INFORMATION:
Study of marine noise highlights need to protect pristine Australian waters
2021-04-28
(Press-News.org) New Curtin research has found urgent action is needed to ensure man-made underwater noise in Australian waters does not escalate to levels which could be harmful to marine animals, such as whales, and negatively impact our pristine oceans.
Lead author Professor Christine Erbe, Director of Curtin's Centre for Marine Science and Technology, said recent studies from the northern hemisphere showed man-made noise, in particular from ships, often dominates the underwater soundscape over large areas, such as entire seas, and could interfere with marine fauna that rely on sound for communication, navigation and foraging.
"When humans go to sea, they generate underwater noise, from boat and ship traffic, dredging, port construction, offshore exploration for oil and gas, offshore drilling, seafloor surveying, fishing and naval exercises, which impacts a wide variety of animals including, whales, dolphins, fishes and crustaceans," Professor Erbe said.
"We set out to measure and model underwater sound in Australia's maritime regions and found that on average, over the course of six months, ship noise dominated only in tightly localised regions or right under the major shipping routes when these are confined to a narrow channel or strip.
"In most of our waters, naturally generated underwater sound dominated and was mostly due to consistently strong winds blowing along Australia's southern coasts and strong whale and fish choruses."
Professor Erbe said while these findings show the vast majority of Australian maritime waters were not as polluted by man-made noise as some northern hemisphere waters, action was required in order for it to remain that way.
"If you define 'pristine' as rich in biological sounds and their diversity, and devoid of man-made noise, then Australia has several regions, not just pockets, where the marine soundscape is undisturbed," Professor Erbe said.
"We need to set out and protect these regions by becoming more proactive in managing our marine environment.
Usually we only become aware of an environmental problem when it's potentially too late, and find ourselves in a race to mitigate negative impacts. But in Australia, we have the opportunity to act early and protect healthy environments now."
The research was funded by the Federal Government's National Environmental Science Program and the paper, 'It often howls more than it chugs: Wind versus ship noise under water in Australia's maritime regions' was published in Journal of Marine Science and Engineering.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A simple exercise goal protects against unhealthy weight gain
2021-04-28
New research shows that physical activity equivalent to 100 PAI a week can counteract excessive weight gain.
PAI stands for Personal Activity Intelligence and tracks how physically active you are throughout the week. You can measure PAI with just about any device that can measure heart rate.
The activity metric has been developed by the Cardiac Exercise Research Group (CERG) at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) under the leadership of NTNU Professor Ulrik Wisløff.
"Previously, we found that 100 PAI a week can give us a longer and healthier life without cardiovascular disease. Our new study shows that PAI can also help people maintain a healthy body weight," says researcher Javaid ...
More sleep or more exercise: the best time trade-offs for children's health
2021-04-28
More sleep could offset children's excess indulgence over the school holidays as new research from the University of South Australia shows that the same decline in body mass index may be achieved by either extra sleep or extra exercise.
The striking new finding is part of a study that shows how children can achieve equivalent physical and mental health benefits by choosing different activity trade-offs across the 24-hour day.
Conducted in partnership with the Murdoch Children's Research Institute, and supported by the National Heart Foundation of Australia, the team examined the optimal balance between children's physical activity, sleep, and sedentary time across the 24-hour day to better inform tailored ...
Researchers use a nanoscale synthetic antiferromagnet to toggle nonlinear spin dynamics
2021-04-28
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Researchers at the University of California, Riverside, have used a nanoscale synthetic antiferromagnet to control the interaction between magnons -- research that could lead to faster and more energy-efficient computers.
In ferromagnets, electron spins point in the same direction. To make future computer technologies faster and more energy-efficient, spintronics research employs spin dynamics -- fluctuations of the electron spins -- to process information. Magnons, the quantum-mechanical units of spin fluctuations, interact with each other, leading to nonlinear features of the spin dynamics. Such nonlinearities play a central ...
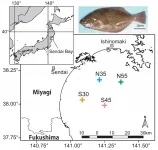
Bone collagen of fish shows individual history of migration and feeding habits
2021-04-28
Collagen is a protein found widely in almost all cells of animals, and scientifically can be used to learn much about an animal's life history including human being in the present or in the past. Scientists at the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature (RIHN) and Japan Fisheries Research and Education Agency (FRA), Japan, prove this point for Japanese flounder by measuring isotope ratios in vertebral-bone collagen. The new study, which can be read in Marine Biology, shows that there exist behavioral groups of fish with different migrating and/or feeding patterns.
A school of fish will decide their habitat on fundamental needs for survival, ...
Lactic acid bacteria can extend the shelf life of foods
2021-04-28
Researchers at the National Food Institute have come up with a solution that can help combat both food loss and food waste: They have generated a natural lactic acid bacterium, which secretes the antimicrobial peptide nisin, when grown on dairy waste.
Nisin is a food-grade preservative, which can extend the shelf life of foods, and thus can be used to reduce food waste. The discovery also makes it possible to better utilize the large quantities of whey generated when cheese is made.
Nisin is approved for use in a number of foods, where it can prevent the growth of certain spoilage microorganisms as well as microorganisms that make consumers sick. It can for instance inhibit spore ...
Dead lithium: The culprit of low Coulombic efficiency with LIBs
2021-04-28
The target of carbon-neutral and net-zero emissions is the development and utilization of renewable energy. High-energy-density energy storage systems are critical technologies for the integration of renewable energy.
Li metal is highly recognized as a promising alternative anode for next-generation rechargeable batteries due to its high theoretical capacity of 3860 mAh g-1 and ultralow electrode potential of -3.04 V compared to the standard hydrogen electrode.
However, Li metal batteries' (LMBs) main issue is their low Coulombic efficiency (CE), which limits batteries' cycle life. The low CE in LMBs occurs ...
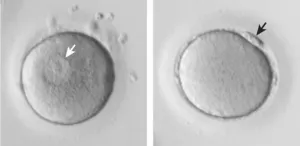
Ageing impairs critical final egg maturation stage
2021-04-28
Age may adversely affect women's fertility by impairing levels of RNA molecules which in turn alter the function of genes involved in key biological pathways during the final maturation stage of a human egg cell, according to the findings of a new study published today in the journal Aging Cell.
Researchers from the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), the Centro Nacional de Análisis Genómico (CNAG-CRG) and Clínica Eugin sequenced the RNA molecules, also known as the transcriptome, within oocytes to understand which genes are affected in their activity by age. They used single-cell sequencing to analyse the transcriptome of 72 individual oocytes ...
Many children with cardiomyopathy have a genetic mutation but few are screened
2021-04-28
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- A national, University at Buffalo-led study on genes in pediatric cardiomyopathy demonstrates strong evidence for routine genetic screening in children with the disease. The study, published April 28 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, revealed wide variation in screening, with some centers conducting routine genetic testing and others conducting none.
Conducted at 14 centers, the National Institutes of Health-funded study of 152 children with cardiomyopathy found that only half had undergone genetic screening. Of those who hadn't undergone screening, 21% were found to have a genetic cause for the ...
Scientists' discovery of blood clotting mechanism could lead to new antithrombotic drugs
2021-04-28
Under normal, healthy circulatory conditions, the von Willebrand Factor (vWF) keeps to itself. The large and mysterious glycoprotein moves through the blood, balled up tightly, its reaction sites unexposed. But when significant bleeding occurs, it springs into action, initiating the clotting process.
When it works properly, vWF helps stop bleeding and saves lives. However, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 60,000 to 100,000 Americans die each year from thrombosis, a disorder characterized by too much clotting. Blood clots can trigger a stroke or heart attack.
According ...
Using microbes to remove microplastics from the environment
2021-04-28
Today at the Microbiology Society's Annual Conference, Yang Liu, researcher at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, will discuss a new technique to trap and recover microplastics.
The method uses bacterial biofilms, a sticky substance created by micro-organisms, to trap microplastic particles. The biofilm is then processed and dispersed, releasing the microplastic particles for processing and recycling.
Liu and colleagues used the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa to capture microplastics in a bioreactor. This species of bacteria is found in all environments and has previously been shown to colonise microplastics in the environment.
P. aeruginosa biofilms ...