Blockchain as 'TechQuity': How tech solutions have the power to help the homeless
2021-05-03
(Press-News.org) AUSTIN, Texas -- For people experiencing homelessness, missing proof of identity can be a major barrier to receiving critical services, from housing to food assistance to health care. Physical documents such as driver's licenses are highly susceptible to loss, theft or damage. However, researchers from Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin say new technology solutions such as blockchain can be used to keep important health care information secure and portable.
"Health care institutions and social services are so fragmented and siloed they're unable to accurately collect, share or verify basic identity information about a person experiencing homelessness," said Tim Mercer, M.D., MPH, director of the Global Health Program in the Department of Population Health at Dell Med and co-author of a new commentary published in the Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved. "This puts the burden on the most underserved people in our communities to navigate complex bureaucracies, just to prove their identities."
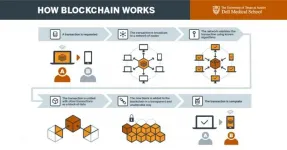
How Blockchain Works
Mercer and co-author Anjum Khurshid, M.D., Ph.D., say blockchain holds great potential as "techQuity"-- technology that provides innovative solutions to advance health equity. Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger system that uses encryption to share information or transactions across a network of computers. Once verified, each "block" of new information is linked to the existing block, creating a chain of secure data that a person can access anytime, anywhere.
"The architecture of blockchain technology makes it a unique solution for managing identities of vulnerable people, allowing them to secure their information and control when and where that data gets shared," said Khurshid, director of data integration in Dell Med's Department of Population Health. "For instance, if you need to prove you're over 18 years old, that information can be validated through blockchain without having to share your driver's license."
Putting the Technology to the Test
In 2018, the City of Austin worked with a team at Dell Med to test the feasibility of blockchain technology to establish an identity system for people experiencing homelessness. The results of the study showed that blockchain allowed them to upload and share documents with service providers, while holding their personal information as an asset in their blockchain account.
In the commentary, Mercer and Khurshid propose a research agenda to address unresolved issues, including:
Defining the scope of the problem,
Mapping infrastructure requirements,
Understanding legal and ethical considerations, and
Testing the overall effectiveness of blockchain to not only solve identity management problems, but also to improve health equity for people experiencing homelessness.
"While blockchain is seeing increased applications across the health care and social sectors, this is still largely uncharted territory," said Mercer. "We have an incredible opportunity to partner with the private technology sector to solve this pernicious problem that plagues one of society's most vulnerable populations."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-03
A study encompassing some 9,000 dogs conducted at the University of Helsinki demonstrated that fearfulness, age, breed, the company of other members of the same species and the owner's previous experience of dogs were associated with aggressive behaviour towards humans. The findings can potentially provide tools for understanding and preventing aggressive behaviour.
Aggressive behaviour in dogs can include growling, barking, snapping and biting. These gestures are part of normal canine communication, and they also occur in non-aggressive situations, such as during play. However, aggressive behaviour ...
2021-05-03
An extraordinary discovery in the Gulf of Eilat: Researchers from Tel Aviv University have discovered a species of ascidian, a marine animal commonly found in the Gulf of Eilat, capable of regenerating all of its organs - even if it is dissected into three fragments. The study was led by Prof. Noa Shenkar, Prof. Dorothee Huchon-Pupko, and Tal Gordon of Tel Aviv University's School of Zoology at the George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences and the Steinhardt Museum of Natural History. The findings of this surprising discovery were published in the leading journal Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
"It is an astounding discovery, as this is an animal that belongs to the Phylum Chordata - animals with a dorsal cord - which also includes us humans," explains Prof. Noa ...
2021-05-03
Water is a scarce resource in many of the Earth's ecosystems. This scarcity is likely to increase in the course of climate change. This, in turn, might lead to a considerable decline in plant diversity. Using experimental data from all over the world, scientists from the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), and the Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have demonstrated for the first time that plant biodiversity in drylands is particularly sensitive to changes in precipitation. In an article published in Nature Communications, the team warns that this can also have consequences for the people living in the ...
2021-05-03
The terms "co-creation" and "co-production", which denote the possibility for laypeople to participate in decision-making processes that affect their lives, have been gaining popularity. A new IIASA-led study explored options for empowering citizens as a driver for moving from awareness about the need to transform energy systems to action and participation.
The European Union's climate and energy policies for 2020-2030 require decarbonization of the energy sector. To this end, EU member countries are working on a number of key goals including greater energy efficiency, greater use of renewable energy, and increased energy security across the EU. The successful ...
2021-05-03
In recent decades, Spain has undergone rapid social changes in terms of gender equality, despite, as a result of the Franco dictatorship, starting from a more backward position than most European countries. This process is hampered by the economic downturn that began in 2008, underlining the importance of the economic context in the development of gender inequality levels. Little attention has been paid in academia to how this gender revolution is associated with factors related to individual wellbeing.
A study by Jordi Gumà, a researcher at the Department of Political and ...
2021-05-03
The human world is, increasingly, an urban one -- and that means elevators. Hong Kong, the hometown of physicist Zhijie Feng (Boston University),* adds new elevators at the rate of roughly 1500 every year...making vertical transport an alluring topic for quantitative research.
"Just in the main building of my undergraduate university, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology," Feng reflects, "there are 37 elevators, all numbered so we can use them to indicate the location of hundreds of classrooms. There is always a line outside each elevator lobby, and if they are shut down, we have to hike for 30 minutes."
Feng and Santa Fe Institute Professor ...
2021-05-03
Myotonic dystrophy is a hereditary degenerative neuromuscular disease that occurs mainly in adults, affecting about 50,000 people only in Spain. Symptoms range from difficulty walking and myotonia (great difficulty in relaxing the contracted muscles) to severe neurological problems, leading to progressive disability that unfortunately puts many of those affected in a wheelchair. This disease is very heterogeneous among patients (age of onset, progression, hereditary transmission, affected muscles), which makes the development of generic treatments especially complex.
Currently, drugs against myotonic ...
2021-05-03
LAWRENCE -- Like much of society, college athletics were thrown into disarray by the COVID-19 pandemic. While student athletes were suddenly prevented from competing, training or seeing as much of their teammates and coaches, those who perceived they were part of a positive sporting environment also coped better during the early days of the crisis, a new study from the University of Kansas has found.
KU researchers have long studied a caring, task-involved sporting climate, in which young athletes receive support and recognition for their efforts, while mistakes are treated as learning opportunities. But the pandemic provided a unique opportunity to see whether the approach helped collegiate athletes cope with the unique stresses and challenges that came with the disruption ...
2021-05-03
Social media may make it easier for people to engage online, but I does not provide certain benefits of real-life human interactions, says a Michigan State University researcher.
"Problematic social media use has been associated with depression, anxiety and social isolation, and having a good social support system helps insulate people from negative mental health," said Dar Meshi, an assistant professor in the Department of Advertising and Public Relations at MSU. "We wanted to compare the differences between real-life support and support provided over social media to see if the support provided over social media could have beneficial effects."
The research was published online April 29 in the journal Addictive Behaviors.
While ...
2021-05-03
Living materials, which are made by housing biological cells within a non-living matrix, have gained popularity in recent years as scientists recognize that often the most robust materials are those that mimic nature.
For the first time, an international team of researchers from the University of Rochester and Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands used 3D printers and a novel bioprinting technique to print algae into living, photosynthetic materials that are tough and resilient. The material has a variety of applications in the energy, medical, and fashion sectors. The research is published in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Blockchain as 'TechQuity': How tech solutions have the power to help the homeless