Tailor-made therapy of multi-resistant tuberculosis
2021-05-03
(Press-News.org) Globally, tuberculosis is the most common bacterial infectious disease leading to death. The pathogen causing tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, has a number of peculiarities. One is that it is growing very slowly. While other typical pathogens, such as pneumococcal and pseudomonads, can already be identified by their growth in the microbiological laboratory in the first 72 hours, several weeks usually pass before tuberculosis bacteria grow in the lab. Thus it often takes one to two months before the efficacy of individual medicines can be tested.
However, these efficacy tests are essential for the effective treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), which is becoming increasingly common. In these cases, the pathogen has become resistant, i.e. insensitive, to the best tuberculosis drugs, rifampicin and isoniazid. This is due to changes in the genome, so-called mutations, which almost always occur at the same points in the genome. Treatment of MDR-TB is protracted, costly and frequently associated with side effects.
For the selection of antibiotics in a combination therapy, doctors have so far depended on the results of the drug test after cultivation. "Currently, 15 drugs are available for second-line therapy, of which at least four are used in combination," explains Prof. Christoph Lange, coordinator of the clinical study at the Research Center Borstel.
In order to accelerate the choice of the most effective antibiotics, DZIF scientists at the Research Center Borstel, led by Prof. Stefan Niemann, have created a catalogue of mutations in the genetic material of tuberculosis bacteria that permits prediction of antibiotic resistances of the bacteria against all drugs. Unlike many other bacteria, the genetic material of the tuberculosis bacteria hardly changes over time. The genome of tuberculosis bacteria carries roughly 4.4 millions of building blocks (base pairs) that store the information for about 4,000 genes.
Hans-Peter Grobbel, medical student and predoctoral DZIF fellow in Christoph Lange's team, supported by his fellow student Niklas Köhler, Professor Matthias Merker, Dr Sönke Andres and Dr Harald Hoffmans, has examined the results of antibiotic resistance predictions through overall genome analyses. Using tuberculosis bacteria from70 patients with MDR-TB treated at the Borstel Department of Medicine, researchers compared the molecular prediction of antibiotic resistance with actual cultural test results. They were contributed by Prof. Florian Maurer, Head of the National Reference Laboratory for Tuberculosis Bacteria in Borstel. The scientists also examined whether reliable combinations of drugs for the treatment of MDR-TB could be compiled based on the prediction of the bacteria´s genetic material.
"Ninety-nine per cent of all drugs in combination therapies that we have assembled based on the results of molecular predictions from the genetic material of tuberculosis bacteria are also effective according to traditional microbiological antibiotic resistance testing," Grobbel explains. By now, the molecular methods are both cheap and fast. Ideally, patients can already receive tailored MDR-TB treatment in the first week of their tuberculosis diagnosis.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-03
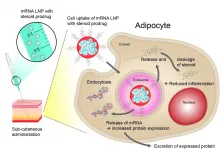
If not before, then certainly since the first messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines to combat the SARS CoV2 virus were approved in Germany, mRNA has become a recognized term even outside scientific circles. What is less well known is that mRNA can be used to produce much more than just vaccines. Around 50 different procedures for the treatment of diseases including cancer are already being studied in clinical trials. Scientists from the pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca, with the support of neutron researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich, have now discovered how the subcutaneous administration of mRNA can be improved. The goal is for chronically ill ...
2021-05-03
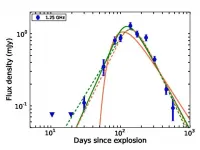
Scientists from the National Centre for radio Astrophysics of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (NCRA-TIFR) Pune used the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT) to determine that AT 2018 cow, the first of a newly discovered class of cosmic explosions, has an extremely patchy environment. Sources like AT 2018cow release an enormous amount of energy, nonetheless fade extremely rapidly. This along with their extremely blue color has led to them being called FBOTs for Fast Blue Optical Transient. This is the first observational evidence of inhomogeneous emission from an FBOT. The origins of FBOTs are still under debate, but proposed models include explosion of a massive star, collision of an accreting neutron star and ...
2021-05-03
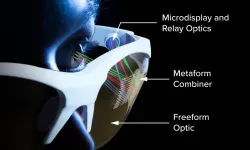
"Image" is everything in the $20 billion market for AR/VR glasses. Consumers are looking for glasses that are compact and easy to wear, delivering high-quality imagery with socially acceptable optics that don't look like "bug eyes."
University of Rochester researchers at the Institute of Optics have come up with a novel technology to deliver those attributes with maximum effect. In a paper in Science Advances, they describe imprinting freeform optics with a nanophotonic optical element called "a metasurface."
The metasurface is a veritable forest of tiny, silver, nanoscale structures on a thin metallic film that conforms, in this advance, to the freeform shape of ...
2021-05-03
According to Michael Twidale, professor in the School of Information Sciences at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, bad usability can be an irritation for everyone but "especially awful" for the underprivileged. In "Everyone Everywhere: A Distributed and Embedded Paradigm for Usability," which was recently published in the Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology (JASIST), Twidale and coauthors David M. Nichols (University of Waikato, New Zealand) and Christopher P. Lueg (Bern University of Applied Sciences, Switzerland) present a new paradigm to address the persistence of difficulties that people have ...
2021-05-03
(New York, NY) - May 3, 2021 - In advance of a wildfire season projected to be among the worst, the American Thoracic Society has released a report that calls for a unified federal response to wildfires that includes investment in research on smoke exposure and forecasting, health impacts of smoke, evaluation of interventions, and a clear and coordinated communication strategy to protect public health.
The report, Respiratory Impacts of Wildland Fire Smoke: Future Challenges and Policy Opportunities, was published online ahead of print in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society on May 3, 2021.
The report comes at a time when the U.S. is experiencing an increasing frequency of very large destructive wildfires, due to years ...
2021-05-03
Over 400 common disinfectants currently in use could be made safer for people and the environment and could better fight the COVID-19 virus with the simple application of UVC light, a new study from the University of Waterloo shows.
Benzalkonium chloride (BAK) is the most common active ingredient in many disinfectants regularly used in hospitals, households, and food processing plants to protect against a wide range of viruses and bacteria - including all strains of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 - but its toxicity means that it can't be used in high concentrations. It also means that products containing BAK are harmful to humans ...
2021-05-03
LUGANO, Switzerland, 3 May 2021 - As breast cancer becomes a largely curable disease, with more than 70% of women surviving at least 10 years after diagnosis across most of Europe thanks to early detection and treatment, (1) the quality of life after cancer has become an important aspect of the patient journey - one that may be inadequately addressed with current standards of follow-up. A study presented at the ESMO Breast Cancer 2021 Virtual Congress (2) has shown that breast cancer survivors differ widely in the burden of symptoms they experience after the end of treatment and thereby revealed an unmet need for tailored approaches to follow-up care. (3)
Lead author Kelly de Ligt ...
2021-05-03
TORONTO - Scientists at the Krembil Brain Institute, part of University Health Network (UHN), in collaboration with colleagues at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH), have used precious and rare access to live human cortical tissue to identify functionally important features that make human neurons unique.
This experimental work is among the first of its kind on live human neurons and one of the largest studies of the diversity of human cortical pyramidal cells to date.
"The goal of this study was to understand what makes human brain cells 'human,' and how human neuron circuitry functions as it does," says Dr. Taufik Valiante, neurosurgeon, scientist at the Krembil Brain Institute at UHN and co-senior author on the paper.
"In our study, we wanted ...
2021-05-03
Customised medicines could one day be manufactured to patients' individual needs, with University of East Anglia (UEA) researchers investigating technology to 3D 'print' pills.
The team, including Dr Andy Gleadall and Prof Richard Bibb at Loughborough University, identified a new additive manufacturing method to allow the 3D printing of medicine in highly porous structures, which can be used to regulate the rate of drug release from the medicine to the body when taken orally.
Dr Sheng Qi, a Reader in Pharmaceutics at UEA's School of Pharmacy, led the research. The project findings, 'Effects of porosity on drug release kinetics of swellable and erodible porous pharmaceutical solid dosage forms ...
2021-05-03
A research team from the Institut de Neurociències at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (INc-UAB) has showed that inhibition through a drug of the Tac2 neuronal circuit, involved in the formation of the memory of fear, has opposite effects on the ability to remember aversive events in mice according to sex: it is reduced in male mice and increased in female mice.
Is the first time that a drug has been shown to produce this opposite effect on the memory of male and female mice. The study also evidences that opposing molecular mechanisms and behaviours can occur ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tailor-made therapy of multi-resistant tuberculosis