New law of physics helps humans and robots grasp the friction of touch
2021-04-29
(Press-News.org) Although robotic devices are used in everything from assembly lines to medicine, engineers have a hard time accounting for the friction that occurs when those robots grip objects - particularly in wet environments. Researchers have now discovered a new law of physics that accounts for this type of friction, which should advance a wide range of robotic technologies.
"Our work here opens the door to creating more reliable and functional haptic and robotic devices in applications such as telesurgery and manufacturing," says Lilian Hsiao, an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at North Carolina State University and corresponding author of a paper on the work.
At issue is something called elastohydrodynamic lubrication (EHL) friction, which is the friction that occurs when two solid surfaces come into contact with a thin layer of fluid between them. This would include the friction that occurs when you rub your fingertips together, with the fluid being the thin layer of naturally occurring oil on your skin. But it could also apply to a robotic claw lifting an object that has been coated with oil, or to a surgical device that is being used inside the human body.
One reason friction is important is because it helps us hold things without dropping them.
"Understanding friction is intuitive for humans - even when we're handling soapy dishes," Hsiao says. "But it is extremely difficult to account for EHL friction when developing materials that controls grasping capabilities in robots."
To develop materials that help control EHL friction, engineers would need a framework that can be applied uniformly to a wide variety of patterns, materials and dynamic operating conditions. And that is exactly what the researchers have discovered.
"This law can be used to account for EHL friction, and can be applied to many different soft systems - as long as the surfaces of the objects are patterned," Hsiao says.
In this context, surface patterns could be anything from the slightly raised surfaces on the tips of our fingers to grooves in the surface of a robotic tool.
The new physical principle, developed jointly by Hsiao and her graduate student Yunhu Peng, makes use of four equations to account for all of the physical forces at play in understanding EHL friction. In the paper, the research team demonstrated the law in three systems: human fingers; a bio-inspired robotic fingertip; and a tool called a tribo-rheometer, which is used to measure frictional forces. Peng is first author of the paper.
"These results are very useful in robotic hands that have more nuanced controls for reliably handling manufacturing processes," Hsiao says. "And it has obvious applications in the realm of telesurgery, in which surgeons remotely control robotic devices to perform surgical procedures. We view this as a fundamental advancement for understanding touch and for controlling touch in synthetic systems."
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Elastohydrodynamic friction of robotic and human fingers on soft micropatterned substrates," is published in Nature Materials. The paper was co-authored by Christopher Serfass, a Ph.D. student at NC State; Catherine Hill, an undergraduate student at NC State; Anzu Kawazoe, Yitian Shao and Yon Visell of the University of California-Santa Barbara; and Kenneth Gutierrez and Veronica J. Santos of the University of California-Los Angeles.
The work was done with support from the AAAS Marion Milligan Mason Award and from the National Science Foundation, under grant number CBET-2042635.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-29
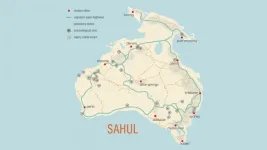
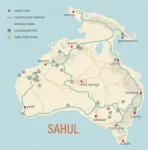
The best path across the desert is rarely the straightest. For the first human inhabitants of Sahul -- the super-continent that underlies modern Australia and New Guinea -- camping at the next spring, stream, or rock shelter allowed them to thrive for hundreds of generations. Those who successfully traversed the landmarks made their way across the continent, spreading from their landfall in the Northwest across the continent, making their way to all corners of Australia and New Guinea.
By simulating the physiology and decisions of early way-finders, an international team* of archaeologists, geographers, ecologists, and computer scientists has mapped the probable "superhighways" that led ...
2021-04-29
BOSTON - Concerns about fertility often influence how young women with breast cancer approach treatment decisions and are a reason for forgoing or delaying hormone-blocking therapy, a new study by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators shows.
The findings, published online today by the journal Cancer, reinforce the need for physicians to talk with patients about their fertility-related priorities and address them in treatment plans, the study authors write. Such conversations are important not only at the start of treatment but during its entire course, as patients' goals ...
2021-04-29
Scientists from the University of Bristol's Quantum Engineering Technology Labs (QETLabs) have developed an algorithm that provides valuable insights into the physics underlying quantum systems - paving the way for significant advances in quantum computation and sensing, and potentially turning a new page in scientific investigation.
In physics, systems of particles and their evolution are described by mathematical models, requiring the successful interplay of theoretical arguments and experimental verification. Even more complex is the description of systems of particles interacting with each other at the quantum mechanical level, which is often done using a Hamiltonian model. The process of formulating Hamiltonian models from observations is made even harder by the nature ...
2021-04-29
'Superhighways' used by a population of up to 6.5 million Indigenous Australians to navigate the continent tens of thousands of years ago have been revealed by new research using sophisticated modelling of past people and landscapes.
The new insights into how people not only survived, but thrived, in harsh environments provide further evidence of the capacity and resilience of the ancestors of Indigenous people, and help paint a picture of large, well-organised groups navigating tough terrain.
The 'peopling' of Sahul -- the combined mega continent that joined Australia with New Guinea when ...
2021-04-29
There was a hope that as more plants start to grow in Arctic and boreal latitudes as our warming climate makes those regions more hospitable for plants, those photosynthesizing plants would work to help sequester the atmospheric carbon dioxide that helped them flourish in the first place. But new research led by scientists at UC Irvine and Boston University, out in Nature Climate Change, suggests that all the new green biomass is not as large a carbon sink as scientists had hoped.
"What does greening really mean? Can we really trust it to save us from climate change?" said Jon Wang, an Earth system scientist at UCI who the led the work alongside BU Earth & Environment professor Mark Friedl. "A big question is: What'll happen to the carbon that's currently ...
2021-04-29
What The Study Did: This survey study examines the associations of school closure and exposure to COVID-19-related stressors with caregivers' perceptions of their children's mental well-being.
Authors: Tali Raviv, Ph.D., of the Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11103)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article ...
2021-04-29
What The Study Did: Using insurance claims data, the change in screening rates for breast, colorectal and prostate cancers during the COVID-19 pandemic were estimated as well as the overall decline in cancer screening last year among the U.S. population.
Authors: Ronald Chen, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Kansas in Kansas City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
2021-04-29
What The Study Did: This case series investigates the frequency and type of SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal test complications in Helsinki, Finland.
Authors: Anni Koskinen, M.D., Ph.D., of the Helsinki University Hospital in Finland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0715)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This ...
2021-04-29
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated whether spending a year aboard the International Space Station was associated with worsening of spaceflight-associated structural changes to the eye.
Authors: Brandon R. Macias, Ph.D., of the NASA Johnson Space Center in Houston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.0931)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
2021-04-29
What The Study Did: The association between exposure to antibiotics before birth and during the first year of life and the development of eczema during childhood was evaluated among children in Sweden.
Authors: Mwenya Mubanga, M.D., Ph.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.5245)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New law of physics helps humans and robots grasp the friction of touch