Research shows consuming prebiotic supplements once a day has a positive impact on anxiety levels
2021-04-27
(Press-News.org) In a paper published in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers from Surrey investigated whether the daily consumption of a prebiotic food supplement could improve overall wellbeing in a group of 18 to 25 year-olds. The study found that those who received a daily dose of prebiotics improved mental wellbeing by reducing anxiety levels and had better gut health than the control group.
Researchers studied a group of 64 healthy female participants with no current or previous clinical diagnoses of anxiety. Participants received either a daily dose of the prebiotic galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) or a placebo for 28 days.
All those involved in the trial completed surveys about their health experiences, including mood, anxiety and sleep quality and provided a stool sample for gut microbiome sequencing analysis.
Dr Kathrin Cohen Kadosh, Reader in Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience at the University of Surrey and Head of the Social Brain and Development Lab, said:
"This new research marks a significant step forward in that we were able to show that we can use a simple and safe food supplement such as prebiotics to improve both the abundance of beneficial gut bacteria in the gut and to improve mental health and wellbeing in young women."
Dr Nicola Johnstone, Research Fellow from the University of Surrey, said:
"This is an exciting study that brings together different dimensions in mental health research; finding prebiotic effects in a sub-clinical group shows promise for translational clinical research on multiple markers of mental health."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-27
New studies from the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) shed more light on the economic and environmental costs of mandates in the Renewable Fuels Standard (RFS), a federal program to expand the nation's biofuels sector.
Researchers said the studies indicate the need to adopt more targeted policies that value the environmental and ecosystem benefits of perennial bioenergy crops over cheaper options -- and provide financial incentives for farmers to grow them.
The RFS was issued in 2005 and updated through the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 ...
2021-04-27
MEMPHIS, Tenn. - For the first time in published literature, Le Bonheur Children's Hospital and University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC) researchers showed that a variety of white blood cells known as eosinophils modify the respiratory barrier during influenza A (IAV) infection, according to a recent paper in the journal Cells. This research could have implications in understanding SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection in asthmatic patients.
The Le Bonheur/UTHSC study found that eosinophils immunomodulate airway epithelial cells during IAV infection, helping to neutralize the virus and ...
2021-04-27
The legend of the "kraken" has captivated humans for millennia. Stories of deep-sea squid dragging sailors and even entire ships to their doom can be found in everything from ancient Greek mythology to modern-day movie blockbusters. It is therefore ironic that the species that inspired these stories, the giant squid Architeuthis dux, is camera-shy. In fact, filming this species in the wild has proven an insurmountable challenge for countless scientists, explorers, and filmmakers. To date, only one scientist, Dr. Edith Widder of the Ocean Research & Conservation Association, has repeatedly caught a live giant squid on camera. In a new study, Dr. Widder and her colleagues have finally revealed the secrets behind their success. This study, which is free to access, also ...
2021-04-27
An Academic Analytics Research Center (AARC) study published in the journal Scientometrics found that senior faculty (scholars who earned their terminal degree 30 or more years ago) research publication activity exceeded expectations based on age cohort population for book chapters and book publications, and senior scholars largely kept pace in terms of journal article publications. "Across all disciplines, senior faculty may be uniquely positioned to invest their time in a longer-term publication effort, shifting their research focus to the review and synthesis of ideas through the publication of books and chapters," said AARC Senior Researcher and Co-Author of the study, Bill Savage, Ph.D.
The study explored the publishing activity of 167,299 unique faculty members at American ...
2021-04-27
Aromatics are major building blocks of polymers, or plastics, that turn up as everything from PET bottles for water to breathable, wrinkle-resistant polyester clothing. These petrochemicals comprise a specialized, value-added sector of the energy industry. The process for refining crude oil into useful aromatic streams for derivative use often involves the usage of a catalyst to facilitate chemical reactions. Among the various types of catalysts, many are zeolites - porous aluminosilicates - such as ZSM-5, a unique synthetic zeolite prolifically used in the upgrading of chemicals in alkylation and isomerization. Petrochemicals producers are constantly looking to minimize overhead costs to weather the volatility in commodity markets and provide a competitive end product ...
2021-04-27
NEWPORT NEWS - Nuclear physicists have made a new, highly accurate measurement of the thickness of the neutron "skin" that encompasses the lead nucleus in experiments conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility and just published in Physical Review Letters. The result, which revealed a neutron skin thickness of .28 millionths of a nanometer, has important implications for the structure and size of neutron stars.
The protons and neutrons that form the nucleus at the heart of every atom in the universe help determine each atom's identity and properties. Nuclear physicists are studying different nuclei to learn more about how these protons and neutrons act inside the nucleus. The Lead Radius Experiment collaboration, called PREx (after ...
2021-04-27
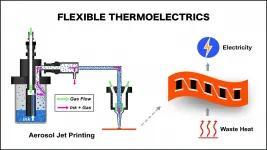
WASHINGTON, April 27, 2021 -- A wide variety of portable and wearable electronics have become a large part of our daily lives, so a group of Stanford University researchers wondered if these could be powered by harvesting electricity from the waste heat that exists all around us.
Further inspiration came from a desire to ultimately fabricate energy converting devices from the same materials as the active devices themselves, so they can blend in as an integral part of the total system. Today, many biomedical nanodevices' power supplies come from several types of batteries that must be separated from the active portion of the systems, which is not ...
2021-04-27
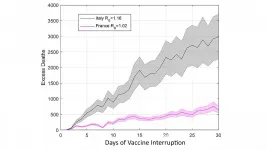
WASHINGTON, April 27, 2021 -- The AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine is suspected of being linked to a small number of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) cases, which recently emerged within Europe as millions of people received vaccinations. This led several countries to suspend AstraZeneca injections and investigate the causal links to DVT.
Researchers within Europe teamed up to explore a hypothesis that pausing AstraZeneca vaccinations, even for a short duration, could cause additional deaths from the faster spread of COVID-19 within a population of susceptible ...
2021-04-27
What The Study Did: Researchers examined whether younger age at onset of type 2 diabetes was associated with an increased risk of subsequent dementia.
Authors: Archana Singh-Manoux, Ph.D., of the Université de Paris, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4001)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
2021-04-27
What The Study Did: Survey data were used to estimate the rate of human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination among young adults ages 18 to 21 in the United States.
Authors: Michelle M. Chen, M.D., M.H.S., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0725)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: The full study is linked ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research shows consuming prebiotic supplements once a day has a positive impact on anxiety levels