Causes of extreme weather and climate events in China during 2020/21
2021-04-28
(Press-News.org) During the summer of 2020, especially June and July, periods of extreme heavy rainfall occurred in China's Yangtze River Valley (YRV). These rain events caused the severest floods for the region since the summer of 1998. Despite this, the 2020 western North Pacific (WNP) typhoon season started slowly, but eventually produced 23 named tropical cyclones, still slightly below 27, the WNP seasonal average. As summer transitioned to winter, three severe cold surges swept most parts of China during late 2020 and early 2021, prompting the National Meteorological Center to issue its highest cold surge warning alert for the first time in four years. After a volatile weather year, scientists are finding answers as to why the past year featured so many extreme weather and climate events in China.
Professor Chunzai Wang and his team in the State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences were tasked to analyze global and regional climate influences that may have played roles in the 2020/21 extreme weather events. The researchers found many key oceanographic and meteorological connections, which have just been published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences.
Sea surface temperature (SST) fluctuations in the tropical Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic Oceans can contribute to heavy rainfall events in China. However, observational data suggest that Atlantic and Indian Ocean influences dominate over those from the Pacific. Beginning in May 2020, positive SST anomalies, or change from average, throughout the tropical western North Atlantic (WNA) induced positive geopotential height anomalies in June over the mid-latitude North Atlantic. Geopotential height is the altitude above sea level at which a certain pressure surface exists, typically analyzed at 500mb. This metric is excellent for identifying the ridges and troughs which affect the rainfall anomalies in the YRV via an Atlantic-induced atmospheric "wave train" across Eurasia. Further analysis suggests that the Indian Ocean did not significantly affect June rainfall over the YRV. However, when considering June and July rainfall together, both the Indian Ocean and WNA influences are important.
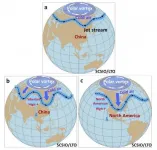
Regarding the extremely cold surges during the 2020/21 winter, Prof. Wang's team points to the Siberian High. An enhancement and northward movement of the Siberian High force the jet stream to develop a wavy pattern. This disrupts the polar vortex, allowing cold polar air to invade southward, thus inducing the cold surges in China (Fig. 1b) and North America (Fig. 1c).
The below average 2020 typhoon season is associated with large vertical wind shear (which is defined as the wind difference between the upper and lower troposphere) and low humidity in the WNP. Tropical cyclones do not form and develop in heavily sheared and dry environments. Scientists believe that these are responsible for fewer typhoons in the first half of the 2020 typhoon season.
This study points out the importance of three-ocean interactions and their influences across the Northern Hemisphere. The tropical Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic Oceans can affect the anticyclone in the WNP, providing moisture transport to its northwest side, therefore increasing summer rainfall in China. The same anticyclone also modifies atmospheric circulation and thermodynamic factors in the WNP, influencing typhoon activity. Global warming can increase the occurrence of extreme weather and climate events. However, future studies are needed to quantify the influences of global warming on an individual extreme weather and climate event.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-28
The research by RMIT University looked at the ramifications on the stock market following Google's withdrawal from mainland China in 2010.
It found access to unbiased information about companies' performance - aided by unrestricted internet search results - led to investors making more informed decisions.
On the flip side, search results manipulated to show overly positive information led to stocks for those companies being overvalued temporarily, increasing the stock market crash risk by 19%.
The study has been published in the Journal of Financial Economics.
Lead researcher Dr Gaoping Zheng, a lecturer in finance at RMIT, said the study showed search results influenced decisions, a challenge to previous thinking that they merely justified people's existing ideas.
"Until ...
2021-04-28
In almost ten per cent of myocardial infarctions, no obvious cause in the coronary artery can be found. Some of the patients are diagnosed with broken-heart syndrome, while others are left without a diagnosis. A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden suggests that early magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of the heart can greatly increase the rate of diagnosis. The study has been published in the journal JACC Cardiovascular Imaging.
Myocardial infarction is one of the most common diseases in the West, and is usually caused by a blood clot that blocks the coronary artery on the heart's surface. However, in up to ten per cent of all myocardial infarctions, no obvious cause ...
2021-04-28
The National Climate Center (NCC) of China has just completed a report that gives an authoritative assessment of China's climate in 2020. It provides a summary of China's climate as well as the major weather and climate events that took place throughout the year. This is the third consecutive year that the NCC has published an annual national climate statement in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters (AOSL).
"Against the background of global warming, extreme weather and climate events occur more frequently and have wide influence on society and economies. Last year, floods, droughts, typhoons, low-temperature freezing and snow disasters, and dust storms attacked ...
2021-04-28
Ishikawa, Japan - Human beings have the ability to recognize emotions in others, but the same cannot be said for robots. Although perfectly capable of communicating with humans through speech, robots and virtual agents are only good at processing logical instructions, which greatly restricts human-robot interaction (HRI). Consequently, a great deal of research in HRI is about emotion recognition from speech. But first, how do we describe emotions?
Categorical emotions such as happiness, sadness, and anger are well-understood by us but can be hard for robots to register. Researchers have focused on "dimensional emotions," which constitute a gradual emotional transition in natural speech. "Continuous dimensional ...
2021-04-28
New Curtin research has found urgent action is needed to ensure man-made underwater noise in Australian waters does not escalate to levels which could be harmful to marine animals, such as whales, and negatively impact our pristine oceans.
Lead author Professor Christine Erbe, Director of Curtin's Centre for Marine Science and Technology, said recent studies from the northern hemisphere showed man-made noise, in particular from ships, often dominates the underwater soundscape over large areas, such as entire seas, and could interfere with marine fauna that rely on sound for communication, navigation and foraging.
"When ...
2021-04-28
New research shows that physical activity equivalent to 100 PAI a week can counteract excessive weight gain.
PAI stands for Personal Activity Intelligence and tracks how physically active you are throughout the week. You can measure PAI with just about any device that can measure heart rate.
The activity metric has been developed by the Cardiac Exercise Research Group (CERG) at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) under the leadership of NTNU Professor Ulrik Wisløff.
"Previously, we found that 100 PAI a week can give us a longer and healthier life without cardiovascular disease. Our new study shows that PAI can also help people maintain a healthy body weight," says researcher Javaid ...
2021-04-28
More sleep could offset children's excess indulgence over the school holidays as new research from the University of South Australia shows that the same decline in body mass index may be achieved by either extra sleep or extra exercise.
The striking new finding is part of a study that shows how children can achieve equivalent physical and mental health benefits by choosing different activity trade-offs across the 24-hour day.
Conducted in partnership with the Murdoch Children's Research Institute, and supported by the National Heart Foundation of Australia, the team examined the optimal balance between children's physical activity, sleep, and sedentary time across the 24-hour day to better inform tailored ...
2021-04-28
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Researchers at the University of California, Riverside, have used a nanoscale synthetic antiferromagnet to control the interaction between magnons -- research that could lead to faster and more energy-efficient computers.
In ferromagnets, electron spins point in the same direction. To make future computer technologies faster and more energy-efficient, spintronics research employs spin dynamics -- fluctuations of the electron spins -- to process information. Magnons, the quantum-mechanical units of spin fluctuations, interact with each other, leading to nonlinear features of the spin dynamics. Such nonlinearities play a central ...
2021-04-28
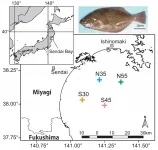
Collagen is a protein found widely in almost all cells of animals, and scientifically can be used to learn much about an animal's life history including human being in the present or in the past. Scientists at the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature (RIHN) and Japan Fisheries Research and Education Agency (FRA), Japan, prove this point for Japanese flounder by measuring isotope ratios in vertebral-bone collagen. The new study, which can be read in Marine Biology, shows that there exist behavioral groups of fish with different migrating and/or feeding patterns.
A school of fish will decide their habitat on fundamental needs for survival, ...
2021-04-28
Researchers at the National Food Institute have come up with a solution that can help combat both food loss and food waste: They have generated a natural lactic acid bacterium, which secretes the antimicrobial peptide nisin, when grown on dairy waste.
Nisin is a food-grade preservative, which can extend the shelf life of foods, and thus can be used to reduce food waste. The discovery also makes it possible to better utilize the large quantities of whey generated when cheese is made.
Nisin is approved for use in a number of foods, where it can prevent the growth of certain spoilage microorganisms as well as microorganisms that make consumers sick. It can for instance inhibit spore ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Causes of extreme weather and climate events in China during 2020/21