(Press-News.org) New York nurses caring for COVID-19 patients during the first wave of the pandemic experienced anxiety, depression, and illness--but steps their hospitals took to protect them and support from their coworkers helped buffer against the stressful conditions, according to a study led by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing.
"A critical part of the public health response to the COVID-19 pandemic should be supporting the mental health of our frontline workers. Our study demonstrates that institutional resources--such as supportive staff relationships, professional development, providing temporary housing, and access to personal protective equipment--were associated with lower levels of anxiety and depression among nurses," said Christine T. Kovner, RN, PhD, the Mathey Mezey Professor of Geriatric Nursing at NYU Meyers and the study's lead author.
The COVID-19 pandemic has strained health systems around the world. The public health crisis has subjected nurses--the largest group of healthcare professionals responding to the pandemic--and other frontline workers to situations of unparalleled stress, as routine roles and responsibilities were disrupted. Not only have nurses worked tirelessly to care for very ill patients, many of whom died, but they themselves have been at risk of exposure to a life-threatening disease and worry about bringing it home to their loved ones.
Research shows that nurses responding to disasters can experience anxiety and depression, but a variety of factors--both personal and in the workplace--can help nurses cope with, adapt to, and recover from stressful conditions. This study, END
Study: New York City nurses experienced anxiety, depression during first wave of COVID-19
Research highlights how hospitals can support nurses during public health crises to protect their mental health
2021-04-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
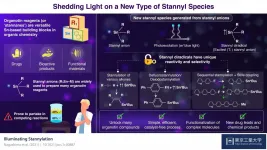
Touched by light: Photoexcited stannyl anions are great for producing organotin compounds
2021-04-29
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology developed a new strategy for producing a wide range of organotin compounds, which are the building blocks of many organic synthesis methods. Their approach is based on the photoexcitation of stannyl anions, which alters their electronic state and increases their selectivity and reactivity to form useful compounds. This protocol will be helpful for the efficient synthesis of many bioactive products, novel drugs, and functional materials.
Organotin compounds, also known as stannanes, are made of tin (Sn), hydrocarbons, and sometimes other elements like nitrogen and oxygen. During the 1970s, ...
Skipping the second shot could prolong pandemic, study finds
2021-04-29
ITHACA, N.Y. - Though more than 131 million Americans have received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine to date, public confusion and uncertainty about the importance of second doses and continued public health precautions threaten to delay a U.S. return to normalcy, according to Cornell-led research published April 28 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In a nationally representative survey of more than 1,000 American adults conducted in February, less than half of respondents said they believed the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines provided strong protection against COVID-19 a week or two after a second dose, consistent with guidance from the U.S. Centers for Diseases ...
Algorithm scours electronic health records to reveal hidden kidney disease
2021-04-28
NEW YORK, NY-- Diagnosing chronic kidney disease, which is often undetected until it causes irreversible damage, may soon become automated with a new algorithm that interprets data from electronic medical records.
The algorithm, developed by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, automatically scours a patient's electronic medical record for results of blood and urine tests and, using a mix of established equations and machine learning to process the data, can alert physicians to patients in the earliest stages of chronic kidney disease.
A study of the algorithm was published in the journal npj Digital Medicine in April.
"Identifying ...
UC San Diego engineering professor solves deep earthquake mystery
2021-04-28
These mysterious earthquakes originate between 400 and 700 kilometers below the surface of the Earth and have been recorded with magnitudes up to 8.3 on the Richter scale.
Xanthippi Markenscoff, a distinguished professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, is the person who solved this mystery. Her paper " END ...
FSU researchers develop tool to track marine litter polluting the ocean
2021-04-28
In an effort to fight the millions of tons of marine litter floating in the ocean, Florida State University researchers have developed a new virtual tool to track this debris.
Their work, which was published in Frontiers in Marine Science, will help provide answers to help monitor and deal with the problem of marine litter.
Eric Chassignet, director of the Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies and professor in the Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Science.
"Marine litter is found around the world, and we do not fully understand its ...
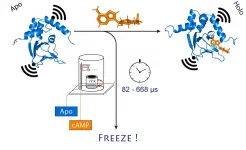
Researchers investigate structural changes in snap-frozen proteins
2021-04-28
Researchers at the University of Bonn and the research center caesar have succeeded in ultra-fast freezing proteins after a precisely defined period of time. They were able to follow structural changes on the microsecond time scale and with sub-nanometer precision. Owing to its high spatial and temporal resolution, the method allows tracking rapid structural changes in enzymes and nucleic acids. The results are published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
If you want to know what the spatial structure of a biomolecule looks like, you have a formidable arsenal of tools at your disposal. The most popular ones are electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction, which can reveal even the smallest ...
Eye movements of those with dyslexia reveal laborious and inefficient reading strategies
2021-04-28
Researchers have long noted that readers with dyslexia employ eye movements that are significantly different from non-dyslexics. While these movements have been studied in small sample sizes in the past, a new paper written by Concordia researchers and published in the Nature journal END ...
CCNY team makes single photon switch advance
2021-04-28
The ability to turn on and off a physical process with just one photon is a fundamental building block for quantum photonic technologies. Realizing this in a chip-scale architecture is important for scalability, which amplifies a breakthrough by City College of New York researchers led by physicist Vinod Menon. They've demonstrated for the first time the use of "Rydberg states" in solid state materials (previously shown in cold atom gases) to enhance nonlinear optical interactions to unprecedented levels in solid state systems. This feat is a first step towards realizing chip-scale scalable single photon switches.
In solid state systems, exciton-polaritons, half-light ...
Cave deposits show surprising shift in permafrost over the last 400,000 years
2021-04-28
Nearly one quarter of the land in the Northern Hemisphere, amounting to some 9 million square miles, is layered with permafrost -- soil, sediment, and rocks that are frozen solid for years at a time. Vast stretches of permafrost can be found in Alaska, Siberia, and the Canadian Arctic, where persistently freezing temperatures have kept carbon, in the form of decayed bits of plants and animals, locked in the ground.
Scientists estimate that more than 1,400 gigatons of carbon is trapped in the Earth's permafrost. As global temperatures climb, and permafrost thaws, this frozen reservoir could potentially escape into the ...
Cave deposits reveal Pleistocene permafrost thaw, absent predicted levels of CO2 release
2021-04-28
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (4/28/2021) -- The vast frozen terrain of Arctic permafrost thawed several times in North America within the past 1 million years when the world's climate was not much warmer than today, researchers from the United States and Canada report in today's edition of Science Advances.
Arctic permafrost contains twice as much carbon as the atmosphere. But the researchers found that the thawings -- which expel stores of carbon dioxide sequestered deep in frozen vegetation -- were not accompanied by increased levels of CO2 in the atmosphere. The surprising finding runs counter to predictions that as the planet ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Study: New York City nurses experienced anxiety, depression during first wave of COVID-19Research highlights how hospitals can support nurses during public health crises to protect their mental health