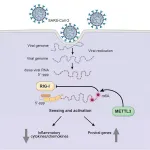
(Press-News.org) Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have discovered one way in which SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, hijacks human cell machinery to blunt the immune response, allowing it to establish infection, replicate and cause disease.
In short, the virus' genome gets tagged with a special marker by a human enzyme that tells the immune system to stand down, while at the same time ramping up production of the surface proteins that SARS-CoV-2 uses as a "doorknob" to enter cells.
The study, published April 22, 2021 in END
How SARS-CoV-2 hijacks human cells to evade immune system
2021-04-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Finding the optimal way to repay student debt
2021-04-29
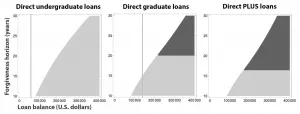
The burden of student loans in the U.S. continues to grow unabatedly, currently accounting for a total of $1.7 trillion in household debt among nearly 45 million borrowers. "The introduction of income-based repayment over the past decade has made student loans rather complicated products," Paolo Guasoni of Dublin City University said. As borrowers navigate this complex process, they face long-term consequences; people with student debt are less likely to own homes or become entrepreneurs, and generally postpone their enrollment in graduate or professional studies. Though legislative reform is necessary to combat this problem on a grand scale, individual borrowers can take steps to ...
New optical hydrogen sensors eliminate risk of sparking
2021-04-29
Hydrogen as a clean, renewable alternative to fossil fuels is part of a sustainable-energy future, and very much already here. However, lingering concerns about flammability have limited widespread use of hydrogen as a power source for electric vehicles. Previous advances have minimized the risk, but new research from the University of Georgia now puts that risk in the rearview mirror.
Hydrogen vehicles can refuel much more quickly and go farther without refueling than today's electric vehicles, which use battery power. But one of the final hurdles to hydrogen power is securing a safe method for detecting hydrogen leaks.
A new study published in Nature Communications documents an inexpensive, spark-free, optical-based hydrogen sensor that is more sensitive ...
NSU researcher part of a flagship study on vertebrate genomes
2021-04-29
Study Take-Aways
Unprecedented novel discoveries have implications for characterizing biodiversity for all life, conservation, and human health and disease.
o This finding provides novel avenues of research to increase immune defenses, particularly relevant for emerging infectious diseases, such as the current COVID-19 pandemic.
The flagship paper presented whole genome sequence analyses of 16 vertebrate species to illustrate high quality, near error free, near complete, low cost reference genome assemblies.
o Though near 400 species have been sequenced at some level, the quality today reflects ...
Alzheimer's disease is composed of four distinct subtypes
2021-04-29
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by the abnormal accumulation and spread of the tau protein in the brain. An international study can now show how tau spreads according to four distinct patterns that lead to different symptoms with different prognoses of the affected individuals. The study was published in Nature Medicine.
"In contrast to how we have so far interpreted the spread of tau in the brain, these findings indicate that tau pathology in the brain varies according to at least four distinct patterns. This would suggest that Alzheimer's is an even more heterogeneous disease than previously thought. We now have reason to reevaluate the concept of typical Alzheimer's, and in the long ...
More stringent public health measures associated with lower COVID-19 cases, deaths
2021-04-29
As state and local policymakers and politicians made the decision to enact stay-at-home orders last March in response to the coronavirus pandemic, a recent study found that more stringent public health measures put in place directly correlated with lower virus case numbers during the first two months of the pandemic.
The study, "More Stringent Measures Against Covid-19 Are Associated With Lower Cases and Deaths in Florida and Miami-Dade," was recently published in the American Journal of Emergency Medicine.
Utilizing The New York Times' GitHub repository of cases and deaths and the COVID-19 Government Response Stringency Index developed by Oxford University's Blavatnik School of Government for the ...
Six out of every 10 teachers believe that changing the design of the classroom is key to improving learning
2021-04-29
The image of rows of chairs and desks facing a teacher at a blackboard has been a reality for decades. However, research reveals that this way of organizing the classroom furniture in schools is not the best way for favouring the learning process. Especially if the needs of 21st-century students are taken into account, who, according to the OECD, require a social environment that fosters autonomy, flexibility, decision-making capacity and the connection of knowledge by individual students or through teamwork.
It is also the opinion of 6 out of every 10 teachers that changing the ...
Wearable glucose monitors shed light on progression of Type 2 diabetes in Hispanic adults
2021-04-29
HOUSTON - (April 29, 2021) - In one of the first studies of its kind, medical and engineering researchers have shown wearable devices that continuously monitor blood sugar provide new insights into the progression of Type 2 diabetes among at-risk Hispanic/Latino adults.
The findings by researchers from Sansum Diabetes Research Institute (SDRI) and Rice University are available online this week in EClinicalMedicine, an open-access clinical journal published by The Lancet.
"The fresh look at the glucose data sheds new light on disease progression, which could have a direct impact on better management," said Rice study co-author Ashutosh Sabharwal, professor and department chair in electrical and ...
Silicon chip will drive next generation communications
2021-04-29
Researchers from Osaka University, Japan and the University of Adelaide, Australia have worked together to produce the new multiplexer made from pure silicon for terahertz-range communications in the 300-GHz band.
"In order to control the great spectral bandwidth of terahertz waves, a multiplexer, which is used to split and join signals, is critical for dividing the information into manageable chunks that can be more easily processed and so can be transmitted faster from one device to another," said Associate Professor Withawat Withayachumnankul from the University of Adelaide's School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering.
"Up ...
A third of kids develop a mental health problem after concussion
2021-04-29
A third of children and adolescents develop a mental health problem after a concussion, which could persist for several years post-injury, according to a new literature review.
The research, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, found mental health should be evaluated as part of standard pediatric concussion assessment and management.
MCRI researcher and Monash University PhD candidate Alice Gornall said despite many post-concussion and mental health symptoms overlapping, the relationship between delayed recovery and mental health had remained poorly understood until this literature review.
The review of 69 articles published between 1980 to June 2020, involved ...
International task force determines current Parkinson's disease subtyping may not fit all patients
2021-04-29
Amsterdam, April 29, 2021 - The clinical presentation and underlying biology of Parkinson's disease (PD) varies significantly, but attempts to cluster cases into a limited number of subtypes have questionable applicability and relevance, reports the international Task Force for PD Subtypes in the Journal of Parkinson's Disease. Their systematic review of studies reporting a subtyping system for the first time concludes that new approaches are needed that acknowledge the individual nature of the disease and are more aligned with personalized medicine.
In 2018, the International Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders Society (MDS) convened the Task Force for PD Subtypes to critically appraise ...