(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C. - April 28, 2021 - As of April 2021, more than 3 million people worldwide have died of COVID-19. Early in the pandemic, researchers developed accurate diagnostic tests and identified health conditions that correlated with worse outcomes. However, a clinical predictor of who faces the highest risk of being hospitalized, put on a ventilator or dying from the disease has remained largely out of reach.
This week in mSphere, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, researchers describe a two-step prognostic test that can help predict a patient's response to infection with SARS-CoV-2. The test combines a disease risk factor score with a test for antibodies produced early in the infection. It could be administered at the time of diagnosis to help guide therapeutic choices before the most severe symptoms appear, the researchers said.
"You can predict with really high sensitivity that someone is going to have a severe case of COVID-19," said Emily Sanders, a graduate student in the lab of chemical biologist Gregory Weiss, Ph.D, at the University of California, Irvine. Sanders led the study together with Sanjana Sen and Kristin Gabriel, also graduate students in Weiss's lab.
Most diagnostic tests search for antibodies associated with interrupting the virus. Weiss said the group initially set out to develop their own diagnostic, following this same strategy, but quickly realized that plenty of competing tests would soon be available. Instead, they pivoted to focus on other, unstudied antibodies--ones that wouldn't necessarily disrupt the virus or help the immune system fight the infection.
"Everyone else was looking for the good antibodies that neutralize the virus," said Weiss, senior author on the study. "We weren't seeing enough about antibodies that are unhelpful."
"Being able to identify a 'bad' antibody response helps to fill in a research gap," said Gabriel.
Previous studies have predicted that the SARS-CoV-2 particle has more than 55 epitopes, or sites on the virus where antibodies can attach. The best studied epitopes to date are those found on the S, or spike, protein, but the virus has three other structural proteins, each with epitopes worth investigating, said Sen. Using ELISAs, or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, the researchers compiled a list of antibodies that might correlate with worse prognosis and ultimately focused on one that attaches to epitope 9 on the N, or nucleocapsid, protein. The group also developed a tool that used data on factors including age, sex, and pre-existing health conditions to produce a disease risk factor score (DRFS).
They tested their tool on a group of 86 people who had tested positive for the coronavirus. Patients whose tests revealed the presence of epitope 9 antibodies were more likely to have prolonged illness and worse outcomes than people without the antibodies. Of the 23 people in the study who did have the antibodies associated with epitope 9, a high DRFS predicted disease severity with more than 92% sensitivity.
The test uses technology and tools readily available in testing labs, Weiss said. "Detecting antibodies is super easy to do," he said, and an inexpensive prognostic test could inform treatment decisions early in the disease progression. The researchers found that the epitope-9 antibodies become detectable between 1 and 6 days after the onset of symptoms.
"We've all had friends and family impacted by this disease," said Weiss, "and we wanted to do something that might be useful, that might help the physicians who are being overwhelmed."
INFORMATION:
The American Society for Microbiology is one of the largest professional societies dedicated to the life sciences and is composed of 30,000 scientists and health practitioners. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications, educational opportunities and advocacy efforts. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
LAWRENCE -- College students across the country struggle with a vicious cycle: Test anxiety triggers poor sleep, which in turn reduces performance on the tests that caused the anxiety in the first place.
New research from the University of Kansas just published in the International Journal of Behavioral Medicine is shedding light on this biopsychosocial process that can lead to poor grades, withdrawal from classes and even students who drop out. Indeed, about 40% of freshman don't return to their universities for a second year in the United States.
"We were interested ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Socially just policies aimed at limiting the Earth's human population hold tremendous potential for advancing equity while simultaneously helping to mitigate the effects of climate change, Oregon State University researchers say.
In a paper published this week in Sustainability Science, William Ripple and Christopher Wolf of the OSU College of Forestry also note that fertility rates are a dramatically understudied and overlooked aspect of the climate emergency. That's especially true relative to the attention devoted to other climate-related topics including energy, short-lived pollutants and ...
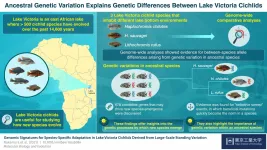
Biologists use the term adaptive radiation to describe a phenomenon in which new species rapidly evolve from an ancestral species, often in response to changes in the local environment that lead to new biological niches becoming available. To understand this process, biologists often turn to the cichlids of Lake Victoria, in which over 500 species of the fish have evolved over the past 14,600 years. As Professor Masato Nikaido of Tokyo Tech explains, "The level of genetic differentiation among species is considered very low due to the short period of time after these different species began evolving, and this limited genetic differentiation provides us with a great opportunity to find candidate genes that have contributed to adaptive ...
Predatory bacteria--bacteria that eat other bacteria--grow faster and consume more resources than non-predators in the same soil, according to a new study out this week from Northern Arizona University. These active predators, which use wolfpack-like behavior, enzymes, and cytoskeletal 'fangs' to hunt and feast on other bacteria, wield important power in determining where soil nutrients go. The results of the study, published in the journal mBio this week, show predation is an important dynamic in the wild microbial realm, and suggest that these predators play an outsized role in how elements are stored in or released from soil.
Like every other life form on earth, bacteria belong to intricate food webs in which organisms are connected ...
Constantina Theofanopoulou wanted to study oxytocin. Her graduate work had focused on how the hormone influences human speech development, and now she was preparing to use those findings to investigate how songbirds learn to sing. The problem was that birds do not have oxytocin. Or so she was told.
"Everywhere that I looked in the genome," she says, "I was unable to find a gene called oxytocin in birds."
Theofanopoulou eventually came across mesotocin, the analogue for oxytocin in birds, reptiles, and amphibians. But as she plumped the literature in Erich Jarvis's lab at Rockefeller, the waters grew muddier. If she and Jarvis wanted to find studies on oxytocin in fish, they ...
Researchers from Erasmus School of Economics, IESE Business School, and New York University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines what business schools do wrong when conducting academic research and what changes they can make so that research contributes to improving society.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Faculty Research Incentives and Business School Health: A New Perspective from and for Marketing" and is authored by Stefan Stremersch, Russell Winer, and Nuno Camacho.
In February 2020, an article in ...
The flightless kakapo of New Zealand is in trouble. The world's heaviest parrot--representing one of the most ancestral branches of the parrot family tree--is nearly extinct, with barely 200 adults plodding the underbrush of four small islands. Whether the last of the kakapos had the genetic resilience to survive was a question that only high-quality genomic analysis could answer.
But a high-quality genome assembly did not exist for the kakapo--nor for most of the 70,000 vertebrate species alive today.
Questions about how best to prevent the extinction of species ranging ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Difficult-to-treat, chronic wounds in preclinical models healed with normal scar-free skin after treatment with an acellular product discovered at Mayo Clinic. Derived from platelets, the purified exosomal product, known as PEP, was used to deliver healing messages into cells of preclinical animal models of ischemic wounds. The Mayo Clinic research team documented restoration of skin integrity, hair follicles, sweat glands, skin oils and normal hydration.
Ischemic wounds occur when arteries are clogged or blocked, preventing important nutrients and oxygen from reaching the skin to drive repair. This groundbreaking study titled, "TGF-β Donor Exosome Accelerates Ischemic ...
To be more energy efficient, many people have replaced their incandescent lights with light-emitting diode (LED) bulbs. However, those currently on the market emit a lot of blue light, which has been linked to eye troubles and sleep disturbances. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have developed a prototype LED that reduces -- instead of masks -- the blue component, while also making colors appear just as they do in natural sunlight.
LED light bulbs are popular because of their low energy consumption, long lifespan and ability to turn on and off quickly. Inside the bulb, an LED chip converts electrical current into high-energy light, including invisible ultraviolet (UV), violet ...
The highly infectious SARS-CoV-2 variant that recently emerged in South Africa, known as B.1.351, has scientists wondering how existing COVID-19 vaccines and therapies can be improved to ensure strong protection. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Journal of Medicinal Chemistry have used computer modeling to reveal that one of the three mutations that make variant B.1.351 different from the original SARS-CoV-2 reduces the virus' binding to human cells -- but potentially allows it to escape some antibodies.
Since the original SARS-CoV-2 was first detected in late 2019, several new variants have emerged, including ones from the U.K., South Africa and Brazil. Because the new variants appear to be more highly ...