Study reveals extent of human impact on the world's plant-life
2021-04-29
(Press-News.org) Research has shed new light on the impact of humans on Earth's biodiversity. The findings suggest that the rate of change in an ecosystem's plant-life increases significantly during the years following human settlement, with the most dramatic changes occurring in locations settled in the last 1500 years.
An international research team studied fossilised pollen dating back 5000 years, extracted from sediments on 27 islands. By analysing the fossils they were able to build up an understanding of the composition of each island's vegetation and how it changed from the oldest to the most recent pollen samples.
The study was led by Dr Sandra Nogué, Lecturer in Palaeoenvironmental Science at the University of Southampton, UK and Professor Manuel Steinbauer from the University of Bayreuth, Germany and University of Bergen, Norway. PhD student Dr Alvaro Castilla-Beltrán was also a member of the Southampton team.
Dr Nogué said, "Islands provide the ideal environment to measure human impact as most were settled in the past 3000 years when climates were similar to today's conditions. Knowing when the settlers arrived on an island means that scientists can study how the composition of its ecosystem changed in the years before and after."
The results, published in Science, showed a consistent pattern on 24 of the islands where human arrival accelerated the turnover of vegetation by, on average, a factor of eleven. The most rapid changes occurred in islands that were settled more recently - such as the Galápagos, first inhabited in the 16th Century. Islands where humans arrived more than 1500 years ago, such as Fiji and New Caledonia, saw a slower rate of change.
"This difference in change could mean that the islands populated earlier were more resilient to human arrival but it is more likely that the land-use practices, technology and introduced species brought in by the later settlers were more transformative than those of the earlier settlers," explained Dr Nogué.
The trends were observed across a range of geographic locations and climates, with islands such as Iceland producing similar results to Tenerife and other tropical and temperate islands.
Ecosystem change can also be driven by a number of natural factors such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, extreme weather and changing sea levels, however the researchers have found that disturbance caused by humans surpasses all of these events and the change is often irreversible. They therefore advise that conservation strategies must account for the long-term impact of humans and the degree to which ecological changes today differ from prehuman times.
"Whilst it is unrealistic to expect ecosystems to return to their pre-settlement conditions, our findings may help to inform targeted restoration efforts and provide greater understanding into the islands' responsiveness to change," concludes Dr Nogué.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-29
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have discovered a mechanism through which meningitis-causing bacteria can evade our immune system. In laboratory tests, they found that Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae respond to increasing temperatures by producing safeguards that keep them from getting killed. This may prime their defenses against our immune system and increase their chances of survival, the researchers say. The findings are published in the journal PLoS Pathogens.
"This discovery helps to increase our understanding of the mechanisms these bacteria use to evade our normal immune defenses," ...
2021-04-29
Scientists have been able to track how a multi-drug resistant organism is able to evolve and spread widely among cystic fibrosis patients - showing that it can evolve rapidly within an individual during chronic infection. The researchers say their findings highlight the need to treat patients with Mycobacterium abscessus infection immediately, counter to current medical practice.
Around one in 2,500 children in the UK is born with cystic fibrosis, a hereditary condition that causes the lungs to become clogged up with thick, sticky mucus. The condition tends to decrease life expectancy among patients.
In recent years, M. abscessus, a species of multi-drug resistant bacteria, has emerged as a significant global threat to individuals with cystic fibrosis and other lung diseases. ...
2021-04-29
Considerable gap in evidence around whether portable air filters reduce the incidence of COVID-19 and other respiratory infections
There is an important absence of evidence regarding the effectiveness of a potentially cost-efficient intervention to prevent indoor transmission of respiratory infections, including COVID-19, warns a study by researchers at the University of Bristol.
Respiratory infections such as coughs, colds, and influenza, are common in all age groups, and can be either viral or bacterial. Bacteria and viruses can become airborne via talking, coughing or sneezing. The current global coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic is also spread primarily by airborne droplets, and to date has led to over three million deaths ...
2021-04-29
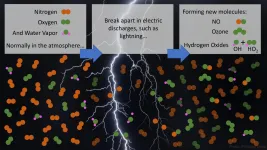
Lightning bolts break apart nitrogen and oxygen molecules in the atmosphere and create reactive chemicals that affect greenhouse gases. Now, a team of atmospheric chemists and lightning scientists have found that lightning bolts and, surprisingly, subvisible discharges that cannot be seen by cameras or the naked eye produce extreme amounts of the hydroxyl radical -- OH -- and hydroperoxyl radical -- HO2.
The hydroxyl radical is important in the atmosphere because it initiates chemical reactions and breaks down molecules like the greenhouse gas methane. OH is the main driver of many compositional changes in the atmosphere.
"Initially, we looked at these huge OH and HO2 signals found in the clouds and asked, what is wrong with our instrument?" said William ...
2021-04-29
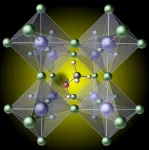
Researchers in the materials department in UC Santa Barbara's College of Engineering have uncovered a major cause of limitations to efficiency in a new generation of solar cells.
Various possible defects in the lattice of what are known as hybrid perovskites had previously been considered as the potential cause of such limitations, but it was assumed that the organic molecules (the components responsible for the "hybrid" moniker) would remain intact. Cutting-edge computations have now revealed that missing hydrogen atoms in these molecules can cause massive efficiency losses. The findings are published in ...
2021-04-29
An international team led by Xiangming Xiao, George Lynn Cross Research Professor in the Department of Microbiology and Plant Biology, University of Oklahoma College of Arts and Sciences, published a paper in the April issue of the journal Nature Climate Change that has major implications on forest policies, conservation and management practices in the Brazilian Amazon. Xiao also is director of OU's Center for Earth Observation and Modeling. Yuanwei Qin, a research scientist at the Center for Earth Observation and Modeling, is the lead author of the study.
For the study described in the paper, "Carbon loss ...
2021-04-29
As part of a laboratory experiment, Rebecca Holmes examined water bottles that had been acquired from abroad expecting to find bisphenol A (BPA), a human-made component commonly found in polycarbonate plastics used to make consumer products.
What she found, however, was that those water bottles were just fine, yet some control bottles purchased in the United States and supposedly BPA-free actually contained traces of the chemical now thought to negatively impact heart health.
Holmes, a researcher formerly in the laboratory of Hong-Sheng Wang, PhD, professor in the University of Cincinnati Department of Pharmacology and Systems Physiology, was working on her master's degree in molecular, cellular and biochemical ...
2021-04-29
WASHINGTON, D.C. (APRIL 29, 2021) - Results from a new study find a broad range of patients who typically undergo revascularization for stable ischemic heart disease (SIHD) in the U.S. did not meet enrollment criteria for the ISCHEMIA trial. The data, which was presented today as late-breaking clinical science at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Scientific Sessions, demonstrates a minority of SIHD patients referred for coronary intervention in contemporary practice clearly resemble those enrolled in the ISCHEMIA trial.
Ischemic heart disease impacts more than 13 million people in the United States and is the leading cause ...
2021-04-29
WASHINGTON, D.C, (April 29, 2021) - An analysis of growth patterns in transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) programs across United States hospitals is being presented as late-breaking clinical science at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography& Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Scientific Sessions. The findings indicate that TAVR hospital programs are predominately located in metropolitan areas serving patients with higher socioeconomic status, potentially contributing to the disparities in cardiac care.
TAVR is a minimally invasive procedure for patients in need of a valve repair or replacement and is an alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR), a treatment ...
2021-04-29
Washington, D.C., April 29, 2021 - Two studies related to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) evaluating the use of risk-avoidance strategies and robotic-assisted technology, respectively, are being presented as late-breaking clinical science at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2021 Scientific Sessions. An analysis of strategically avoiding high-risk PCI cases indicates systematic risk-avoidance does not improve, and may worsen, the quality of hospital PCI programs. A study of a robotic-assisted PCI shows the technology is safe and effective for the treatment of both simple and complex lesions; this has the potential to address the occupational ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study reveals extent of human impact on the world's plant-life