrial processes, computer servers, time-varying solar illumination, and even the human body," said Hye Ryoung Lee, lead author and a research scientist.
"To eliminate hindrances to large-scale application of thermoelectric materials -- toxicity, materials scarcity, mechanical brittleness -- carbon nanotubes offer an excellent alternative to other commonly used materials," Lee said.
The group's approach demonstrates a path to using carbon nanotubes with printable electrodes on flexible polymer substrates in a process anticipated to be economical for large-volume manufacturing. It is also "greener" than other processes, because water is used as the solvent and additional dopants are avoided.
Flexible and wearable energy harvesters can be embedded into fabrics or clothes or placed on unusual shapes and form factors.
"In contrast, traditional thermoelectrics that rely on bismuth telluride are brittle and stiff, with limited applications," Pop said. "Carbon-based thermoelectrics are also more environmentally friendly than those based on rare or toxic materials like bismuth and tellurium."
The most important concept in the group's work is to "recycle energy as much as we can, converting uneven heat distribution to electrical energy for use for the next cycle of operation, which we demonstrated by using nontoxic nanotube-based thermoelectric generation," said Yoshio Nishi, a professor of electrical engineering. "This concept is in full alliance with the world's goal of reducing our total energy consumption."
INFORMATION:
The article "Carbon nanotube thermoelectric devices by direct printing: Towards wearable energy converters" is authored by Hye Ryoung Lee, Naoki Furukawa, Antonio J. Ricco, Eric Pop, Yi Cui, and Yoshio Nishi. The article will appear in Applied Physics Letters on April 27 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0042349). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0042349.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Letters features rapid reports on significant discoveries in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/apl.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-27
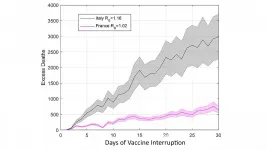
WASHINGTON, April 27, 2021 -- The AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine is suspected of being linked to a small number of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) cases, which recently emerged within Europe as millions of people received vaccinations. This led several countries to suspend AstraZeneca injections and investigate the causal links to DVT.
Researchers within Europe teamed up to explore a hypothesis that pausing AstraZeneca vaccinations, even for a short duration, could cause additional deaths from the faster spread of COVID-19 within a population of susceptible ...
2021-04-27
What The Study Did: Researchers examined whether younger age at onset of type 2 diabetes was associated with an increased risk of subsequent dementia.
Authors: Archana Singh-Manoux, Ph.D., of the Université de Paris, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4001)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
2021-04-27
What The Study Did: Survey data were used to estimate the rate of human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination among young adults ages 18 to 21 in the United States.
Authors: Michelle M. Chen, M.D., M.H.S., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0725)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: The full study is linked ...
2021-04-27
What The Study Did: Researchers compared reasons for hospitalizations in children's hospitals in the United States before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Jay G. Berry, M.D., M.P.H., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4382)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# ...
2021-04-27
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) reaffirms its earlier recommendation of screening for high blood pressure in adults 18 years or older with office blood pressure measurement and obtaining measurements outside of the clinical setting for confirming a diagnosis of high blood pressure before starting treatment. Hypertension affects approximately 45% of adults in the United States and is a major contributing risk factor for heart failure, heart attack, stroke and chronic kidney disease. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this recommendation reaffirms its 2015 statement.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4987)
Editor's ...
2021-04-27
What The Study Did: This analysis uses the World Health Organization pharmacovigilance database to explore the potential safety signal of facial paralysis after COVID-19 vaccination. When compared with other viral vaccines, mRNA COVID-19 vaccines did not display a signal of facial paralysis.
Authors: Charles Khouri, Pharm.D., of the University Grenoble Alpes and Grenoble Alpes University Hospital in Grenoble, France, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.2219)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
2021-04-27
Ambitious climate policies could help to reduce extreme poverty in developing countries. This is the result of a new study by scientists of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) - a result that is in contrast to wide-spread assumptions that climate change mitigation comes with a trade-off for poverty reduction. To turn climate policies and poverty reduction into a win-win situation for planet and people, a progressive redistribution of emission pricing revenues and a fair international burden sharing are key.
"Climate policies safeguard people from climate change impacts like extreme weather risks or crop failures. Yet they can also imply increased energy and food prices," says Bjoern Soergel from PIK, lead-author of the study. "This could result in an additional ...
2021-04-27
A four-year effort has reduced the rate of cesarean sections for low-risk, first-time mothers in California, according to a study led by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine and the California Maternal Quality Care Collaborative.
The study will be published April 27 in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Several coordinated initiatives to reduce C-sections took place across the state during the 2015-19 study period, including messaging to all hospitals from state agencies and health plans, annual public reporting of hospitals' C-section rates, and a quality improvement program targeting hospitals with the highest rates.
The study examined the collective effect of these projects, which have led California to become the first state in the country ...
2021-04-27
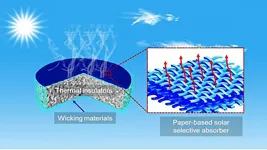
WASHINGTON, April 27, 2021 -- Despite the vast amount of water on Earth, most of it is nonpotable seawater. Freshwater accounts for only about 2.5% of the total, so much of the world experiences serious water shortages.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, scientists in China report the development of a highly efficient desalination device powered by solar energy. The device consists of a titanium-containing layer, TiNO, or titanium nitride oxide, capable of absorbing solar energy. The TiNO is deposited on a special type of paper and foam that allows the solar absorber ...
2021-04-27
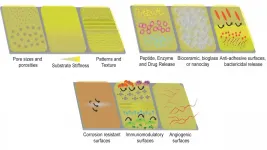
WASHINGTON, April 27, 2021 -- Traffic accidents, tumor resections, and congenital diseases can cause significant trauma, which can lead to large bone deformations and/or bone loss. Although bone has some capacity to regenerate, large bone defects cannot be healed without major medical procedures.
In these situations, metallic implants are widely used, but the bioinertness of such implants poses a major challenge in bone tissue engineering. Bioinert metal implants lack bone integration, loosen over time, and may lead to adverse reactions around the area in which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nontoxic, flexible energy converters could power wearable devices
Nontoxic, nanotube-based thermoelectric generation converts uneven heat distribution from wearables to electrical energy for their next cycle of operation.