Data from China's Fengyun meteorological satellites available to global Earth system science applications
2021-04-29
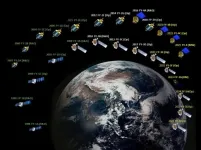
(Press-News.org) Many meteorological satellite networks are constantly scanning Earth, providing vital research data and real-time life-saving weather information. Since China began its initial development in 1970, the Fengyun (FY) series of meteorological satellites have advanced considerably throughout more than 50 years. While FY satellites primarily focus on the atmosphere, they are capable of observing complex variables within the Earth-atmosphere system. Since the initial FY dispatch, China has successfully launched 17 FY satellites, seven of which are currently operating in orbit.
The Fengyun Meteorological Satellite Ground Application System generates more than 90 Earth observation products every day, producing more than 10TB of daily data volume. The FY Satellite Data Center has continuously stored Earth observation data, beginning when FY-1A successfully launched in 1988, to today. More than 12PB of archived satellite data exists in the database through more than 30 years.
"Several approaches for FY satellite data access have been developed for real-time users, scientific researchers, and public users." said Dr. Peng Zhang, the deputy director of National Satellite Meteorological Center of China Meteorological Administration. "All FY satellite data products are open to the world users and free to download."
Dr. Zhang is also the corresponding author of a data description article recently published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences. The article showcases FY data products used to observe wildfires, lightning, vegetation indices, aerosol products, soil moisture, and precipitation estimation. All of these metrics have been validated with in-situ observations and have been cross referenced with other well-known satellite products.
The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) and weather forecasting agencies in China have assimilated the wide array of FY data into many numerical weather prediction (NWP) models. Since the 1990s, coupled meteorological satellites and numerical models have changed the way scientists understand the Earth. As numerical weather prediction and Earth system models continue to evolve, meteorological satellites will play a more important role in the future of Earth sciences.
"FY is included in the World Meteorological Organization's global operational meteorological satellite sequence. It provides data and products to more than 110 countries and regions as well as 2,700 broadcasting users." Dr. Zhang added. "We have been working with scientists from ECMWF, UK MetOffice, and other countries to improve data verification and application. We welcome scientists and forecasters all over the world to use FY data."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-29
Claiming that something has a defect normally suggests an undesirable feature. That's not the case in solid-state systems, such as the semiconductors at the heart of modern classical electronic devices. They work because of defects introduced into the rigidly ordered arrangement of atoms in crystalline materials like silicon. Surprisingly, in the quantum world, defects also play an important role.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, the University of Chicago and scientific institutes and universities in Japan, Korea and Hungary have established guidelines that will be an invaluable resource for the discovery of new defect-based ...
2021-04-29
A compound in avocados may ultimately offer a route to better leukemia treatment, says a new University of Guelph study.
The compound targets an enzyme that scientists have identified for the first time as being critical to cancer cell growth, said Dr. Paul Spagnuolo, Department of Food Science.
Published recently in the journal Blood, the study focused on acute myeloid leukemia (AML), which is the most devastating form of leukemia. Most cases occur in people over age 65, and fewer than 10 per cent of patients survive five years after diagnosis.
Leukemia cells have higher amounts of an enzyme called VLCAD involved in their metabolism, said Spagnuolo.
"The cell relies on that pathway to ...
2021-04-29
Coral reefs provide shelter, sustenance and stability to a range of organisms, but these vital ecosystems would not exist if not for the skeletal structure created by stony corals. Now, KAUST scientists together with an international team have revealed the underlying genetic story of how corals evolved from soft-bodied organisms to build the myriad calcified structures we see today.
"While the processes involved in coral calcification are well understood, it is less clear how corals' ability to grow calcium carbonate skeletons actually evolved," says Xin Wang, a former KAUST Ph.D. student who worked on the project under the supervision of Manual Aranda.
"How did a squishy anemone-like organism begin to build reefs?" ...
2021-04-29
CLEVELAND - In a Correspondence article published in the April 29, 2021 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers from University Hospitals (UH) Cleveland Medical Center, and New York Presbyterian Hospital - Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, found a substantial reduction in the use of minimally invasive surgery for cervical cancer after publication of the results a major study called the Laparoscopic Approach to Cervical Cancer (LACC) in November 2018.
The earlier study, which compared minimally invasive surgery with open abdominal radical hysterectomy in patients with early-stage cervical cancer, found that minimally invasive surgery was associated with worse disease-free and overall ...
2021-04-29
LAWRENCE -- Researchers commonly work with the criminal justice system to implement reforms, bringing with them the latest science and data pointing to why a certain practice will help improve outcomes. New research from the University of Kansas shows if community corrections agencies are to sustain evidence-based reforms, they need to view them as legitimate.
Researchers worked with eight federal community corrections agencies to implement Contingency Management, an evidence-based practice used to help people convicted of drug offenses set and achieve goals to end addiction, avoid repeat offenses and increase pro-social behavior. Such evidence-based practices and reforms are frequently put in place across the criminal justice system.
Shannon Portillo"We've ...
2021-04-29
Nanopore technology shows promise for making it possible to develop small, portable, inexpensive devices that can sequence DNA in real time. One of the challenges, however, has been to make the technology more accurate.
Researchers at The University of Texas at Dallas have moved closer toward this goal by developing a nanopore sequencing platform that, for the first time, can detect the presence of nucleobases, the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The study was published online Feb. 11 and is featured on the back cover of the April print edition of the ...
2021-04-29
A study by University of Guam researchers has found that shade can mitigate the effects of heat stress on corals. The study, which was funded by the university's National Science Foundation EPSCoR grant, was published in February in the peer-reviewed Marine Biology Research journal.
"We wanted to see what role light has in coral bleaching," said UOG Assistant Professor Bastian Bentlage, the supervisor and co-author of the study. "Usually, people talk about temperature as a cause for bleaching, but we show that both light and temperature work together."
Previous UOG research led by Laurie J. Raymundo found that more than one-third of all coral reefs in Guam were killed from 2013 to 2017 over the ...
2021-04-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Hispanic Americans have died of COVID-19 at a disproportionately high rate compared to whites because of workplace exposure to the virus, a new study suggests.
It's widely documented that Hispanics are overrepresented among workers in essential industries and occupations ranging from warehousing and grocery stores to health care and construction, much of which kept operating when most of the country shut down last spring.
The analysis of federal data showed that, considering their representation in the U.S. population, far higher percentages of Hispanics of working ...
2021-04-29
New Haven, Conn. -- Researchers at Yale and Princeton say the scientific community sorely needs a new way to compare the cascading effects of ecosystem loss due to human-induced environmental change to major crises of the past.
For too long, scientists have relied upon metrics that compare current rates of species loss with those characterizing mass extinctions in the distant past, according to Pincelli Hull, an assistant professor of Earth and planetary sciences at Yale, and Christopher Spalding, an astrophysicist at Princeton.
The result has been projections of extinction rates in the next few decades that are on the order ...
2021-04-29
DALLAS - April 28, 2021 - Depression screening among cancer patients improved by 40 percent to cover more than 90 percent of patients under a quality improvement program launched by a multidisciplinary team at UT Southwestern Medical Center and Southwestern Health Resources.
Cancer patients with depression are at an increased risk of mortality and suicide compared with those without depression. Although rates vary based on cancer type and stage, depression is estimated to affect 10 to 30 percent of patients with cancer compared with 7 to 8 percent of adults without a diagnosis or history of cancer, and impact both men and women equally.
Due to the higher risk, medical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Data from China's Fengyun meteorological satellites available to global Earth system science applications






