Research delves into link between test anxiety and poor sleep
2021-04-28
(Press-News.org) LAWRENCE -- College students across the country struggle with a vicious cycle: Test anxiety triggers poor sleep, which in turn reduces performance on the tests that caused the anxiety in the first place.
New research from the University of Kansas just published in the International Journal of Behavioral Medicine is shedding light on this biopsychosocial process that can lead to poor grades, withdrawal from classes and even students who drop out. Indeed, about 40% of freshman don't return to their universities for a second year in the United States.
"We were interested in finding out what predicted students' performance in statistics classes -- stats classes are usually the most dreaded undergrad class," said lead author Nancy Hamilton, professor of psychology at KU. "It can be a particular problem that can be a sticking point for a lot of students. I'm interested in sleep, and sleep and anxiety are related. So, we wanted to find out what the relationship was between sleep, anxiety and test performance to find the correlation and how it unfolds over time."
Hamilton and graduate student co-authors Ronald Freche and Ian Carroll and undergraduates Yichi Zhang and Gabriella Zeller surveyed the sleep quality, anxiety levels and test scores for 167 students enrolled in a statistics class at KU. Participants completed an electronic battery of measures and filled out Sleep Mood Study Diaries during the mornings in the days before a statistics exam. Instructors confirmed exam scores. The study showed "sleep and anxiety feed one another" and can hurt academic performance predictably.
"We looked at test anxiety to determine whether that did predict who passed, and it was a predictor," Hamilton said. "It was a predictor even after controlling for students' past performance and increased the likelihood of students failing in class. When you look at students who are especially anxious, it was almost a five-point difference in their score over students who had average levels of anxiety. This is not small potatoes. It's the difference between a C-minus abd a D. It's the difference between a B-plus and an A-minus. It's real."
Beyond falling grades, a student's overall health could suffer when test anxiety and poor sleep reinforce each other.
"Studies have shown students tend to cope with anxiety through health behaviors," Hamilton said. "Students may use more caffeine to combat sleep problems associated with anxiety, and caffeine can actually enhance sleep problems, specifically if you're using caffeine in the afternoon or in the evening. Students sometimes self-medicate for anxiety by using alcohol or other sedating drugs. Those are things that we know are related."
Hamilton said universities could do more to communicate to students the prevalence of test anxiety and provide them with resources.
"What would be really helpful for a university to do is to talk about testing anxiety and to talk about the fact that it's very common and that there are things that can be done for students who have test anxiety," she said. "A university can also talk to instructors about doing things that they can do to help minimize the effect of testing anxiety."
According to Hamilton, instructors are hindered by the phenomenon as well: Anxiety and associated sleep problems actually distort instructors' ability to measure student knowledge in a given subject.
"As an instructor, my goal when I'm writing a test is to assess how much a student understands," she said. "So having a psychological or an emotional problem gets in the way of that. It actually impedes my ability to effectively assess learning. It's noise. It's unrelated to what they understand and what they know. So, I think it behooves all of us to see if we can figure out ways to help students minimize the effects of anxiety on their performance."
The KU researcher said testing itself isn't the problem and suggested an increase in regular tests might reduce anxiety through regular exposure. However, she said a few small changes to how tests are administered also could calm student anxiety.
"In classes that use performance-based measures like math or statistics, classes that tend to really induce a lot of anxiety for some students, encouraging those students to take five minutes right before an exam to physically write about what they're anxious about can help -- that's cheap, that's easy," Hamilton said. "Also, eliminating a time limit on a test can help. There's just really nothing to be gained by telling students, 'You have an hour to complete a test and what you don't get done you just don't get done.' That's really not assessing what a student can do -- it's only assessing what a student can do quickly."
Hamilton said going forward she'd like research into the link between test anxiety and poor sleep broadened to include a more diverse group of students and also to include its influence on remote learning.
"The students in this study were mostly middle-class, Caucasian students," she said. "So, I hesitate to say these results would generalize necessarily to universities that have a more heterogeneous student body. I also would hesitate to say how this would generalize into our current Zoom environment. I don't know how that shakes out because the demands of doing exams online are likely to be very different."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-28
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Socially just policies aimed at limiting the Earth's human population hold tremendous potential for advancing equity while simultaneously helping to mitigate the effects of climate change, Oregon State University researchers say.
In a paper published this week in Sustainability Science, William Ripple and Christopher Wolf of the OSU College of Forestry also note that fertility rates are a dramatically understudied and overlooked aspect of the climate emergency. That's especially true relative to the attention devoted to other climate-related topics including energy, short-lived pollutants and ...
2021-04-28
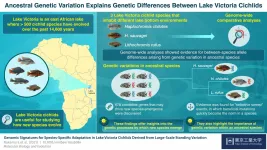
Biologists use the term adaptive radiation to describe a phenomenon in which new species rapidly evolve from an ancestral species, often in response to changes in the local environment that lead to new biological niches becoming available. To understand this process, biologists often turn to the cichlids of Lake Victoria, in which over 500 species of the fish have evolved over the past 14,600 years. As Professor Masato Nikaido of Tokyo Tech explains, "The level of genetic differentiation among species is considered very low due to the short period of time after these different species began evolving, and this limited genetic differentiation provides us with a great opportunity to find candidate genes that have contributed to adaptive ...
2021-04-28
Predatory bacteria--bacteria that eat other bacteria--grow faster and consume more resources than non-predators in the same soil, according to a new study out this week from Northern Arizona University. These active predators, which use wolfpack-like behavior, enzymes, and cytoskeletal 'fangs' to hunt and feast on other bacteria, wield important power in determining where soil nutrients go. The results of the study, published in the journal mBio this week, show predation is an important dynamic in the wild microbial realm, and suggest that these predators play an outsized role in how elements are stored in or released from soil.
Like every other life form on earth, bacteria belong to intricate food webs in which organisms are connected ...
2021-04-28
Constantina Theofanopoulou wanted to study oxytocin. Her graduate work had focused on how the hormone influences human speech development, and now she was preparing to use those findings to investigate how songbirds learn to sing. The problem was that birds do not have oxytocin. Or so she was told.
"Everywhere that I looked in the genome," she says, "I was unable to find a gene called oxytocin in birds."
Theofanopoulou eventually came across mesotocin, the analogue for oxytocin in birds, reptiles, and amphibians. But as she plumped the literature in Erich Jarvis's lab at Rockefeller, the waters grew muddier. If she and Jarvis wanted to find studies on oxytocin in fish, they ...
2021-04-28
Researchers from Erasmus School of Economics, IESE Business School, and New York University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines what business schools do wrong when conducting academic research and what changes they can make so that research contributes to improving society.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Faculty Research Incentives and Business School Health: A New Perspective from and for Marketing" and is authored by Stefan Stremersch, Russell Winer, and Nuno Camacho.
In February 2020, an article in ...
2021-04-28
The flightless kakapo of New Zealand is in trouble. The world's heaviest parrot--representing one of the most ancestral branches of the parrot family tree--is nearly extinct, with barely 200 adults plodding the underbrush of four small islands. Whether the last of the kakapos had the genetic resilience to survive was a question that only high-quality genomic analysis could answer.
But a high-quality genome assembly did not exist for the kakapo--nor for most of the 70,000 vertebrate species alive today.
Questions about how best to prevent the extinction of species ranging ...
2021-04-28
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Difficult-to-treat, chronic wounds in preclinical models healed with normal scar-free skin after treatment with an acellular product discovered at Mayo Clinic. Derived from platelets, the purified exosomal product, known as PEP, was used to deliver healing messages into cells of preclinical animal models of ischemic wounds. The Mayo Clinic research team documented restoration of skin integrity, hair follicles, sweat glands, skin oils and normal hydration.
Ischemic wounds occur when arteries are clogged or blocked, preventing important nutrients and oxygen from reaching the skin to drive repair. This groundbreaking study titled, "TGF-β Donor Exosome Accelerates Ischemic ...
2021-04-28
To be more energy efficient, many people have replaced their incandescent lights with light-emitting diode (LED) bulbs. However, those currently on the market emit a lot of blue light, which has been linked to eye troubles and sleep disturbances. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed a prototype LED that reduces -- instead of masks -- the blue component, while also making colors appear just as they do in natural sunlight.
LED light bulbs are popular because of their low energy consumption, long lifespan and ability to turn on and off quickly. Inside the bulb, an LED chip converts electrical current into high-energy light, including invisible ultraviolet (UV), violet ...
2021-04-28
The highly infectious SARS-CoV-2 variant that recently emerged in South Africa, known as B.1.351, has scientists wondering how existing COVID-19 vaccines and therapies can be improved to ensure strong protection. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Medicinal Chemistry have used computer modeling to reveal that one of the three mutations that make variant B.1.351 different from the original SARS-CoV-2 reduces the virus' binding to human cells -- but potentially allows it to escape some antibodies.
Since the original SARS-CoV-2 was first detected in late 2019, several new variants have emerged, including ones from the U.K., South Africa and Brazil. Because the new variants appear to be more highly ...
2021-04-28
Uncapped, idle oil wells could be leaking millions of kilograms of methane each year into the atmosphere and surface water, according to a study by the University of Cincinnati.
Amy Townsend-Small, an associate professor of geology and geography in UC's College of Arts and Sciences, studied 37 wells on private property in the Permian Basin of Texas, the largest oil production region on Earth. She found that seven had methane emissions of as much as 132 grams per hour. The average rate was 6.2 grams per hour.
"Some of them were leaking a lot. Most of them were leaking a little or not at all, which is a ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research delves into link between test anxiety and poor sleep