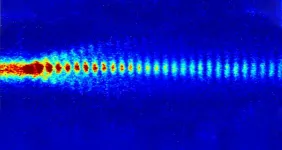
(Press-News.org) The future of particle acceleration has begun. Awake is a promising concept for a completely new method with which particles can be accelerated even over short distances. The basis for this is a plasma wave that accelerates electrons and thus brings them to high energies. A team led by the Max Planck Institute for Physics now reports a breakthrough in this context. For the first time, they were able to precisely time the production of the proton microbunches that drive the wave in the plasma. This fulfills an important prerequisite for using the Awake technology for collision experiments.
How do you create a wave for electrons? The carrier substance for this is a plasma (i.e., an ionized gas in which positive and negative charges are separated). Directing a proton beam through the plasma creates a wave on which electrons ride and are accelerated to high energies.
The proton source of Awake is the SPS ring at Cern, a pre-accelerator for the 27-kilometer circumference ring of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). It produces proton bunches about 10-cm long. "However, in order to generate a large amplitude plasma wave, the proton bunch length must be much shorter - in the millimeter range," explains Fabian Batsch, PhD student at the Max Planck Institute for Physics.
The scientists take advantage of self-modulation, a "natural" interaction between the bunch and plasma. "In the process, the longer proton bunch is split into high-energy proton microbunches of only a few millimeters in length, building the train beam," says Batsch. "This process forms a plasma wave, which propagates with the train travelling through the plasma field."
Precise timing allows ideal electron acceleration
However, a stable and reproducible field is required to accelerate electrons and bring them to collision. This is exactly what the team has found a solution for now. "If a sufficiently large electric field is applied when the long proton bunch is injected and the self-modulation is thus immediately set in motion."
"Since the plasma is formed right away, we can exactly time the phase of the short proton microbunches," says Patric Muggli, head of the Awake working group at the Max Planck Insstitute for Physics. "This allows us to set the pace for the train. Thus, the electrons are caught and accelerated by the wave at the ideal moment."
First research projects in sight
The Awake technology is still in the early stages of development. However, with each step toward success, the chances of this accelerator technology actually being used in the coming decades increase. The first proposals for smaller accelerator projects (e.g., for example to study the fine structure of protons) are to be made as early as 2024.
According to Muggli, the advantages of the novel accelerator technology - plasma wakefield acceleration - are obvious: "With this technology, we can reduce the distance needed to accelerate electrons to peak energy by a factor of 20. The accelerators of the future could therefore be much smaller. This means: Less space, less effort, and therefore lower costs."
INFORMATION:
Original publication
F. Batsch et al.
Transition between instability and seeded self-modulation of a relativistic particle bunch in plasma
Physical Review Letters, 23 April 2021 (Vol. 126, No. 16)
The human immune system comprises functionally specialised cellular defence mechanisms that protect the body against disease. These include the dendritic cells. Their main function is to present antigens to other immune cells, especially T cells, thereby activating a primary immune response. Dendritic cells are divided into Type 1 (DC1) and Type 2 (DC2) dendritic cells. Each type fulfils different functions: DC1 provide an immune response to bacteria and viruses, DC2 protect against fungal or parasitic infections. In a recent study conducted at MedUni Vienna's Institute of Cancer Research, researchers found that a particular group of proteins plays a major role in the development of Type 1 dendritic ...
WHAT:
In a mouse study, National Institutes of Health researchers have identified and mapped a diverse spectrum of motor neurons along the spinal cord. These neurons, which send and receive messages throughout the body, include a subset that is susceptible to neurodegenerative diseases. Created with a genetic sequencing technique, the atlas reveals 21 subtypes of neurons in discrete areas throughout the spinal cord and offers insight into how these neurons control movement, how they contribute to the functioning of organ systems and why some are disproportionately affected in neurodegenerative diseases.
The study ...
Researchers have developed a brain-like computing device that is capable of learning by association.
Similar to how famed physiologist Ivan Pavlov conditioned dogs to associate a bell with food, researchers at Northwestern University and the University of Hong Kong successfully conditioned their circuit to associate light with pressure.
The research will be published April 30 in the journal Nature Communications.
The device's secret lies within its novel organic, electrochemical "synaptic transistors," which simultaneously process and store information just like the human brain. The researchers demonstrated ...
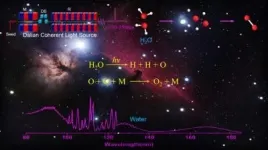
The provenance of oxygen on Earth and other solar planetary bodies is a fundamental issue. It is widely accepted that the prebiotic pathway of oxygen production in the Earth primitive atmosphere was via vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) photodissociation of CO2 and subsequent recombination of two O atoms.
In contrast, the photodissociation of H2O, one of the dominant oxygen carriers, has long been assumed to proceed mainly to produce hydroxyl (OH)- and hydrogen (H)-atom primary products, and its contribution to oxygen production is limited.
Recently, a research group ...
The Worldwide Innovative Network in personalized cancer medicine consortium - WIN Consortium announces the publication of the Digital Display Precision Predictor: the prototype of a global biomarker model to guide treatments with targeted therapy and predict progression-free survival for cancer patients in NPJ Precision Oncology (10.1038/s41698-021-00171-6)
Precision oncology has led to approved, molecularly specific, biomarker-defined indications for targeted therapies. With the number of validated drug targets increasing, testing each patient's tumor for all markers related to all possible targeted therapies becomes infeasible due to limited amount of tissue usually obtained by biopsies. In addition, the current companion diagnostic approach ...
Targeting a pathway that is essential for the survival of certain types of acute myeloid leukaemia could provide a new therapy avenue for patients, the latest research has found.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute found that a specific genetic mutation, which is linked with poor prognosis in blood cancer, is involved in the development of the disease when combined with other mutations in mice and human cell lines.
The study, published today (30th April) in Nature Communications, provides a greater understanding of how the loss-of-function mutation in the CUX1 gene leads to the development and survival of acute myeloid leukaemia. ...
A new study finds Black patients are more likely to die after their heart bypass surgery if they're at a hospital where some care teams see mostly white patients and others see mostly Black patients. On the other hand, mortality rates are comparable between Black and white patients after heart bypass surgery when the teams of health care providers at their hospitals all care for patients of all races.
Some level of care team segregation within hospitals was very common, and the findings bring up another angle to better understand racial inequities in surgical outcomes, says co-first author John Hollingsworth, M.D., M.Sc., a professor of urology at Michigan Medicine and of health management and policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health.
Previous studies ...
Most detailed study to date including 345,000 people from 48 randomised clinical trials finds that blood pressure-lowering medication is effective in adults regardless of starting blood pressure level.
Each 5mmHg reduction in systolic blood pressure lowered the relative risk of cardiovascular events by around 10%, even in people with normal blood pressure and those who had never had a heart attack or stroke.
Authors call for global guidelines to be changed so that anyone with increased risk of cardiovascular disease is considered for blood-pressure lowering ...
BOSTON - After patients with cancer undergo surgery to remove a tumor and sometimes additional chemotherapy, tools are used to identify patients at highest risk of recurrence. Non-invasive tools to detect microscopic disease are of especially high value. In a new study published in END ...
Researchers from the HSE International Laboratory for Supercomputer Atomistic Modelling and Multi-scale Analysis, JIHT RAS and MIPT have compared the performance of popular molecular modelling programs on GPU accelerators produced by AMD and Nvidia. In a paper published by the International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications, the scholars ported LAMMPS on the new open-source GPU technology, AMD HIP, for the first time.
The scholars thoroughly analysed the performance of three molecular modelling programs - LAMMPS, Gromacs and OpenMM - on GPU ...